Regularities of cleaning and dewatering of gas cleaning sludge from coal dust at thermal power plants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.333183Keywords:
coal dust emissions, coal sludge, dehydration efficiency, gas treatment sludge purification, environmental safetyAbstract
The object of this study is the technology of cleaning and dewatering of sludges from wet gas purification systems of dust preparation department emissions in Ecomash SHS521AS-113 settling centrifuges in order to solve the problem of increasing the efficiency of treatment facilities and secondary use of purified water.
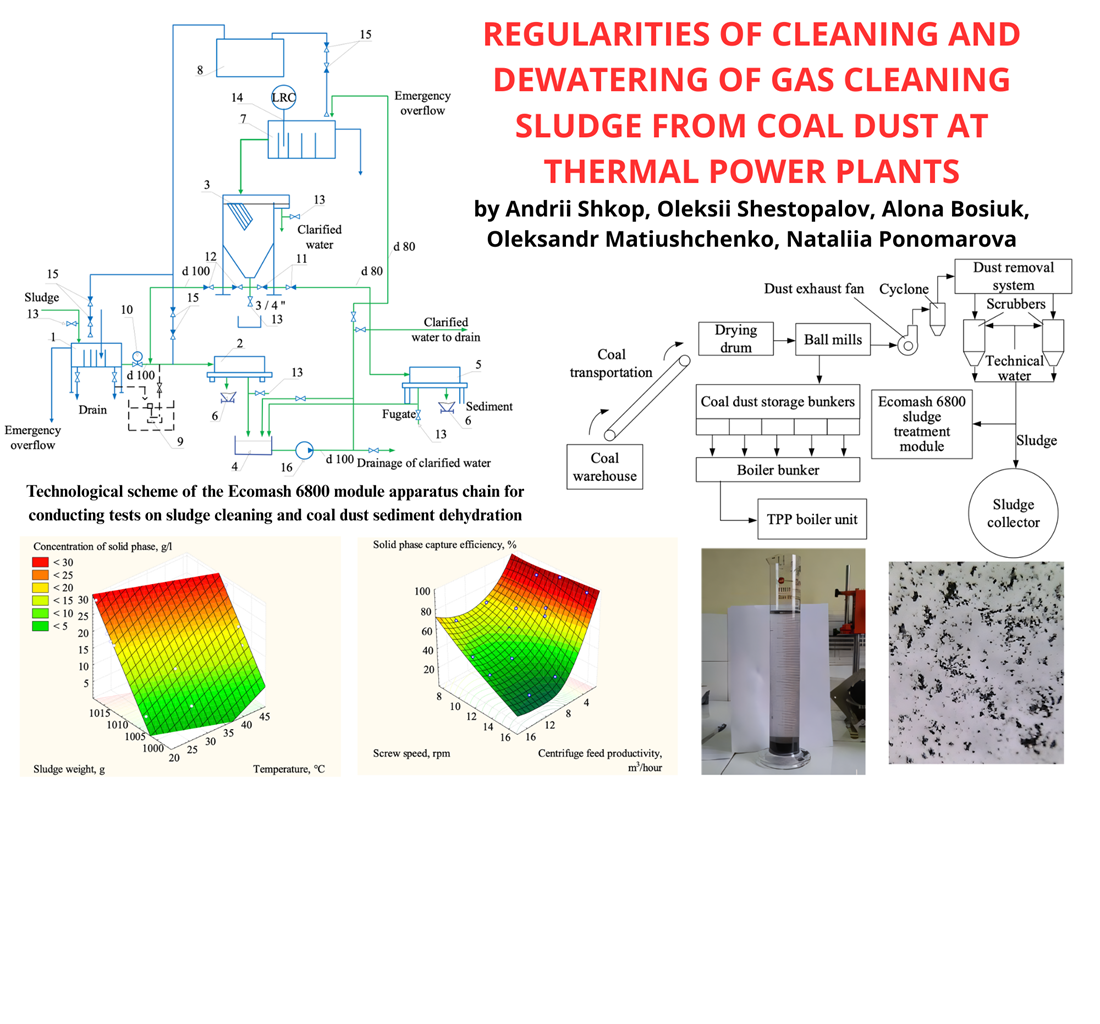
Samples of gas purification sludges have been analyzed under industrial conditions, and it was found that sludges from thermal power plants contain finely dispersed dust particles less than 20 microns, which during the hydration process stick together into aggregates up to 250 microns in size.
It was found that the use of settling tanks without chemical reinforcement of the process is long-term; however, they are effectively precipitated using the anionic flocculant A-19. The optimal dose of flocculant for sludges with a concentration of 20–30 g/l was selected, which was 130–150 g/t. In this case, flocs are formed with a sedimentation rate of 8.2–8.6 mm/s, which is sufficient for effective settling. In order to quickly determine the concentration of the solid phase in the sludge, a relationship was established between the concentration of the dispersed phase, the temperature in the range of 20–45°C, and the density of the sludge.
The study of sludge purification in centrifuges without the use of reagents has made it possible to identify the relationship between the efficiency of solid phase retention, centrifuge productivity, and the value of the relative screw revolutions. It was found that the efficiency of solid phase retention in centrifuges increases with a decrease in work productivity, as well as a decrease in the value of the relative screw revolutions. The purification productivity of up to 15–20 m3/h was achieved with an efficiency of over 97% and a residual concentration of suspended particles of less than 0.5 g/l. The use of a modular sludge purification and dewatering unit based on a thin-layer clarifier and centrifugal units with the introduction of a flocculant before the clarifier has been proposed. It was found that the degree of sludge dehydration in Ecomash SHS521AS-113 centrifuges of wet gas treatment sludge was 32–36%
References
- Hamraoui, L., Bergani, A., Ettoumi, M., Aboulaich, A., Taha, Y., Khalil, A. et al. (2024). Towards a Circular Economy in the Mining Industry: Possible Solutions for Water Recovery through Advanced Mineral Tailings Dewatering. Minerals, 14 (3), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030319
- Tang, Q., Xing, J., Sun, Z., Gan, M., Fan, X., Ji, Z. et al. (2022). Enhancing the Dewaterability of Oily Cold Rolling Mill Sludge Using Quicklime as a Conditioning Agent. ACS Omega, 7 (48), 44278–44286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c05771
- Tong, Y., Gao, J., Ma, J. (2023). Emission Characteristics, Speciation, and Potential Environmental Risks of Heavy Metals from Coal-Fired Boilers: A Review. Sustainability, 15 (15), 11653. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511653
- Li, L., Ma, C., Lin, M., Liu, M., Yu, H., Wang, Q. et al. (2021). Study of sodium lignosulfonate prepare low-rank coal-water slurry: Experiments and simulations. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 29, 344–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.07.064
- Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., Tu, Y., Wang, J., Li, J. (2020). Study on properties of coal-sludge-slurry prepared by sludge from coal chemical industry. Powder Technology, 366, 552–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.03.005
- You, X., He, M., Zhu, X., Wei, H., Cao, X., Wang, P., Li, L. (2019). Influence of surfactant for improving dewatering of brown coal: A comparative experimental and MD simulation study. Separation and Purification Technology, 210, 473–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.08.020
- Wang, S., Ma, C., Zhu, Y., Yang, Y., Du, G., Li, J. (2018). Deep dewatering process of sludge by chemical conditioning and its potential influence on wastewater treatment plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26 (33), 33838–33846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2351-1
- Li, K., Zhou, F., Fu, S., Zhang, Y., Dai, C., Yuan, H., Yu, S. (2023). Study on the separation performance of a decanter centrifuge used for dewatering coal water slurry. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 195, 711–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2023.06.013
- Shestopalov, O., Briankin, O., Rykusova, N., Hetta, O., Raiko, V., Tseitlin, M. (2020). Optimization of floccular cleaning and drainage of thin dispersed sludges. EUREKA: Physics and Engineering, 3, 75–86. https://doi.org/10.21303/2461-4262.2020.001239
- Shkop, A., Shestopalov, O., Sakun, A., Tseitlin, M., Ponomarova, N., Bosiuk, A. et al. (2025). Research of efficiency of cleaning and dehydration of coal slims in centrifuges. International Journal of Mechatronics and Applied Mechanics, 1 (19). https://doi.org/10.17683/ijomam/issue19.13
- Khazaie, A., Mazarji, M., Samali, B., Osborne, D., Minkina, T., Sushkova, S. et al. (2022). A Review on Coagulation/Flocculation in Dewatering of Coal Slurry. Water, 14 (6), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060918
- Zhang, F., Bournival, G., Ata, S. (2024). Overview of Fine Coal Filtration. Part I: Evaluation of Filtration Performance and Filter Cake Structure. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 46 (3), 457–478. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2024.2334956
- Zhang, F., Bournival, G., Ata, S. (2025). Overview of fine coal filtration. Part II: Filtration aiding treatments and reagents. Separation and Purification Technology, 353, 128584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.128584
- Shkop, A., Tseitlin, M., Shestopalov, O. (2016). Exploring the ways to intensify the dewatering process of polydisperse suspensions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (10 (84)), 35–40. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2016.86085
- Shkop, A., Tseitlin, M., Shestopalov, O., Raiko, V. (2017). Study of the strength of flocculated structures of polydispersed coal suspensions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (10 (85)), 20–26. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.91031
- Shestopalov, O., Briankin, O., Tseitlin, M., Raiko, V., Hetta, O. (2019). Studying patterns in the flocculation of sludges from wet gas treatment in metallurgical production. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (10 (101)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.181300
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andrii Shkop, Oleksіi Shestopalov, Alona Bosiuk, Oleksandr Matiushchenko, Natalііa Ponomarova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








