Enhancing retrieval performance in social media with corpus-based query expansion using bidirectional encoder representations from transformers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.340258Keywords:
information retrieval, query expansion, corpus-based retrieval, BERT, social media, e-governmentAbstract
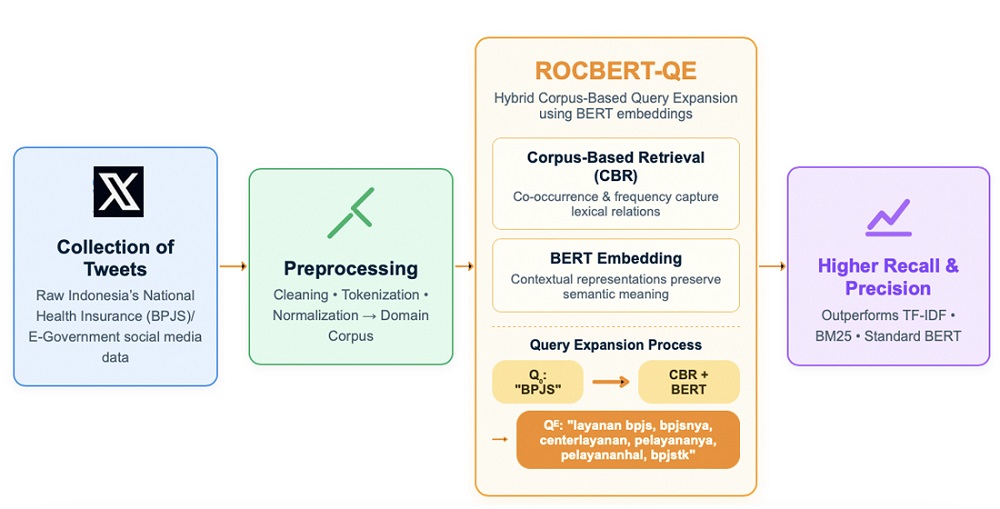
This study focuses on a collection of tweets related to government services (e-government), which are preprocessed and transformed into a domain-specific corpus for query expansion. Conventional IR models struggle with unstructured and noisy content containing informal language and abbreviations, which reduces retrieval accuracy. To overcome these issues, this study proposes a hybrid query expansion (QE) model named ROCBERT-QE, which combines corpus-based retrieval (CBR) with bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT). The model applies dual expansion, using corpus-based co-occurrence frequencies to capture lexical relationships and BERT embeddings to preserve semantic context. A domain-specific corpus consisting of 5,017 preprocessed tweets related to Indonesia’s National Health Insurance (BPJS) was constructed, encompassing 6,215 unique terms that represent linguistic variation and informality in public discourse. Experimental results demonstrate that ROCBERT-QE outperforms baseline retrieval methods such as TF-IDF, BM25, and standard BERT. For single-word queries, Recall reached 0.8574 and Precision 0.8807, while for sentence-level queries, Recall was 0.8932 and Precision 0.9175. The synergy of frequency-based and contextual expansion enables effective handling of lexical noise and semantic ambiguity. The results confirm the scientific potential of combining corpus-based and transformer-based approaches in IR tasks involving unstructured content. Practically, ROCBERT-QE can be applied for real-time analysis of citizen discourse in e-government contexts, such as service evaluation, policy feedback, and early detection of public issues. The framework is scalable and adaptable to other domains with informal or multilingual data characteristics
References
- Ghanem, F. A., Padma, M. C., Alkhatib, R. (2023). Automatic Short Text Summarization Techniques in Social Media Platforms. Future Internet, 15 (9), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15090311
- Sharma, S., Panda, S. P. (2023). Efficient information retrieval model: overcoming challenges in search engines-an overview. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 32 (2), 925. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v32.i2.pp925-932
- Iamnitchi, A., Hall, L. O., Horawalavithana, S., Mubang, F., Ng, K. W., Skvoretz, J. (2023). Modeling information diffusion in social media: data-driven observations. Frontiers in Big Data, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdata.2023.1135191
- Benamara, F., Inkpen, D., Taboada, M. (2018). Introduction to the Special Issue on Language in Social Media: Exploiting Discourse and Other Contextual Information. Computational Linguistics, 44 (4), 663–681. https://doi.org/10.1162/coli_a_00333
- Andreasen, T., Bordogna, G., Tré, G. D., Kacprzyk, J., Larsen, H. L., Zadrożny, S. (2024). The power and potentials of Flexible Query Answering Systems: A critical and comprehensive analysis. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 149, 102246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.datak.2023.102246
- Killingback, J., Zamani, H. (2025). Benchmarking Information Retrieval Models on Complex Retrieval Tasks. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2509.07253
- Allahim, A., Cherif, A., Imine, A. (2025). Semantic approaches for query expansion: taxonomy, challenges, and future research directions. PeerJ Computer Science, 11, e2664. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.2664
- Massai, L. (2024). Evaluation of semantic relations impact in query expansion-based retrieval systems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 283, 111183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.111183
- Alshanik, F., Apon, A., Du, Y., Herzog, A., Safro, I. (2022). Proactive Query Expansion for Streaming Data Using External Sources. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), 701–708. https://doi.org/10.1109/bigdata55660.2022.10020577
- Silva, S., Seara Vieira, A., Celard, P., Iglesias, E. L., Borrajo, L. (2021). A Query Expansion Method Using Multinomial Naive Bayes. Applied Sciences, 11 (21), 10284. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110284
- Chen, Z., Wang, J., Yang, X. (2022). A Concept Net-based semantic constraint method for query expansion. 2022 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Joint Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT), 906–913. https://doi.org/10.1109/wi-iat55865.2022.00147
- Xia, Y., Wu, J., Kim, S., Yu, T., Rossi, R. A., Wang, H., McAuley, J. (2025). Knowledge-Aware Query Expansion with Large Language Models for Textual and Relational Retrieval. Proceedings of the 2025 Conference of the Nations of the Americas Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers), 4275–4286. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2025.naacl-long.216
- Fan, Y., Xie, X., Cai, Y., Chen, J., Ma, X., Li, X., Zhang, R., Guo, J. (2022). Pre-training Methods in Information Retrieval. IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1561/9781638280637
- Claveau, V. (2020). Query expansion with artificially generated texts. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.08787
- Kumar, R., Sharma, S. C. (2022). Hybrid optimization and ontology-based semantic model for efficient text-based information retrieval. The Journal of Supercomputing, 79 (2), 2251–2280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04708-9
- Moreno-Ortiz, A., García-Gámez, M. (2023). Strategies for the Analysis of Large Social Media Corpora: Sampling and Keyword Extraction Methods. Corpus Pragmatics, 7 (3), 241–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41701-023-00143-0
- Seo, W., An, H., Lee, S. (2025). A New Query Expansion Approach via Agent-Mediated Dialogic Inquiry. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2502.08557
- Shyrokykh, K., Girnyk, M., Dellmuth, L. (2023). Short text classification with machine learning in the social sciences: The case of climate change on Twitter. PLOS ONE, 18 (9), e0290762. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0290762
- Mutiarin, D., Wahyuni, H., Ismail, N. S. A., Kumorotomo, W. (2023). Social Media in Support of Indonesia’s One Data Interoperability Process for Implementing Data Governance Policies. E3S Web of Conferences, 440, 03022. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202344003022
- Yulita, I. N., Al-Auza’i, A. F., Prabuwono, A. S., Sholahuddin, A., Ardiansyah, F., Sarathan, I., Djuyandi, Y. (2023). Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory for Analysis of Public Opinion Sentiment on Government Policy During the COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 14 (11). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2023.0141189
- Wahyudi, W., Loilatu, M. J., Omrilio, O. (2024). Capturing Political Conversation: An Analysis of Public Response on Social Media during Indonesian Election. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 12 (09), 163–182. https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2024.129009
- Abdelazim, H., Tharwat, M., Mohamed, A. (2023). Semantic Embeddings for Arabic Retrieval Augmented Generation (ARAG). International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 14 (11). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2023.01411135
- Faggioli, G. (2023). Modelling and Explaining IR System Performance Towards Predictive Evaluation. ACM SIGIR Forum, 57 (1), 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1145/3636341.3636361
- Wang, Y., Huang, H., Feng, C. (2017). Query Expansion Based on a Feedback Concept Model for Microblog Retrieval. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web, 559–568. https://doi.org/10.1145/3038912.3052710
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Roberto Kaban, Poltak Sihombing, Syahril Efendi, Maya Silvi Lydia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








