Development of an image quality enhancement approach for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.335570Keywords:
diabetic retinopathy, fundus images, image preprocessing, contrast enhancement, data augmentationAbstract
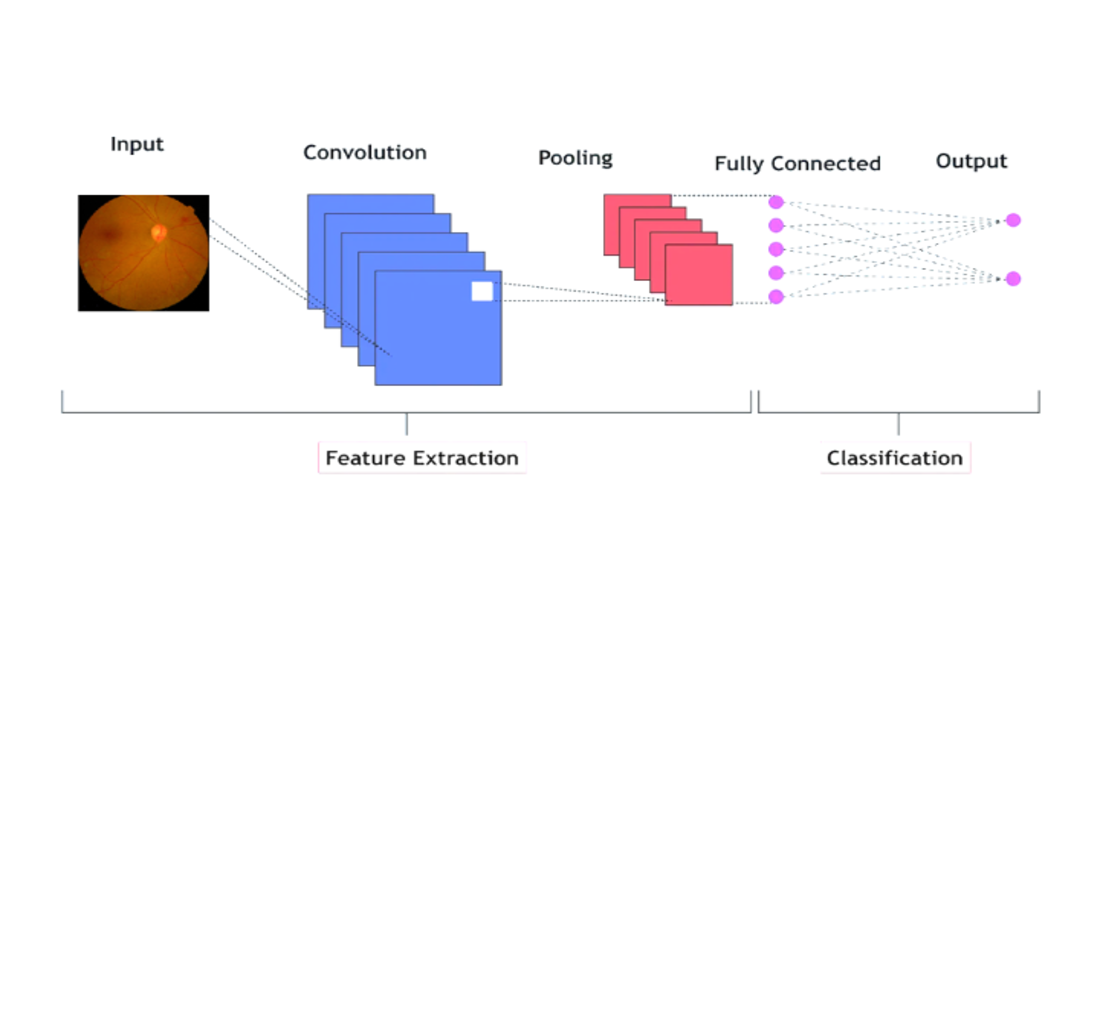
The object of the study is the accuracy of diabetic retinopathy diagnosis based on retinal images. This study investigates convolutional neural network (CNN) models for the automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy (DR) from retinal images. The main problem lies in the insufficient effectiveness of basic CNN models in recognizing DR stages on fundus images. The core problem addressed is the suboptimal performance of baseline CNNs in identifying DR stages from medical imagery. To solve this, two CNN architectures were thoroughly evaluated: a baseline model and an enhanced model integrating advanced preprocessing techniques such as image resizing (256 × 256 and 512 × 512), the image normalization, and data augmentation methods. The enhanced model outperformed the original, achieving a validation accuracy of 91% compared to 88% for the baseline, and demonstrating reduced loss during both training and validation. This improvement is attributed to the optimized input image quality and increased variability in the training set, which enhanced the model’s ability to generalize and avoid overfitting. A distinctive feature of the results lies in the synergy between preprocessing and CNN architecture, which enabled significantly improved classification performance even under hardware constraints. These limitations suggest that further gains are possible with extended computational resources and access to larger datasets. The practical applicability of the findings is evident in the potential deployment of such models in clinical screening systems to support early and accurate DR diagnosis. The models were trained on a proprietary dataset of expert-labeled, high-resolution retinal images, similar in format to EyePACS and APTOS, though not publicly available due to ethical considerations
References
- Şahin, M. A., Beyca, Ö. F. (2024). Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis with Image Processing. 2024 32nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/siu61531.2024.10601116
- Demin, N. S., Ilyasova, N. Yu., Paringer, R. A. (2023). Automatic Selection of the Optimal Zone for Laser Exposure According to the Fundus Images for Laser Coagulation. Journal of Biomedical Photonics & Engineering, 9 (4), 040308. https://doi.org/10.18287/jbpe23.09.040308
- Cisek, A., Korycinska, K., Pyziak, L., Malicka, M., Wiecek, T., Gruzel, G. et al. (2023). Algorithm-based diagnostic application for diabetic retinopathy detection. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2312.00529
- Saut Parulian, O., Na`am, J. (2024). Advanced Filtering and Enhancement Techniques for Diabetic Retinopathy Image Analysis. Journal Medical Informatics Technology, 69–75. https://doi.org/10.37034/medinftech.v2i3.40
- Mohd Sharif, N. A., Harun, N. H., Yusof, Y. (2024). Image enhancement optimization on bright and dark spots of retinal fundus image. International Journal of Advances in Applied Sciences, 13 (3), 539. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijaas.v13.i3.pp539-545
- Fayyad, M. F., Mustakim. (2024). Application of AlexNet, EfficientNetV2B0, and VGG19 with Explainable AI for Cataract and Glaucoma Image Classification. 2024 International Electronics Symposium (IES), 406–412. https://doi.org/10.1109/ies63037.2024.10665856
- Suresh, G. V., Sri, G. P. N. P., Angidi, K. S., Dheeraj, T. S., Snehitha, G. N. V. (2024). Automated Denoising of Diabetic Retinopathy Images for Enhanced Medical Diagnosis. 2024 3rd International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence and Computing (ICAAIC), 1234–1240. https://doi.org/10.1109/icaaic60222.2024.10574928
- Mohd Sharif, N. A., Harun, N. H., Yusof, Y. (2024). Colour Image Enhancement Model of Retinal Fundus Image for Diabetic Retinopathy Recognition. Journal of Information and Communication Technology, 23 (2), 293–334. https://doi.org/10.32890/jict2024.23.2.5
- Toresa, D., Wiza, F., Anggraini, K., Taslim, T., Edriyansyah, Lisnawita, L. (2023). Comparison of Image Enhancement Methods for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening. Jurnal RESTI (Rekayasa Sistem Dan Teknologi Informasi), 7 (5), 1111–1117. https://doi.org/10.29207/resti.v7i5.5193
- Vishwanath, C. S., Divya, K. L., Vamsika, A., Murali, B. S., Dinesh, B. (2024). Diabetic Retinopathy Classification by Enhanced Image Filtration Techniques Using Deep Learning. 2024 OPJU International Technology Conference (OTCON) on Smart Computing for Innovation and Advancement in Industry 4.0, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/otcon60325.2024.10687473
- Kao, Y.-H., Lin, C.-L. (2024). Enhancing Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Using Pixel Color Amplification and EfficientNetV2: A Novel Approach for Early Disease Identification. Electronics, 13 (11), 2070. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13112070
- Surmayanti, Sumijan, Bukhori, S. (2024). Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy Using the Extraction Method on Fundus Images. 2024 12th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology (ICoICT), 333–340. https://doi.org/10.1109/icoict61617.2024.10698276
- Hou, Q., Cao, P., Jia, L., Chen, L., Yang, J., Zaiane, O. R. (2023). Image Quality Assessment Guided Collaborative Learning of Image Enhancement and Classification for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 27 (3), 1455–1466. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2022.3231276
- Deshpande, A. (2023). Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy using Fundus Images and Image Processing Methods. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology, 11 (5), 3596–3605. https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.52296
- Triwijoyo, B. K., Sabarguna, B. S., Budiharto, W., Abdurachman, E. (2020). Deep learning approach for classification of eye diseases based on color fundus images. Diabetes and Fundus OCT, 25–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-817440-1.00002-4
- Ramya, N., Hemavathi, D. (2022). Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Through Feature Aggregated Generative Adversarial Network. 2022 1st International Conference on Computational Science and Technology (ICCST), 611–614. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccst55948.2022.10040451
- Bhoopal, S., Rao, M., Krishnappa, C. H. (2024). Enhanced diabetic retinopathy detection and classification using fundus images with ResNet50 and CLAHE-GAN. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 35 (1), 366. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v35.i1.pp366-377
- Banupriya, V., Kalaivani, A. (2022). Improved retinal fundus image quality with hybrid image filter and enhanced contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization. International Journal of Health Sciences, 9234–9246. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6ns1.7090
- Bakhshi, A., Hajizadeh, K., Tanhayi, M. R., Jamshidi, R. (2022). Diabetic retinopathy diagnosis using image processing methods. Advances in Obesity, Weight Management & Control, 11 (5), 132–134. https://doi.org/10.15406/aowmc.2022.12.00375
- Mahender, N., Padmaja, S., Shivanadhuni, R., Rao, L. G., Mohmmad, S. (2023). An Enhanced Approach for Detecting and Classifying the Diabetic Retinopathy by Utilizing an Optimized Convolutional Neural Network. 2023 International Conference on Ambient Intelligence, Knowledge Informatics and Industrial Electronics (AIKIIE), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/aikiie60097.2023.10390105
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Saya Sapakova, Nurmaganbet Yesmukhamedov, Askar Sapakov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








