Construction of a simulation model for managing load on computing nodes in a server cluster based on the theory of fuzzy logic and Nash equilibrium
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.340603Keywords:
simulation model, server cluster, optimization, load management, resilienceAbstract
This study’s object is the process of managing (balancing) the load on the computing nodes in a server cluster of information systems. The task addressed is to enable optimal (even) distribution of server resources within a cluster system.
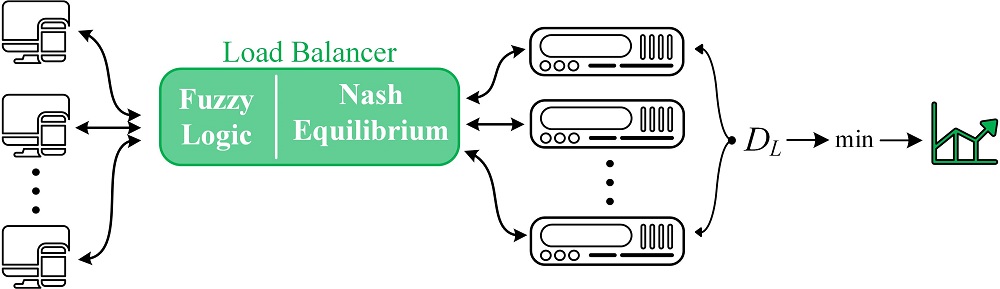
A simulation model of the process that distributes the load on computing nodes of a server cluster has been built, based on an improved model of the optimal use of server resources in a cluster based on Nash equilibrium and an improved method of adaptive load balancing in cluster systems according to Nash equilibrium.
The simulation model has been constructed on the basis of fuzzy logic theory to determine the feasibility of decomposing tasks into subtasks, as well as game theory, in particular Nash equilibrium, to determine the optimal distribution of tasks/subtasks across cluster system servers for their parallel processing.
The model built makes it possible to improve the efficiency (uniformity) of server resource distribution by an average of 13% compared to the classical load management method based on Nash equilibrium, by 61% with the Round Robin method, and by 63% with the Least Connection method throughout the entire process of cluster operation. This, in turn, allows for a more than 2-fold increase in the number of processed tasks from client requests compared to the above load balancing methods.
In addition, the impact of the load balancing process on the processing time of tasks/subtasks by the cluster system servers was estimated. Based on the results of simulation modeling, it can be concluded that the application of the devised model does not exceed the total allowable processing time (no more than 315 ms) of tasks/subtasks from client requests compared to existing load balancing methods
References
- Pro rishennia Rady natsionalnoi bezpeky i oborony Ukrainy vid 20 serpnia 2021 roku "Pro Stratehichnyi oboronnyi biuleten Ukrainy". Ukaz Prezydenta Ukrainy vid 17.09.2021 r. No. 473/2021. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/473/2021#Text
- Pro rishennia Rady natsionalnoi bezpeky i oborony Ukrainy vid 18 chervnia 2021 roku «Pro Stratehiiu rozvytku oboronno-promyslovoho kompleksu Ukrainy»/ Ukaz Prezydenta Ukrainy vid 20.08.2021 r. No. 372/2021. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/372/2021#Text
- Begam, G. S., Sangeetha, M., Shanker, N. R. (2021). Load Balancing in DCN Servers through SDN Machine Learning Algorithm. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 47 (2), 1423–1434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05911-1
- Klots, Y. P., Stefanovytch, K. Y., Shakhoval, Y. S., Demeshko, V. I. (2019). Dynamic traffic balance between several providers. Herald of Khmelnytskyi national university, 4 (275). 62–67. Available at: https://journals.khnu.km.ua/vestnik/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/12-7.pdf
- Naz, N. S., Abbas, S., Adnan, M., Abid, B., Tariq, N., Farrukh, M. (2019). Efficient Load Balancing in Cloud Computing using Multi-Layered Mamdani Fuzzy Inference Expert System. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 10 (3). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2019.0100373
- Chen, L., Wu, K., Li, Y. (2014). A Load Balancing Algorithm Based on Maximum Entropy Methods in Homogeneous Clusters. Entropy, 16 (11), 5677–5697. https://doi.org/10.3390/e16115677
- Priya, S. S., Rajendran, Dr. T. (2025). Enhanced Weighted Round Robin: A New Paradigm in Cloud Load Balancing. Indian Journal Of Science And Technology, 18 (15), 1220–1228. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/v18i15.3976
- Dash, Y., Dalei, R. K., Dhal, K. (2025). Modified Genetic Algorithms (GA) for Load balancing in Cloud Computing. Journal of Information Systems Engineering and Management, 10 (54s), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.52783/jisem.v10i54s.11028
- Matiwure, T., Ndlovu, A. (2025). Enhancing throttled load balancing algorithm with machine learning for dynamic resource allocation in cloud computing environments. International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing, 14 (6), 20–25. https://doi.org/10.47760/ijcsmc.2025.v14i06.003
- Fesokha, V. V., Neroznak, E. I., Sova, O. Ya. (2023). An improved model of optimal use of resources of a cluster system of military assignment based on nash equilibrium. Collection of Scientific Works of the Military Institute of Kyiv National Taras Shevchenko University, 79, 159–171. https://doi.org/10.17721/2519-481x/2023/79-15
- Fesokha, V., Neroznak, Y., Sova, O., Nesterov, O. (2023). Method of adaptive load balancing in cluster systems for military purposes based on Nash equilibrium. Zbirnyk naukovykh prats Tsentru voienno-stratehichnykh doslidzhen NUOU imeni Ivana Cherniakhovskoho, 3 (76), 101–110. https://doi.org/10.33099/2304-2745/2022-3-76/101-110
- Sivanandam, S. N., Sumathi, S., Deepa, S. N. (2007). Introduction to Fuzzy Logic using MATLAB. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-35781-0
- MATLAB. The MathWorks, Inc. Available at: https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/
- Welcome to Nashpy’s documentation! Nashpy. Available at: https://nashpy.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
- Campesato, O. (2020). Python 3 for Machine Learning. Mercury Learning and Information, 364. Available at: https://www.amazon.com/Python-Machine-Learning-Oswald-Campesato/dp/1683924959
- Neroznak, Ye. I., Merkotan, D. Yu., Sova, O. Ya. (2021). Metody ta alhorytmy balansuvannia navantazhennia v klasternykh systemakh na osnovi elementiv shtuchnoho intelektu. Systemy i tekhnolohiyi zviazku, informatyzatsiyi ta kiberbezpeky: aktualni pytannia i tendentsiyi rozvytku: I Mizhnarodna nauk.-tekhn. konf. Kyiv, 215–217.
- Load Balancing Algorithms and Techniques. Available at: https://kemptechnologies.com/load-balancer/load-balancing-algorithms-techniques
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yevhenii Neroznak, Olexandr Trotsko, Vitalii Fesokha, Dmytro Balan, Robert Bieliakov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








