Development of the method of detecting and correcting data transmission errors in IoT systems for monitoring the state of objects
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.298476Keywords:
method of error correction, Hamming codes, Internet of Things, monitoring of the state of objectsAbstract
The object of the study is the IOT system for monitoring the state of objects.
The problem being solved is the development of an innovative method of detecting and correcting data transmission errors in the networks of Internet of Things systems.
The essence of the results is that a method of detecting and correcting multiple transmission errors during byte-by-byte transmission of a block of information has been developed. The method is distinguished by an original coding scheme, which involves the calculation of control bits, as well as the shuffling of block bits by performing bit shift operations. The peculiarity of the method is that any bit can be distorted when transmitting a code word, but it belongs to different code combinations of the Hamming code. This allows multiple data transmission errors to be detected and corrected during decoding, and multiple errors of different bytes belonging to the same block can be corrected.
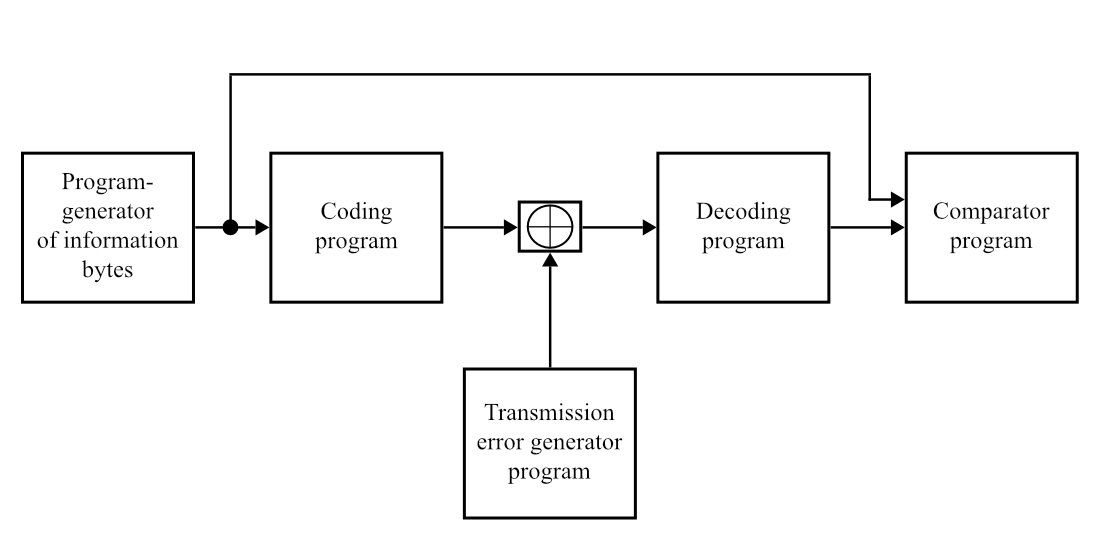
Simple algorithms for encoding and decoding procedures have been developed, and programs for information block encoding procedures and decoding procedures with error detection and correction have been developed. A software model of the data transmission channel was also developed with the possibility of introducing multiple errors when simulating the data transmission process. All programs are developed in Python, although other languages are possible.
An experiment was conducted using the developed software model of the data transmission channel. The efficiency of the developed method has been experimentally confirmed and it has been proven that its use increases the immunity of the data transmission channel. This is due to the fact that the developed method allows detecting and correcting all code word transmission errors with a multiplicity from 1 to 8, which was confirmed experimentally.
The main field of use of the developed method is considered to be IoT system networks. First of all, systems for monitoring the state of objects
References
- Internet Of Things (IoT). Available at: https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/internet-of-things
- IoT Platforms. Available at: https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/iot-platforms
- Shannon, C. E. (1948). A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27 (4), 623–656. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x
- Huffman, W. C., Pless, V. (2003). Fundamentals of Error-Correcting Codes. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511807077
- Subhasri, G., Radha, N. (2019). VLSI design of Parity check Code with Hamming Code for Error Detection and Correction. 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICCS). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccs45141.2019.9065790
- Tolentino, L. K. S., Valenzuela, I. C., Juan, R. O. S. (2019). Overhead Interspersing of Redundancy Bits Reduction Algorithm by Enhanced Error Detection Correction Code. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 12 (2), 34–39. https://doi.org/10.25103/jestr.122.05
- Chen, Z., Zhao, Y., Lu, J., Liang, B., Chen, X., Li, C. (2022). TECED: A Two-Dimensional Error-Correction Codes Based Energy-Efficiency SRAM Design. Electronics, 11 (10), 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11101638
- Tolentino, L. K., Padilla, M. V., Serfa Juan, R. (2018). FPGA-based redundancy bits reduction algorithm using the enhanced error detection correction code. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 7 (3), 1008. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i3.12681
- Koppala, N., Subhas, C. (2022). Low overhead optimal parity codes. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommunication Computing Electronics and Control), 20 (3), 501. https://doi.org/10.12928/telkomnika.v20i3.23301
- Toghuj, W. (2020). Modifying Hamming code and using the replication method to protect memory against triple soft errors. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommunication Computing Electronics and Control), 18 (5), 2533. https://doi.org/10.12928/telkomnika.v18i5.13345
- Saiz-Adalid, L.-J., Gil, P., Ruiz, J.-C., Gracia-Moran, J., Gil-Tomas, D., Baraza-Calvo, J.-C. (2016). Ultrafast Error Correction Codes for Double Error Detection/Correction. 2016 12th European Dependable Computing Conference (EDCC). https://doi.org/10.1109/edcc.2016.28
- Rurik, W., Mazumdar, A. (2016). Hamming codes as error-reducing codes. 2016 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW). https://doi.org/10.1109/itw.2016.7606865
- Moon, T. K. (2005). Error correction coding: mathematical methods and algorithms. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471739219
- Kadel, R., Paudel, K., Guruge, D. B., Halder, S. J. (2020). Opportunities and Challenges for Error Control Schemes for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Review. Electronics, 9 (3), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030504
- Bettayeb, M., Ghunaim, S., Mohamed, N., Nasir, Q. (2019). Error Correction Codes in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Systematic Literature Review. 2019 International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and Their Applications (ICCSPA). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccspa.2019.8713725
- Sridevi, N., Jamal, K., Mannem, K. (2021). Implementation of Error Correction Techniques in Memory Applications. 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccmc51019.2021.9418432
- Clark, G. C., Cain, J. B. (1981). Error-Correction Coding for Digital Communications. Springer US. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-2174-1
- Hamming, R. W. (1950). Error Detecting and Error Correcting Codes. Bell System Technical Journal, 29 (2), 147–160. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1950.tb00463.x
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Vladyslav Sokolovskyi, Eduard Zharikov, Sergii Telenyk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








