Improving the heat transfer characteristics of miniature two-phase thermosyphons with nanofluids based on Ukrainian natural alumosilicates
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286320Keywords:
miniature thermosyphon, nanofluids, concentration, filling factor, heat flow, thermal resistanceAbstract
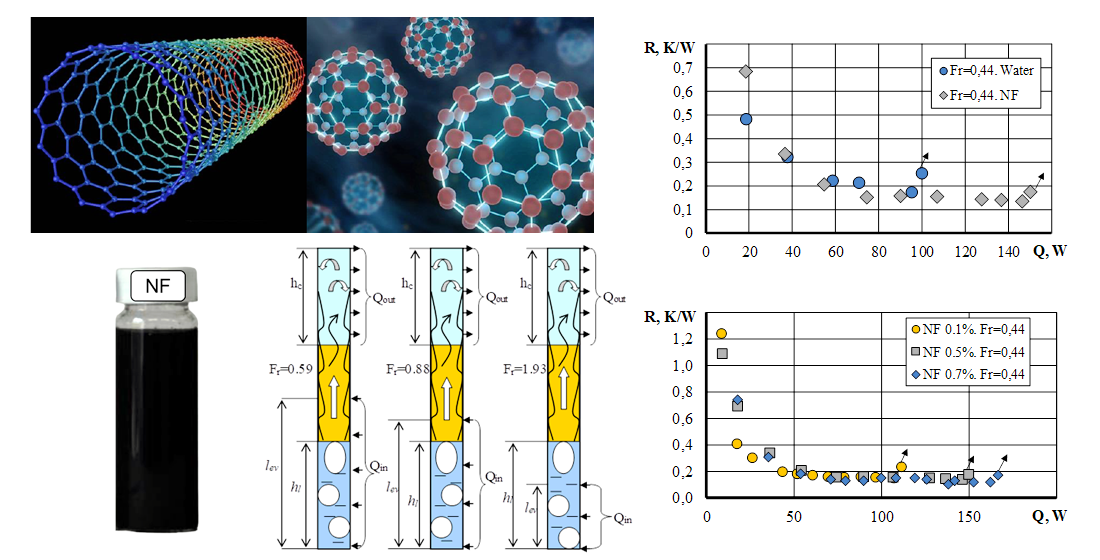
In order to improve the heat transfer characteristics of miniature thermosyphons, a study of the processes of heat transfer by them using water and nanofluids as heat carriers was carried out. A water mixture based on nanoparticles of Ukrainian natural aluminosilicate - attapulgite with the addition of 0.1 % carbon nanotubes was used as nanofluids. The data of the study of the maximum heat flow and the minimum thermal resistance of copper thermosyphons with an internal diameter of 5 mm and a length of 700 mm are presented. Orientation of thermosyphons in space: vertical. The length of the heating zone varied from 50 mm to 200 mm, with the same amount of heat-carrier. The fill factor varied from 0.44 to 1.93.
A comparison was performed of the heat transfer capabilities of thermosyphons with water and with a nanofluid with a mass concentration of 0.5 %. It has been shown that nanofluid thermosyphons transmit 53 % more heat flow compared to water, and thermal resistances are reduced by 25 %.
The influence of the concentration of nanoparticles on the heat transfer characteristics of thermosyphons is shown. Nanofluids with concentrations (0.1 %, 0.5 %, 0.7 %) showed the same level of thermal resistances, with an increase in maximum heat flows compared to distilled water. Thus, when compared with the lowest concentration (0.1 %), the use of 0.5 % nanofluid gives an advantage of up to 40 %, and 0.7 % – an advantage of up to 51 %. This is explained by the appearance of a specific porous structure of anisometric nanoparticles on the heating surface, which contributes to the appearance of additional centers of vaporization during boiling and improves the heat transfer characteristics of thermosyphons.
Thus, the use of such thermosyphons with nanofluids when cooling elements of electronic equipment could improve their functional characteristics
References
- Singh, A., Dubey, S., Dubey, H. (2019) Nanotechnology: the future engineering. International Journal of Advance and Innovative Research, 6 (2), 229–233. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333448927
- Zhang, Y., Zhou, Y. (2022). The recent progress of nanofluids and the state-of-art thermal devices. Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology, 13, 82–89. doi: https://doi.org/10.54097/hset.v13i.1335
- Yang, L., Xu, J., Du, K., Zhang, X. (2017). Recent developments on viscosity and thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Powder Technology, 317, 348–369. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.04.061
- Vanaki, Sh. M., Ganesan, P., Mohammed, H. A. (2016). Numerical study of convective heat transfer of nanofluids: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 54, 1212–1239. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.042
- Akilu, S., Sharma, K. V., Baheta, A. T., Mamat, R. (2016). A review of thermophysical properties of water based composite nanofluids. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 66, 654–678. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.036
- Xu, Y., Xue, Y., Qi, H., Cai, W. (2021). An updated review on working fluids, operation mechanisms, and applications of pulsating heat pipes. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 144, 110995. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110995
- Kim, T. I., Chang, W. J., Chang, S. H. (2011). Flow boiling CHF enhancement using Al2O3 nanofluid and an Al2O3 nanoparticle deposited tube. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 54 (9-10), 2021–2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.12.029
- Sözen, A., Menlik, T., Gürü, M., Boran, K., Kılıç, F., Aktaş, M., Çakır, M. T. (2016). A comparative investigation on the effect of fly-ash and alumina nanofluids on the thermal performance of two-phase closed thermo-syphon heat pipes. Applied Thermal Engineering, 96, 330–337. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.11.038
- Bondarenko, B. I., Moraru, V. N., Sydorenko, S. V., Komysh, D. V., Khovavko, A. I. (2016). Nanostructured Architectures on the Heater Surface at Nanofluids Boiling and Their Role in the Intensification of Heat Transfer. Nanoscience and Nanoengineering, 4 (1), 12–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.13189/nn.2016.040102
- Moraru, V. N. (2017). The Mechanism of Raising And Quantification of Specific Heat Flux at Boiling of Nanofluids in Free Convection Conditions. Energotekhnologii i resursosberezhenie, 3, 25–34. Available at: http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/ETRS_2017_3_5
- Liu, Z. H., Yang, X. F., Guo, G. L. (2007). Effect of nanoparticles in nanofluid on thermal performance in a miniature thermosyphon. Journal of Applied Physics, 102 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2748348
- Paramatthanuwat, T., Boothaisong, S., Rittidech, S., Booddachan, K. (2009). Heat transfer characteristics of a two-phase closed thermosyphon using de ionized water mixed with silver nano. Heat and Mass Transfer, 46 (3), 281–285. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-009-0565-y
- Huminic, G., Huminic, A., Morjan, I., Dumitrache, F. (2011). Experimental study of the thermal performance of thermosyphon heat pipe using iron oxide nanoparticles. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 54 (1–3), 656–661. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.09.005
- Huminic, G., Huminic, A. (2011). Heat transfer characteristics of a two-phase closed thermosyphons using nanofluids. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 35 (3), 550–557. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2010.12.009
- Xue, H. S., Fan, J. R., Hu, Y. C., Hong, R. H., Cen, K. F. (2006). The interface effect of carbon nanotube suspension on the thermal performance of a two-phase closed thermosyphon. Journal of Applied Physics, 100 (10). doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2357705
- Khandekar, S., Joshi, Y. M., Mehta, B. (2008). Thermal performance of closed two-phase thermosyphon using nanofluids. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 47 (6), 659–667. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2007.06.005
- Moraru, V. N., Komysh, D. V., Khovavko, A. I., Snigur, A. V., Gudkov, N. N., Sidorenko, N. A., Marinin, A. I. (2015). Nanofluids on the Basis of Ukrainian Natural Aluminosilicates are Promising Heat-Carriers for Power Engineering. Energotekhnologii i resursosberezhenie, 1, 22–32. Available at: http://dspace.nbuv.gov.ua/handle/123456789/127461
- Khazaee, I., Hosseini, R., Noie, S. H. (2010). Experimental investigation of effective parameters and correlation of geyser boiling in a two-phase closed thermosyphon. Applied Thermal Engineering, 30 (5), 406–412. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2009.09.012
- Kravets, V. Yu. (2018). Protsesy teploobminu u miniatiurnykh vyparno-kondensatsiinykh systemakh okholodzhennia. Kharkiv: FOP Brovin O. V., 288.
- Kravets, V., Konshin, V., Hurov, D., Vorobiov, M., Shevel, I. (2022). Determining the influence of geometric factors and the type of heat carrier on the thermal resistance of miniature two-phase thermosyphons. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (8 (118)), 51–59. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.263180
- Tolubinskii, V. I. (1980). Teploobmen pri kipenii. Kyiv: Naukova dumka, 316.
- Pekur, D. V., Nikolaenko, Yu. E., Sorokin, V. M. (2020). Optimization of the cooling system design for a compact high-power LED luminaire. Semiconductor Physics, Quantum Electronics and Optoelectronics, 23 (1), 91–101. doi: https://doi.org/10.15407/spqeo23.01.091
- Kamyar, A., Ong, K. S., Saidur, R. (2013). Effects of nanofluids on heat transfer characteristics of a two-phase closed thermosyphon. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 65, 610–618. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.06.046
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Vlаdіmіr Kravets, Dmytro Hurov, Vasily Moraru

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








