Development of a multi-agent adaptive recommendation system based on reinforcement learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.340491Keywords:
personalized recommendation, reinforcement learning, multi-agent environment, Actor-Critic modelAbstract
This study's object is the process that improves efficiency and accuracy in delivering personalized recommendations to users in systems based on reinforcement learning.
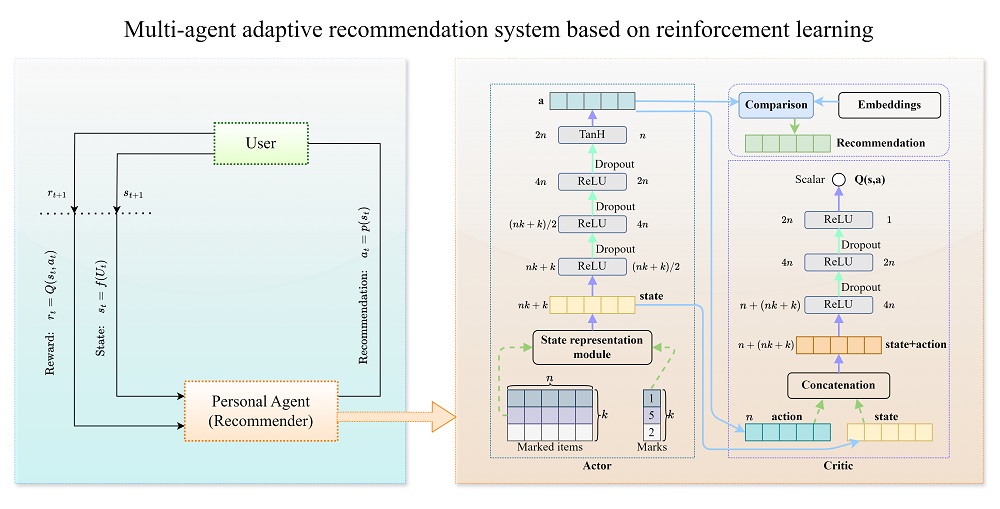
The principal task addressed in the study is to improve recommendation adaptation and personalization by assigning a dedicated agent to each user. This approach reduces the influence of other users’ activity and allows for more precise modeling of individual preferences.
The proposed approach employs an Actor–Critic model implemented using the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient algorithm to achieve more stable training and maximize long-term rewards in sequential decision-making processes. Recommendations are generated using the unique characteristics of items that are based on users’ historical interactions. Neural networks are trained with separate parameter configurations for single-agent and multi-agent models.
Experimental results on the MovieLens dataset demonstrate the superiority of the multi-agent model over the single-agent baseline across key evaluation metrics. For top-5 recommendations, the multi-agent model achieved improvements of + 4% for Precision@5; + 0.32% for Recall@5; and + 2.92% in Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain NDCG@5. For top-10 recommendations, gains were + 1% for Precision@10; + 0.18% for Recall@10; and + 1.14% for NDCG@10, respectively.
Simulations for individual users showed that the multi-agent model outperformed the single-agent baseline in 66 out of 100 cases in terms of cumulative reward. The proposed system demonstrates effectiveness in capturing user preferences, improving recommendation quality, and adapting to evolving user preferences over time.
The main area of practical application for the results includes dynamic online environments such as e-commerce systems, media platforms, social networks, and news aggregators.
References
- Zhang, Y. (2022). An Introduction to Matrix Factorization and Factorization Machines in Recommendation System, and Beyond. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.11026
- Wang, Y., Ren, Z., Sun, W., Yang, J., Liang, Z., Chen, X. et al. (2024). Content-Based Collaborative Generation for Recommender Systems. Proceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, 2420–2430. https://doi.org/10.1145/3627673.3679692
- Saleh, A., Dharshinni, N., Perangin-Angin, D., Azmi, F., Sarif, M. I. (2023). Implementation of Recommendation Systems in Determining Learning Strategies Using the Naïve Bayes Classifier Algorithm. Sinkron, 8 (1), 256–267. https://doi.org/10.33395/sinkron.v8i1.11954
- Silva, N., Werneck, H., Silva, T., Pereira, A. C. M., Rocha, L. (2022). Multi-Armed Bandits in Recommendation Systems: A survey of the state-of-the-art and future directions. Expert Systems with Applications, 197, 116669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116669
- Liu, F., Tang, R., Li, X., Zhang, W., Ye, Y., Chen, H. et al. (2019). Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Recommendation with Explicit User-Item Interactions Modeling. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1810.12027
- Sumiea, E. H., AbdulKadir, S. J., Al-Selwi, S. M., Alqushaibi, A., Ragab, M. G., Fati, S. M., Alhussian, H. S. (2023). Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithm: A Systematic Review. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3544387/v1
- Wang, Z., Yu, Y., Zheng, W., Ma, W., Zhang, M. (2024). MACRec: A Multi-Agent Collaboration Framework for Recommendation. Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, 2760–2764. https://doi.org/10.1145/3626772.3657669
- Zheng, S., Yin, H., Chen, T., Kong, X., Hou, J., Zhao, P. (2025). CADRL: Category-Aware Dual-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Explainable Recommendations over Knowledge Graphs. 2025 IEEE 41st International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), 128–141. https://doi.org/10.1109/icde65448.2025.00017
- Hui, Z., Wei, X., Jiang, Y., Gao, K., Wang, C., Ong, F. et al. (2025). MATCHA: Can Multi-Agent Collaboration Build a Trustworthy Conversational Recommender? arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2504.20094
- Lowe, R., Wu, Y., Tamar, A., Harb, J., Abbeel, P., Mordatch, I. (2017). Multi-Agent Actor-Critic for Mixed Cooperative-Competitive Environments. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.02275
- Alhejaili, A., Fatima, S. (2021). Multi-Agent Recommender System. Recent Advances in Agent-Based Negotiation, 103–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0471-3_7
- Trivedi, P., Hemachandra, N. (2022). Multi-Agent Natural Actor-Critic Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Dynamic Games and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13235-022-00449-9
- Vullam, N., Vellela, S. S., B, V. R., Rao, M. V., SK, K. B., D, R. (2023). Multi-Agent Personalized Recommendation System in E-Commerce based on User. 2023 2nd International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence and Computing (ICAAIC), 1194–1199. https://doi.org/10.1109/icaaic56838.2023.10140756
- He, X., An, B., Li, Y., Chen, H., Wang, R., Wang, X. et al. (2020). Learning to Collaborate in Multi-Module Recommendation via Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning without Communication. Fourteenth ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, 210–219. https://doi.org/10.1145/3383313.3412233
- Wu, Q., Zhang, H., Gao, X., He, P., Weng, P., Gao, H., Chen, G. (2019). Dual Graph Attention Networks for Deep Latent Representation of Multifaceted Social Effects in Recommender Systems. The World Wide Web Conference, 2091–2102. https://doi.org/10.1145/3308558.3313442
- Khangar, N., Kamalja, K. (2017). Multiple Correspondence Analysis and Its Applications. Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis, 10 (2), 432–462. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320694285
- Ghojogh, B., Ghodsi, A., Karray, F., Crowley, M. (2022). Factor Analysis, Probabilistic Principal Component Analysis, Variational Inference, and Variational Autoencoder: Tutorial and Survey. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2101.00734
- Pookduang, P., Klangbunrueang, R., Chansanam, W., Lunrasri, T. (2025). Advancing Sentiment Analysis: Evaluating RoBERTa against Traditional and Deep Learning Models. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research, 15 (1), 20167–20174. https://doi.org/10.48084/etasr.9703
- Jadon, A., Patil, A. (2024). A Comprehensive Survey of Evaluation Techniques for Recommendation Systems. Computation of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, 281–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-71484-9_25
- Harper, F. M., Konstan, J. A. (2015). The MovieLens Datasets. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems, 5 (4), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1145/2827872
- Zhao, X., Wang, M., Zhao, X., Li, J., Zhou, S., Yin, D. et al. (2023). Embedding in Recommender Systems: A Survey. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.18608
- Leon, V., Etesami, S. R. (2023). Online Reinforcement Learning in Markov Decision Process Using Linear Programming. 2023 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), 1973–1978. https://doi.org/10.1109/cdc49753.2023.10383839
- Romaniuk, B., Peliushkevych, O., Shcherbyna, Y. (2021). Recommendation system development using reinforcement learning. Visnyk of the Lviv University. Series Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 29, 150–162. https://doi.org/10.30970/vam.2021.29.11016
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bohdan Romaniuk, Olha Peliushkevych

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








