Normalization of non-sinusoidality indicators of magnetoelectric generator under an autonomous mode of operation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.332187Keywords:
magnetoelectric generator, harmonic voltage, harmonic distortion factor, quality of electric energyAbstract
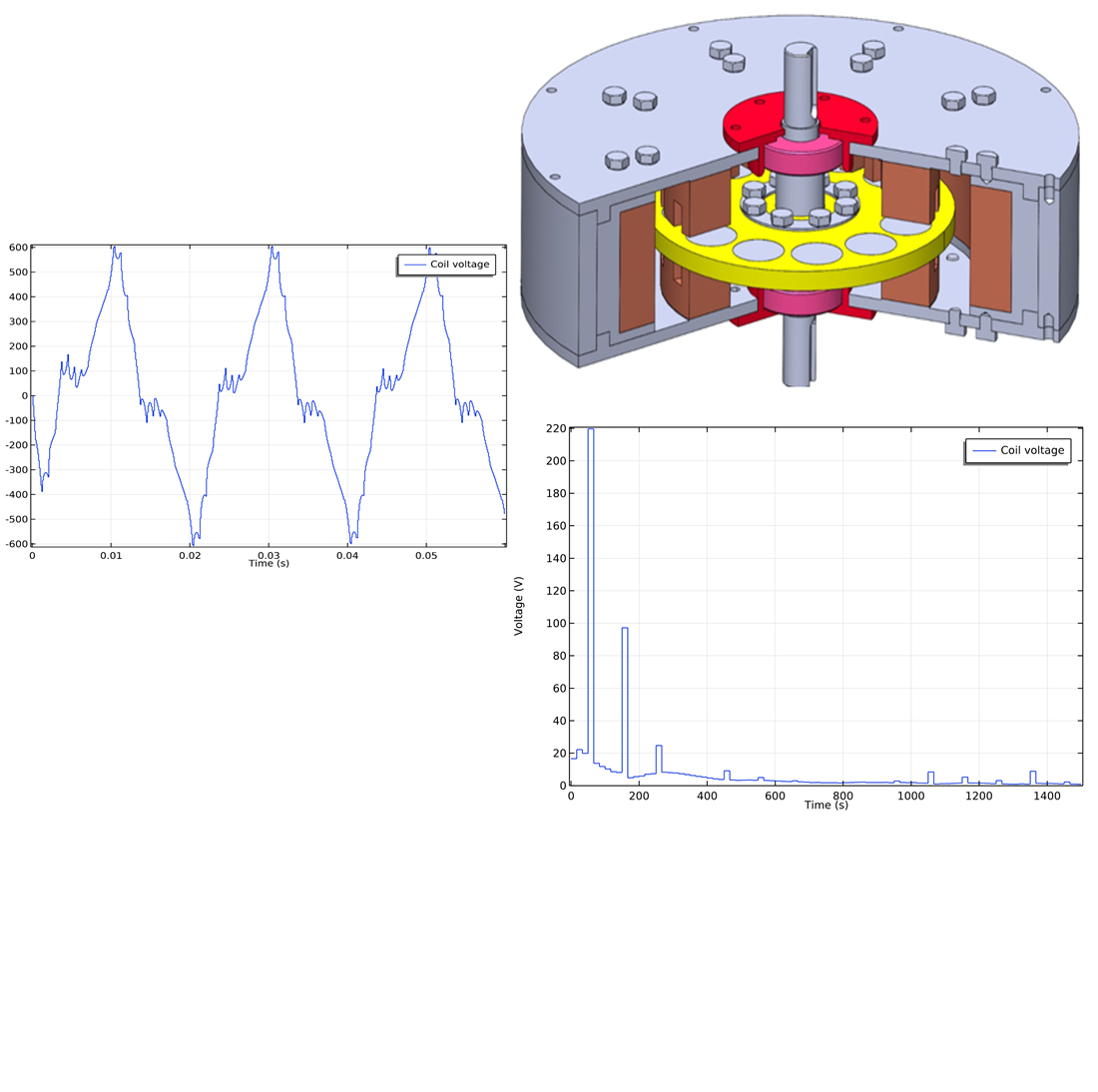
The object of this study is a magnetoelectric generator with an excitation system based on permanent magnets and an additional magnetic system in the form of ferromagnetic shunts.
This paper considers the task of non-sinusoidal voltage in a local electrical network with a magnetoelectric generator. This phenomenon negatively affects the operation of consumers and reduces the energy efficiency of the system. The work investigates the causes of harmonic distortion and proposes a method for reducing their impact. This helps ensure stable and high-quality operation of consumers in the electrical network.
The generated voltage was studied in terms of non-sinusoidality for a magnetoelectric generator at different load levels in isolated operation. The non-compliance of the generated voltage with the requirements of the current standard in terms of the relative voltage of individual harmonics and the total harmonic distortion factor (THDU) was established. The dependences of the relative voltage of harmonics on the generator load level in the range from idle to nominal load were determined. The parameters of single-frequency resonant filters were calculated, which enable the normalization of the generated voltage according to the non-sinusoidality indicators under the conditions of isolated operation of the generator with a rated load.
A feature of the results is the design of adaptive voltage non-sinusoidality filters that take into account the specificity of operation of the magnetoelectric generator in the local network.
Analysis of the generator output voltage revealed that under an isolated operation mode, it is necessary to install filters of the 3rd, 5th, 9th, 21st, and 23rd harmonics in the entire generator load range. The absence of harmonic resonance phenomena is shown if filters with fixed parameters are used in the generator load range from idle to rated load
References
- Ostroverkhov, M., Chumack, V., Falchenko, M., Kovalenko, M. (2022). Development of control algorithms for magnetoelectric generator with axial magnetic flux and double stator based on mathematical modeling. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (5 (120)), 6–17. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.267265
- Kawambwa, S., Mnyanghwalo, D. (2024). Revenue loss reduction in the electrical distribution networks using distributed generators: A case of Tanzania electrical distribution network. Journal of ICT Systems, 2 (2), 67–80. https://doi.org/10.56279/jicts.v2i2.119
- He, Y., Li, Y., Liu, J., Xiang, X., Sheng, F., Zhu, X. et al. (2025). A Two-Stage Fault Reconfiguration Strategy for Distribution Networks with High Penetration of Distributed Generators. Electronics, 14 (9), 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14091872
- Fadi, O., Abbou, A., Gaizen, S. (2023). Optimized MPPT for Aero-generator System built on Autonomous Squirrel Cage Generators Using Feed-Forward Neural Network. International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, 13 (3). https://doi.org/10.20508/ijrer.v13i3.14002.g8785
- Martinez-Bolanos, J. R., Manito, A. R. A., Almeida, M. P., Almeida, J. C., Torres, P. F., Pinho, J. T., Zilles, R. (2025). Improved dynamic model of small stand-alone diesel generators to assess the stability of autonomous microgrids. AIP Advances, 15 (2). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0232151
- Sebastián, R. (2022). Modeling, Simulation and Control of Wind Diesel Power Systems. Energies, 15 (5), 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051712
- Conti, S., Rizzo, S. A. (2017). An open source tool for reliability evaluation of distribution systems with renewable generators. Energy Systems, 10 (2), 385–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-017-0264-6
- Lu, J., Zhao, R., Fang, Y., Gao, Y., Gan, K., Chen, Y. (2025). Fault Equivalence and Calculation Method for Distribution Networks Considering the Influence of Inverters on the Grid Side and the Distribution Network Side. Energies, 18 (8), 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18082111
- Jaradat, T., Khatib, T. (2024). Optimal sizing of battery energy storage system in electrical power distribution network. Energy Exploration & Exploitation. https://doi.org/10.1177/01445987241300183
- Souli, A. (2025). Analysis of Transient Overvoltage in Electrical Networks using Elaborate Code and PSCAD. Electrotehnica, Electronica, Automatica, 73 (1), 70–77. https://doi.org/10.46904/eea.25.73.1.1108007
- Lyu, S., Han, H., Li, J., Yuan, X., Wang, W. (2024). Voltage regulation in distribution networks by electrical vehicles with online parameter estimation. Frontiers in Energy Research, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2024.1506211
- Kryshchuk, R. S. (2024). Application of phase current loops for modeling the harmonic magnetic field of a magnetoelectric generator. Tekhnichna Elektrodynamika, 2024 (5), 30–35. https://doi.org/10.15407/techned2024.05.030
- Li, H., Chen, Z., Polinder, H. (2009). Optimization of Multibrid Permanent-Magnet Wind Generator Systems. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 24 (1), 82–92. https://doi.org/10.1109/tec.2008.2005279
- Chumack, V., Tsyvinskyi, S., Kovalenko, M., Ponomarev, A., Tkachuk, I. (2020). Mathemathical modeling of a synchronous generator with combined excitation. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (5 (103)), 30–36. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.193495
- Bhende, C. N., Mishra, S., Malla, S. G. (2011). Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Standalone Wind Energy Supply System. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2 (4), 361–373. https://doi.org/10.1109/tste.2011.2159253
- Chumack, V., Katsadze, T., Bazenov, V., Kovalenko, M., Geraskin, O. (2025). Determining the impact of a magnetoelectric generator on the operation of a local distribution network. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (8 (133)), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322917
- De La Rosa, F. C. (2015). Harmonics, Power Systems, and Smart Grids. CRC Press: Boca Raton, 278. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315215174
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Teimuraz Katsadze, Volodymyr Chyzhevskyi, Mykhailo Kovalenko, Vadim Chumack, Naina Buslova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








