Development of a distance measurement model using a magnification approach and modification of the YOLOV3 architecture
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.339774Keywords:
detection object, distance estimation, DAS, monocular camera, YOLO, Hybrid DistAbstract
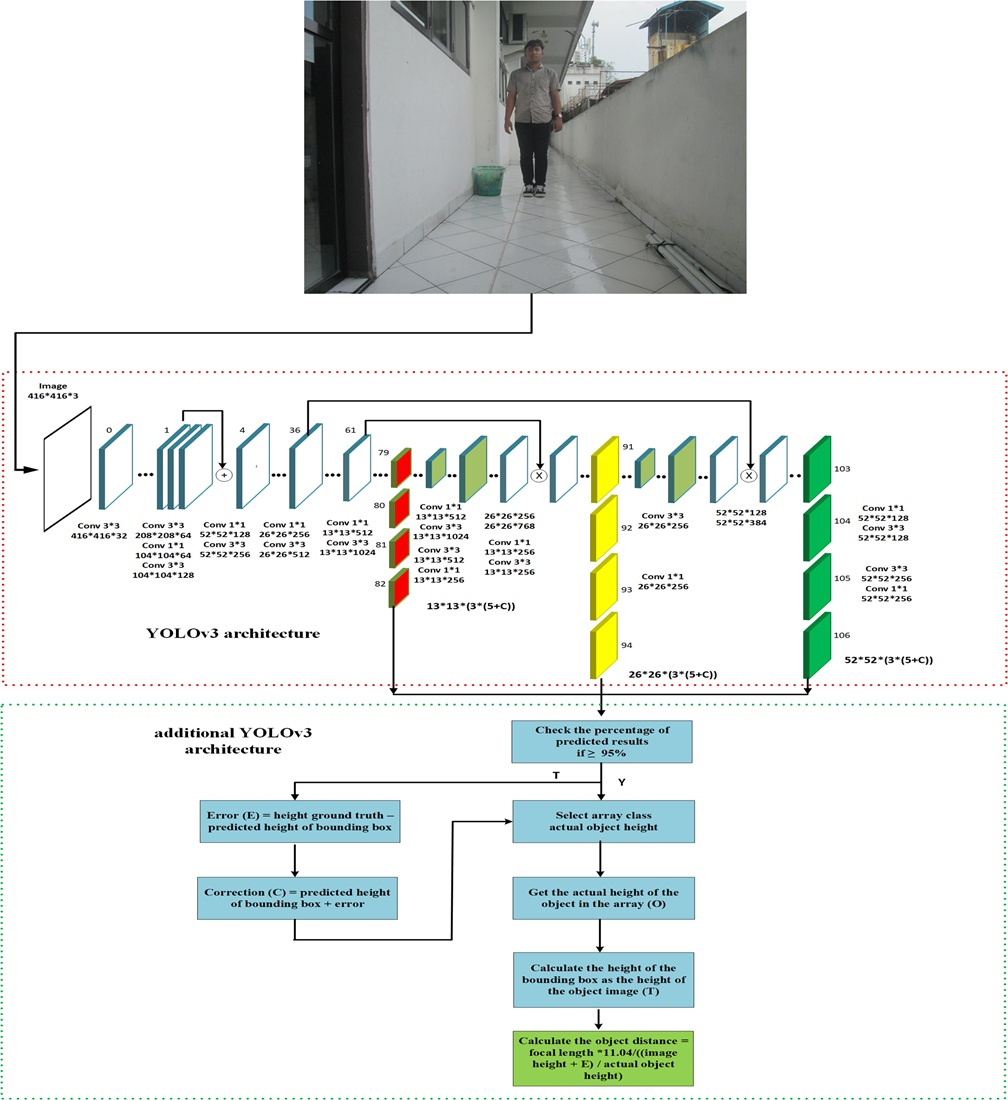
Determining the best model for measuring object distance, the appropriate formula for that model, and modifying the YOLOv3 architecture is the focus of this research. This was done to address the problem of object distance measurement errors using a monocular camera. In this study, the researchers used a magnification approach and modified the YOLOv3 architecture, which was then named Hybrid Dist – YOLOv3. The proposed distance measurement model does not use camera height and camera shift distance variables, so it can still measure objects that are higher than the camera height and the measurement time is faster. The only variable in the measured distance formula is the change in object image height. As for modifications to the YOLOv3 architecture, there are two types of training and test data: initial measurement data and from KITTI. The training data from the initial measurements consisted of three classes, namely person, bottle, and jerrycan, with 24, 10, and 10 samples, respectively. The detection accuracy at mAP0.50 is 0.994, 1.1, with absolute measurement error values (ɛA) of –0.274, –0.153, and –0.163. For the training data from KITTI, there are three object classes, namely pedestrian, car, and truck, with 1150, 7682, and 318 samples, respectively. From the tests conducted, the ɛA values for the pedestrian, car, and truck classes show an improvement from the previous study, which were originally 1.75, 2.49, and 4.63, to 1.37, 2.25, and 3.74. The results of this research can be applied in the automotive industry to driver assistance systems (DAS), soccer robots, or similar systems that require distance measurement
References
- Raj, T., Hashim, F. H., Huddin, A. B., Ibrahim, M. F., Hussain, A. (2020). A Survey on LiDAR Scanning Mechanisms. Electronics, 9 (5), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050741
- Ding, M., Zhang, Z., Jiang, X., Cao, Y. (2020). Vision-Based Distance Measurement in Advanced Driving Assistance Systems. Applied Sciences, 10 (20), 7276. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207276
- Kim, J. B. (2019). Efficient Vehicle Detection and Distance Estimation Based on Aggregated Channel Features and Inverse Perspective Mapping from a Single Camera. Symmetry, 11 (10), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11101205
- Haseeb, M. A., Guan, J., Ristić-Durrant, D., Graser, A. (2018). DisNet: A Novel Method for Distance Estimation from Monocular Camera. In 10th Planning, Perception and Navigation for Intelligent Vehicles. Madrid. Available at: https://project.inria.fr/ppniv18/files/2018/10/paper22.pdf
- Lee, S., Han, K., Park, S., Yang, X. (2022). Vehicle Distance Estimation from a Monocular Camera for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems. Symmetry, 14 (12), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14122657
- Ali, A., Hassan, A., Ali, A. R., Ullah Khan, H., Kazmi, W., Zaheer, A. (2020). Real-time vehicle distance estimation using single view geometry. 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 1100–1109. https://doi.org/10.1109/wacv45572.2020.9093634
- Liang, H., Ma, Z., Zhang, Q. (2022). Self-Supervised Object Distance Estimation Using a Monocular Camera. Sensors, 22 (8), 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22082936
- Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D. et al. (2014). Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. Computer Vision – ECCV 2014, 740–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
- Jamzad, M., Foroughnassiraei, A., Chiniforooshan, E., Ghorbani, R., Kazemi, M., Chitsaz, H. et al. (2000). Middle Sized Soccer Robots: ARVAND. RoboCup-99: Robot Soccer World Cup III, 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45327-x_4
- Jüngel, M., Mellmann, H., Spranger, M. (2008). Improving Vision-Based Distance Measurements Using Reference Objects. RoboCup 2007: Robot Soccer World Cup XI, 89–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-68847-1_8
- Joglekar, A., Joshi, D., Khemani, R., Nair, S., nd Sahare, S. (2011). Depth Estimation Using Monocular Camera. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, 2 (4), 1758–1763. Available at: https://www.ijcsit.com/docs/Volume 2/vol2issue4/ijcsit2011020480.pdf
- Venu Gopala Krishnan, J., Manoharan, N., Sheela Rani, B. (2010). Estimation of Distance To Texture Surface Using Complex Log Mapping. J. Comput. Appl., 3 (3), 16–21. Available at: https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/30862784/50116157_vol3i3p4-libre.pdf?1392203742=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DEstimation_Of_Distance_to_Texture_Surfac.pdf&Expires=1764668791&Signature=HuHi4o78VYI164-U6Swdr~e5-p6cYWI92CSjmgVeRncJDw8ozK8aHhi5gpCo2sgdVRTsUqMdDArIQmvy2QnPDWsKKriFM7lR4TDt056Sb7~ZCP3hv-YDwZFxT~0nC8fjSOGZhkoVx6NJe0HYeuh87m5VSwtOSb0i0nlrx3N72n4CtoiUXFkKo1Wr4kDaYvi4H~CnwlRZRxHbLKY82fPcIKwAGX9M0oKH76LmuhHw~h1ZEoh2~ntoH6PR9-nRv3dfJu0jIxPNip-q6BZsceOBE0Ksyl4FPjw9tPL4NsIA2kJRv2rA-ecSM2TxHN1xzF19uHoe0newY30eGu~QlT8kBQ__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA
- Megalingam, R. K., Shriram, V., Likhith, B., Rajesh, G., Ghanta, S. (2016). Monocular distance estimation using pinhole camera approximation to avoid vehicle crash and back-over accidents. 2016 10th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Control (ISCO). https://doi.org/10.1109/isco.2016.7727017
- Tram, V. T. B., Yoo, M. (2018). Vehicle-to-Vehicle Distance Estimation Using a Low-Resolution Camera Based on Visible Light Communications. IEEE Access, 6, 4521–4527. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2793306
- Qi, S. H., Li, J., Sun, Z. P., Zhang, J. T., Sun, Y. (2019). Distance Estimation of Monocular Based on Vehicle Pose Information. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1168, 032040. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1168/3/032040
- Liu, J., Zhang, R., Hou, S. (2020). Inter-vehicle distance estimation considering camera attitude angles based on monocular vision. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 235 (2-3), 894–900. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954407020941399
- Zhu, J., Fang, Y. (2019). Learning Object-Specific Distance From a Monocular Image. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 3838–3847. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2019.00394
- Zhang, Y., Ding, L., Li, Y., Lin, W., Zhao, M., Yu, X., Zhan, Y. (2021). A regional distance regression network for monocular object distance estimation. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 79, 103224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2021.103224
- Vajgl, M., Hurtik, P., Nejezchleba, T. (2022). Dist-YOLO: Fast Object Detection with Distance Estimation. Applied Sciences, 12 (3), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031354
- Ahishali, M., Yamac, M., Kiranyaz, S., Gabbouj, M. (2023). Representation based regression for object distance estimation. Neural Networks, 158, 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2022.11.011
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Herdianto Herdianto, Poltak Sihombing, Fahmi Fahmi, Tulus Tulus

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








