Optimization of a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrometer with transaxial mirrors providing spatial and energy tof focusing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.346298Keywords:
multi-reflector time-of-flight mass spectrometers, transaxial electrostatic mirror, analytical expressions for potentialAbstract
This study explores a multi-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrometer (TOFMS) based on transaxial electrostatic mirrors providing spatial and energy time-of-flight focusing of the ion beam. Analysis of existing solutions reveals that spatial-energy time-of-flight focusing in compact TOFMSs is achieved using additional focusing elements, which complicates the design, limits resolution, and reduces sensitivity.
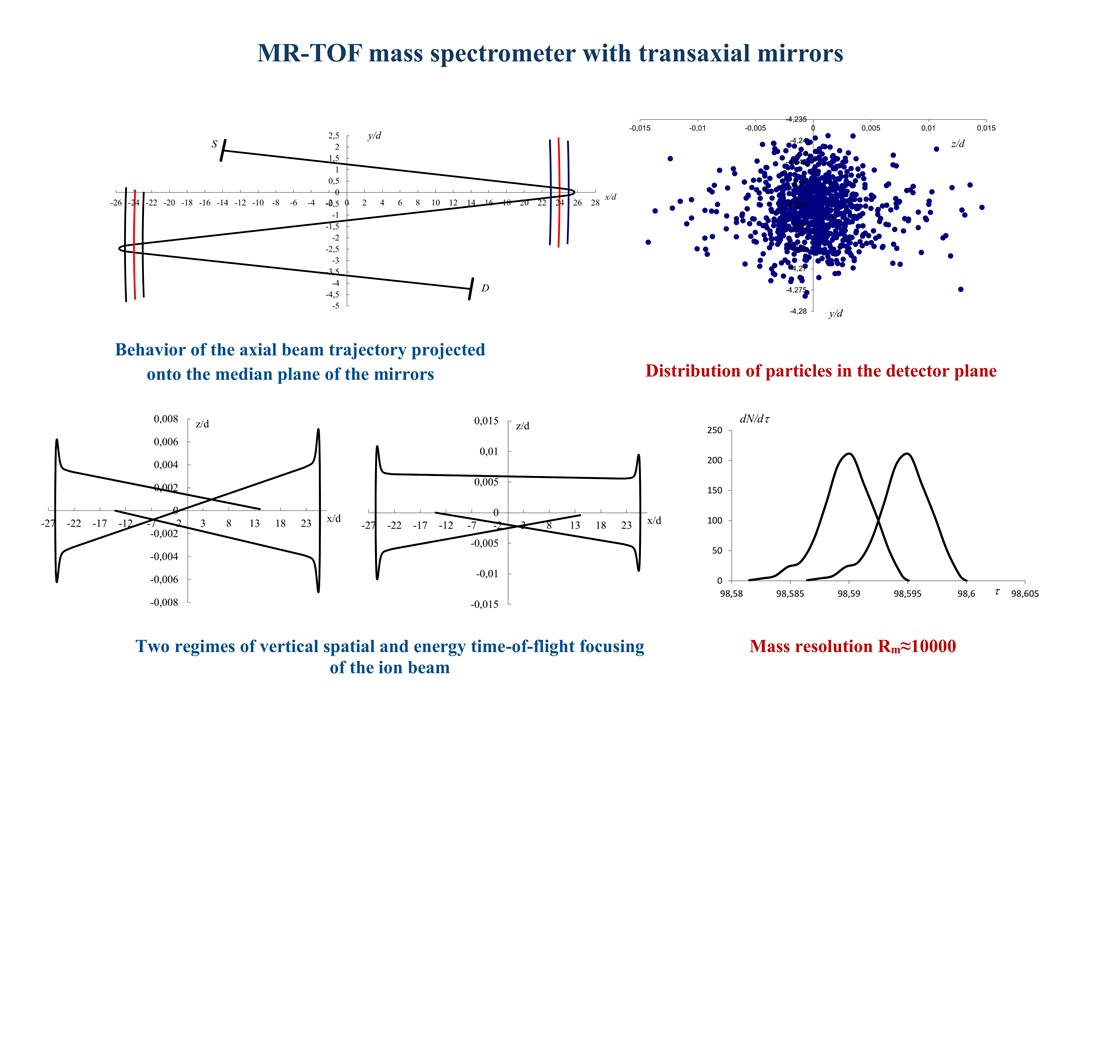
This paper demonstrates that three-electrode transaxial mirrors enable simultaneous spatial and energy time-of-flight focusing of ions without the use of additional focusing elements. Monte Carlo simulation of the beam dynamics has made it possible to determine the trajectories and flight times of ions under various initial conditions.
It was found that two closely spaced vertical focusing modes provide time-of-flight focusing of ions with a relative energy spread of . A mass resolution of 10,000 at half-maximum confirms the high efficiency of the proposed structure. The spatial distributions of the ion beam demonstrate stable focusing in the detector plane when modeling particles larger than 1000.
The results are attributed to the features of transaxial geometry, which enables three-dimensional spatial and energy time-of-flight focusing. The practical significance of this work is the applicability of such multi-reflector mass analyzers in laboratory and space research where a combination of high resolution and instrument compactness is required
References
- Wollnik, H. (2013). History of mass measurements in time-of-flight mass analyzers. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 349-350, 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2013.04.023
- Cotter, R. J. (1989). Time-of-flight mass spectrometry: An increasing role in the life sciences. Biological Mass Spectrometry, 18 (8), 513–532. https://doi.org/10.1002/bms.1200180803
- Wollnik, H., Wada, M., Schury, P., Rosenbusch, M., Ito, Y., Miyatake, H. (2019). Time-of-flight mass spectrographs of high mass resolving power. International Journal of Modern Physics A, 34 (36), 1942001. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0217751x19420016
- Meisel, Z., George, S. (2013). Time-of-flight mass spectrometry of very exotic systems. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 349-350, 145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2013.03.022
- Knauer, S., Fischer, P., Marx, G., Müller, M., Rosenbusch, M., Schabinger, B. et al. (2019). A multi-reflection time-of-flight setup for the improvement and development of new methods and the study of atomic clusters. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 446, 116189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2019.116189
- Yavor, M. I., Pomozov, T. V., Kirillov, S. N., Khasin, Y. I., Verenchikov, A. N. (2018). High performance gridless ion mirrors for multi-reflection time-of-flight and electrostatic trap mass analyzers. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 426, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2018.01.009
- Rosenbusch, M., Wada, M., Chen, S., Takamine, A., Iimura, S., Hou, D. et al. (2023). The new MRTOF mass spectrograph following the ZeroDegree spectrometer at RIKEN’s RIBF facility. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1047, 167824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2022.167824
- Ayet San Andrés, S., Hornung, C., Ebert, J., Plaß, W. R., Dickel, T., Geissel, H. et al. (2019). High-resolution, accurate multiple-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrometry for short-lived, exotic nuclei of a few events in their ground and low-lying isomeric states. Physical Review C, 99 (6). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevc.99.064313
- Cooper-Shepherd, D. A., Wildgoose, J., Kozlov, B., Johnson, W. J., Tyldesley-Worster, R., Palmer, M. E. et al. (2023). Novel Hybrid Quadrupole-Multireflecting Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry System. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 34 (2), 264–272. https://doi.org/10.1021/jasms.2c00281
- Dickel, T., San Andrés, S. A., Beck, S., Bergmann, J., Dilling, J., Greiner, F. et al. (2019). Recent upgrades of the multiple-reflection time-of-flight mass spectrometer at TITAN, TRIUMF. Hyperfine Interactions, 240 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-019-1610-y
- Jiang, J., Hua, L., Xie, Y., Cao, Y., Wen, Y., Chen, P., Li, H. (2021). High Mass Resolution Multireflection Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometer. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 32 (5), 1196–1204. https://doi.org/10.1021/jasms.1c00016
- Spivak-Lavrov, I. (2016). Analytical Methods for the Calculation and Simulation of New Schemes of Static and Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometers. Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, 45–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aiep.2015.10.001
- Spivak-Lavrov, I. F., Kalimatov, T. S., Shugaeva, T. Z. (2019). Prismatic mass analyzer with the conical achromatic prism and transaxial lenses. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 444, 116180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2019.116180
- Spivak-Lavrov, I. F., Nurmukhanova, A. A., Shugaeva, T. Zh. (2019). Mass analyzer with a conic achromatic prism and transaxial lenses. Scientific Instrumentation, Saint Petersburg, 29 (1), 116–125.
- Spivak-Lavrov, I. F., Shugaeva, T. Zh., Sharipov, S. U. (2020). Solutions of the Laplace equation in cylindrical coordinates, driven to 2D harmonic potentials. Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aiep.2020.06.006
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Tilektes Shugayeva, Igor Spivak-Lavrov, Orda Baisanov, Amangul Amantayeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








