Development of a forecasting model for optimizing energy consumption at coal enterprises
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.345073Keywords:
power consumption mode, coal mine, time series, ARIMA, exponential smoothing, neural network model, LSTM, MAPE, test sample, stationarityAbstract
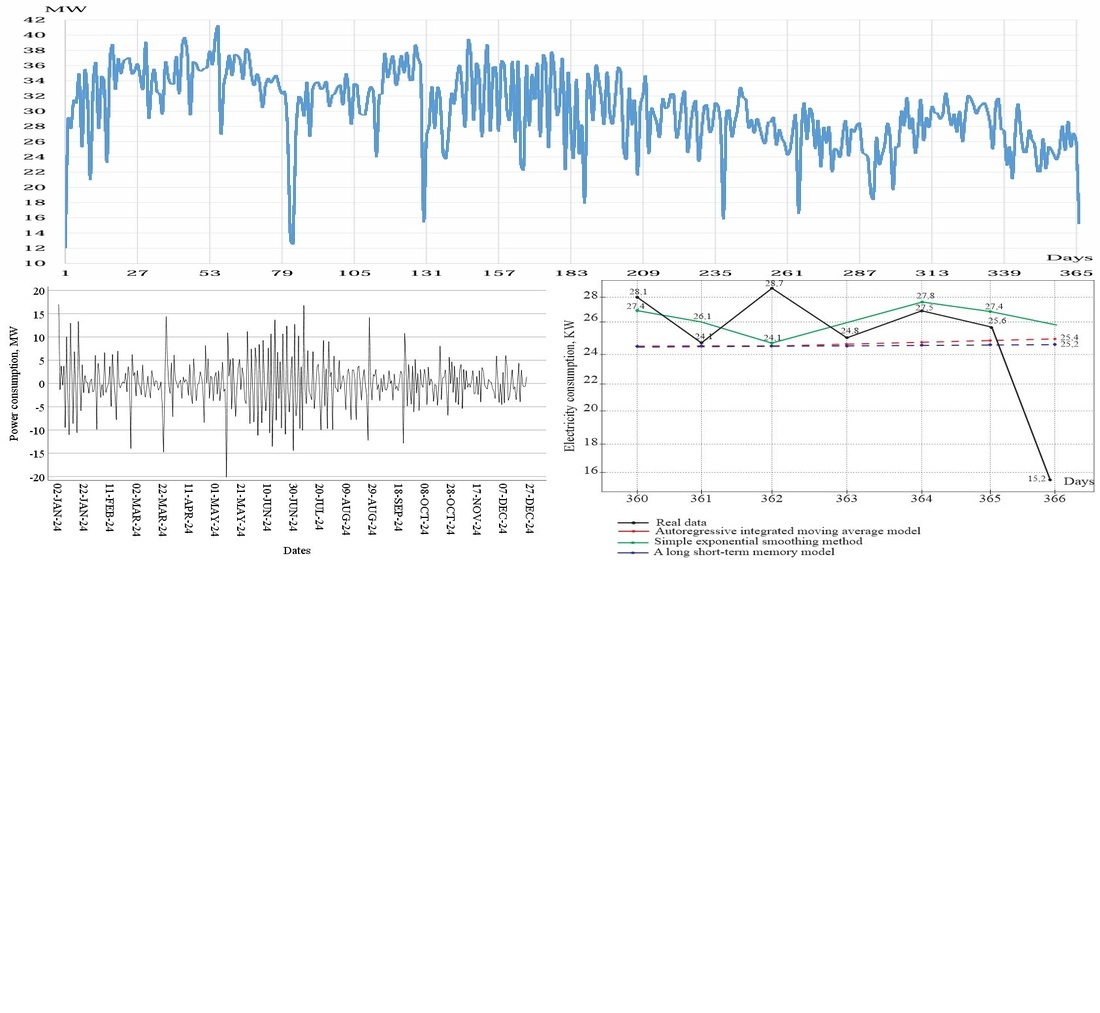
The study object is daily data on electricity consumption of one of the coal mines in the Karaganda basin for 2024. This article solves the problem of the lack of accurate tools that can predict complex and variable modes of energy consumption in a coal mine and thereby ensure more efficient management of energy-intensive installations.
This article presents a comparative analysis of three electricity demand forecasting models using data from a coal mine in the Karaganda basin for 2024. The study explores the effectiveness of both classical approaches (seasonal ARIMA model and simple exponential smoothing) and an LSTM neural network model. To handle non-stationary data, the first difference method was applied, allowing the time series to be stationary. The forecast was generated for 7 days in advance. A comparative analysis of the models’ accuracy was conducted using the MAPE metric on both the training and test sets. The study found that the LSTM model demonstrated the best results with a MAPE of 5.37% on the test set demonstrating its superior ability to capture complex data dynamics compared to ARIMA and simple exponential smoothing.
The developed predictive LSTM model can be effectively used in automated energy monitoring and management systems, providing accurate short-term load forecasts for coal mines and other mining and metallurgical enterprises with complex and volatile energy structures, provided the initial data is highly reliable and complete
References
- Kazakhstan Electric Power Industry Key Factors. Available at: https://www.kegoc.kz/en/electric-power/elektroenergetika-kazakhstana/
- Hu, H.-J., Sun, X., Zeng, B., Gong, D.-W., Zhang, Y. (2024). Multi-time-scale interval optimal dispatch of coal mine integrated energy system considering source-load uncertainty. Control and Decision (Kongzhi yu Juece), 39 (3), 827–835. https://doi.org/10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1507
- Zeng, Z., Li, M. (2021). Bayesian median autoregression for robust time series forecasting. International Journal of Forecasting, 37 (2), 1000–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2020.11.002
- Xiao, H., Wang, B., Zhou, H., Hu, W., Liu, G.-Ping. (2026). Digital twin-empowered power consumption prediction for energy-intensive aluminum annealing furnaces. Expert Systems with Applications, 296, 129079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2025.129079
- Kaytez, F., Taplamacioglu, M. C., Cam, E., Hardalac, F. (2015). Forecasting electricity consumption: A comparison of regression analysis, neural networks and least squares support vector machines. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 67, 431–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.12.036
- De Silva, S. N., Mishra, B. K., Sayers, W., Loukil, Z. (2025). Predicting Long-Term Electricity Consumption Using Time Series Data: Use Case of the UK Electricity Data. Intelligent Systems with Applications in Communications, Computing and IoT, 37–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-92614-3_3
- El-Azab, H.-A. I., Swief, R. A., El-Amary, N. H., Temraz, H. K. (2025). Seasonal forecasting of the hourly electricity demand applying machine and deep learning algorithms impact analysis of different factors. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-91878-0
- Telbayeva, S., Nurmaganbetova, G., Avdeyev, L., Kaverin, V., Issenov, S., Janiszewski, D. et al. (2024). Development of mathematical models of power consumption at coal plants. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (8 (131)), 22–32. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.313932
- Zhou, S., Ni, S., Han, Y., Dong, Z., Lai, C. S. (2025). Adaptive electricity consumption forecasting approach for universal environments. Scientific Reports, 15 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-10147-2
- Bui, T. H., Lee, K. (2025). Forecasting annual electricity consumption in Vietnam using radial basis function neural network. Energy, 334, 137762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2025.137762
- Tolentino, J. A. (2025). Forecasting Electricity Consumption Using ARIMA Model. Smart Trends in Computing and Communications, 41–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-7517-3_4
- Al-Dahhan, I. A. H., Ashour, M. A. H. (2025). A Hybrid ARIMA-ANN Model for Enhanced Electricity Consumption Forecasting in Bahrain. Integrating Big Data and IoT for Enhanced Decision-Making Systems in Business, 399–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-97609-4_34
- ARIMA model. Available at: https://docs.exponenta.ru/econ/arima-model.html
- Exponential smoothing. Available at: https://help.fsight.ru/ru/mergedProjects/lib/02_time_series_analysis/uimodelling_expsmooth.htm
- LSTM – long-term short-term memory networks. Available at: https://habr.com/ru/companies/wunderfund/articles/331310/
- Fundamentals of forecasting theory. Available at: https://openforecast.org/ru/etextbook/about/
- Methods and formulas for Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test. Available at: https://support.minitab.com/en-us/minitab/help-and-how-to/statistical-modeling/time-series/how-to/augmented-dickey-fuller-test/methods-and-formulas/methods-and-formulas/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Shynar Telbayeva, Leonid Avdeyev, Vladimir Kaverin, Dinara Zhumagulova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








