Development of oxide composite materials for cathode element of IT-SOFCs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269852Keywords:
solid oxide fuel cells, cobalt-free cathode composite, perovskite structure, oxygen content, electronic conductivityAbstract
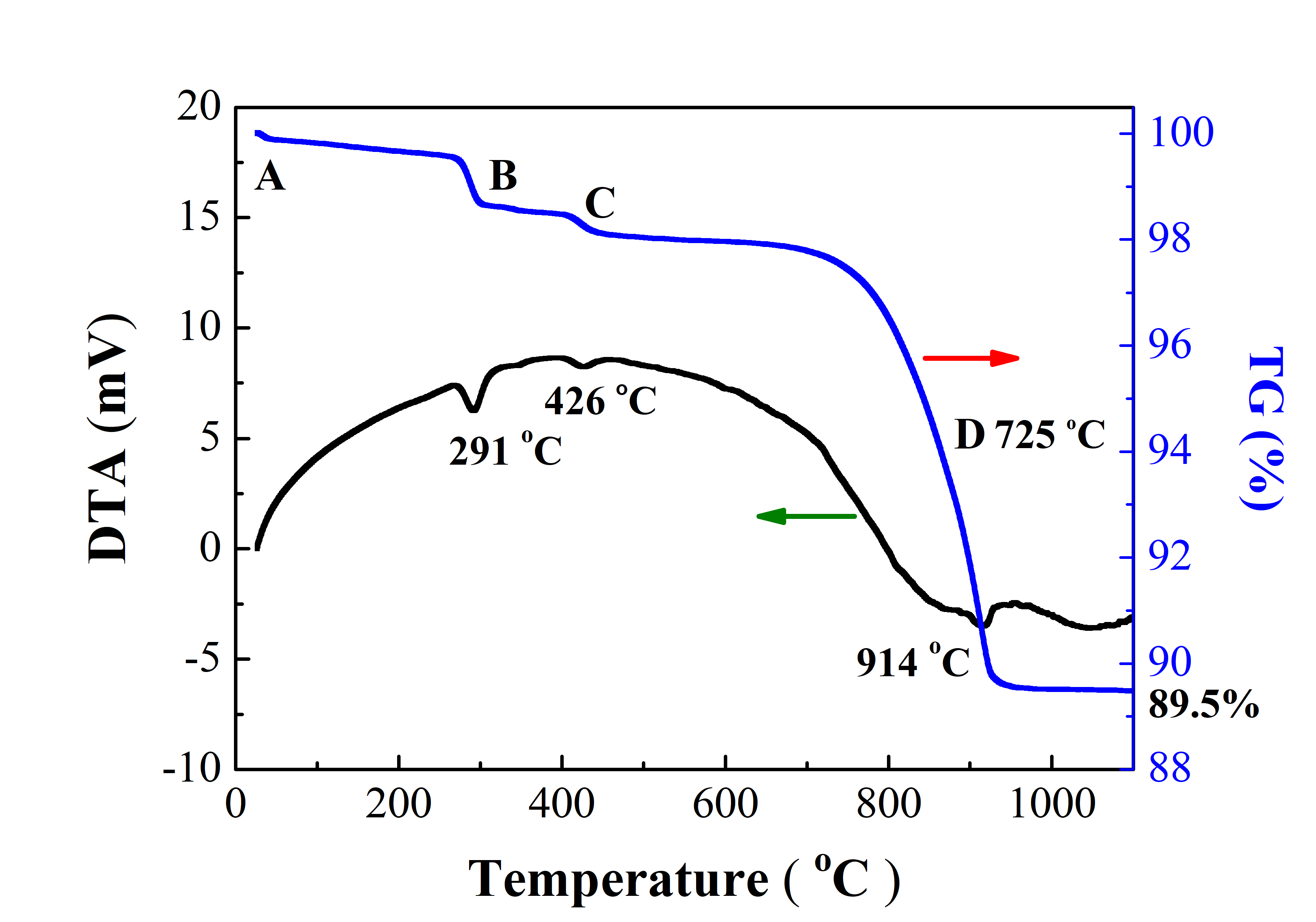
Investigating the properties of composite oxide for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFCs) has been done as a new cathode material. Using a solid-state reaction method, the metallic oxide material has been employed to create the composite model system. During the sintering process, a model system of Sm0.5Sr0.35Ba0.15FeO3-δ (SSBF15) was constructed. Thermal gravimetric analysis (TG) was played to utilize the oxygen content and weight loss of the model. In the meantime, the structure of the composite was characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), and the conductivity properties were tested by thermal conductivity. The structural design was made possible by the findings, which revealed that the composite model structure exhibited the crystalline structure with perovskite phase. Weight losses during the construction of the structure were reflected in the decomposition and evaporation of the composite's constituent parts. After the calcination process up to 950 °C, the model system's formation oxygen content was obtained of 2.94 in 800 °C. The electrical conductivity maximum obtained in 12.2 S·cm-1 at 430 °C. At low temperatures, the conductive behavior was affected by the metallic element, while at higher temperatures, it was influenced by the ionic structure. As a result, mixed ionic and electric conductors (MIEC) were extensively utilized in the process of generating the conductive properties. The SSBF15 composite has a good chance of being used as an alternative cathode material with a perovskite single phase for future IT-SOFCs applications based on the structure and conductivity results. Additional testing and observation are required to determine the resistance's value when incorporated into the electrolyte and its heat expansion properties
Supporting Agency
- The author would like to acknowledge the funding support to this research from the Center of research and community service Politeknik Negeri Jakarta.
References
- Tan, L., Dong, X., Gong, Z., Wang, M. (2018). Analysis on energy efficiency and CO2 emission reduction of an SOFC-based energy system served public buildings with large interior zones. Energy, 165, 1106–1118. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.054
- Bompard, E., Napoli, R., Wan, B., Orsello, G. (2008). Economics evaluation of a 5kW SOFC power system for residential use. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 33 (12), 3243–3247. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.04.017
- Naimaster, E. J., Sleiti, A. K. (2013). Potential of SOFC CHP systems for energy-efficient commercial buildings. Energy and Buildings, 61, 153–160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.09.045
- Fernandes, A., Woudstra, T., van Wijk, A., Verhoef, L., Aravind, P. V. (2016). Fuel cell electric vehicle as a power plant and SOFC as a natural gas reformer: An exergy analysis of different system designs. Applied Energy, 173, 13–28. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.107
- Ramadhani, F., Hussain, M. A., Mokhlis, H., Hajimolana, S. (2017). Optimization strategies for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) application: A literature survey. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 76, 460–484. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.052
- Jiang, S., Sunarso, J., Zhou, W., Shen, J., Ran, R., Shao, Z. (2015). Cobalt-free SrNbxFe1−xO3−δ (x = 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2) perovskite cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 298, 209–216. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.08.063
- Li, C.-H., Hu, S.-H., Tay, K.-W., Fu, Y.-P. (2012). Electrochemical characterization of gradient Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3−δ cathodes on Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9 electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells. Ceramics International, 38 (2), 1557–1562. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.09.041
- Wang, S., Feng, Y., Wang, D. (2014). Electrochemical comparison of cobalt-free La0.5Sr0.5Fe0.9Mo0.1O3−δ based cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Ceramics International, 40 (4), 6359–6363. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.10.133
- Subardi, A., Chen, C.-C., Cheng, M.-H., Chang, W.-K., Fu, Y.-P. (2016). Electrical, thermal and electrochemical properties of SmBa1−xSrxCo2O5+δ cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochimica Acta, 204, 118–127. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.04.069
- Baharuddin, N. A., Muchtar, A., Somalu, M. R. (2017). Short review on cobalt-free cathodes for solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42 (14), 9149–9155. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.097
- Mastin, J., Einarsrud, M.-A., Grande, T. (2006). Structural and Thermal Properties of La1-xSrxCoO3-δ. Chemistry of Materials, 18 (25), 6047–6053. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/cm061539k
- Ji, H.-I., Hwang, J., Yoon, K. J., Son, J.-W., Kim, B.-K., Lee, H.-W., Lee, J.-H. (2013). Enhanced oxygen diffusion in epitaxial lanthanum–strontium–cobaltite thin film cathodes for micro solid oxidefuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci., 6 (1), 116–120. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee21647g
- Shao, Z., Haile, S. M. (2004). A high-performance cathode for the next generation of solid-oxide fuel cells. Nature, 431 (7005), 170–173. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02863
- Yang, W., Hong, T., Li, S., Ma, Z., Sun, C., Xia, C., Chen, L. (2013). Perovskite Sr1–xCexCoO3−δ (0.05 ≤ x ≤ 0.15) as Superior Cathodes for Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5 (3), 1143–1148. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/am3029238
- Wei, B., Lü, Z., Huang, X., Liu, M., Li, N., Su, W. (2008). Synthesis, electrical and electrochemical properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5Zn0.2Fe0.8O3−δ perovskite oxide for IT-SOFC cathode. Journal of Power Sources, 176 (1), 1–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.09.120
- Ling, Y., Zhao, L., Lin, B., Dong, Y., Zhang, X., Meng, G., Liu, X. (2010). Investigation of cobalt-free cathode material Sm0.5Sr0.5Fe0.8Cu0.2O3−δ for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35 (13), 6905–6910. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.04.021
- Liu, H., Zhu, K., Liu, Y., Li, W., Cai, L., Zhu, X. et al. (2018). Structure and electrochemical properties of cobalt-free perovskite cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochimica Acta, 279, 224–230. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.05.086
- Zhao, L., He, B., Zhang, X., Peng, R., Meng, G., Liu, X. (2010). Electrochemical performance of novel cobalt-free oxide Ba0.5Sr0.5Fe0.8Cu0.2O3−δ for solid oxide fuel cell cathode. Journal of Power Sources, 195 (7), 1859–1861. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.09.078
- Pang, S., Wang, W., Chen, T., Shen, X., Wang, Y., Xu, K., Xi, X. (2016). Systematic evaluation of cobalt-free Ln0.5Sr0•5Fe0•8Cu0•2O3−δ (Ln = La, Pr, and Nd) as cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 326, 176–181. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.06.134
- Ding, X., Gao, X., Zhu, W., Wang, J., Jiang, J. (2014). Electrode redox properties of Ba1−xLaxFeO3−δ as cobalt free cathode materials for intermediate-temperature SOFCs. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 39 (23), 12092–12100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.06.009
- Meng, X., Lü, S., Yu, W. W., Ji, Y., Sui, Y., Wei, M. (2018). Layered perovskite LnBa0.5Sr0.5Cu2O5+δ (Ln = Pr and Nd) as cobalt-free cathode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 43 (9), 4458–4470. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.01.033
- Ling, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Wang, S., Zhao, L., Liu, X., Lin, B. (2013). Potentiality of cobalt-free perovskite Ba0.5Sr0.5Fe0.9Mo0.1O3−δ as a single-phase cathode for intermediate-to-low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (33), 14323–14328. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.08.089
- Chen, D., Chen, C., Dong, F., Shao, Z., Ciucci, F. (2014). Cobalt-free polycrystalline Ba0.95La0.05FeO3−δ thin films as cathodes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 250, 188–195. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.11.010
- Fu, Y.-P. (2010). Sm0.5Sr0.5Co0.4Ni0.6O3−δ–Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 as a potential cathode for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35 (16), 8663–8669. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.05.109
- Ding, X., Kong, X., Wu, H., Zhu, Y., Tang, J., Zhong, Y. (2012). SmBa0.5Sr0.5Cu2O5+δ and SmBa0.5Sr0.5CuFeO5+δ layered perovskite oxides as cathodes for IT-SOFCs. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 37 (3), 2546–2551. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.10.080
- Kamal, D. M., Susanto, I., Subarkah, R., Zainuri, F., Zainuri, B., Rahmiati, T. et al. (2021). Design of solid oxide structure on the composite cathode for IT-SOFC. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (5 (112)), 6–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.239162
- Subardi, A., Liao, K.-Y., Fu, Y.-P. (2019). Oxygen transport, thermal and electrochemical properties of NdBa0.5Sr0.5Co2O5+δ cathode for SOFCs. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (1), 30–40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.01.022
- Subardi, A., Susanto, I., Kartikasari, R., Tugino, T., Kuntara, H., Wijaya, A. E. et al. (2021). An analysis of SmBa0.5Sr0.5Co2O5+δ double perovskite oxide for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (12 (110)), 6–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.226342
- Susanto, I., Kamal, D. M., Ruswanto, S., Subarkah, R., Zainuri, F., Permana, S. et al. (2020). Development of cobalt-free oxide (Sm0.5Sr0.5Fe0.8Cr0.2O3-δ) cathode for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFCs). Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (5 (108)), 15–20. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.217282
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Iwan Susanto, Dianta Mustofa Kamal, Tia Rahmiati, Vika Rizkia, Fuad Zainuri, Belyamin Belyamin, Sulaksana Permana, Adi Subardi, Ye-Pei Fu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








