Overcoming barriers to digitalization of small and medium-sized enterprises under martial law
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.304997Keywords:
digitalization barriers, small and medium enterprises, martial law, platform modelAbstract
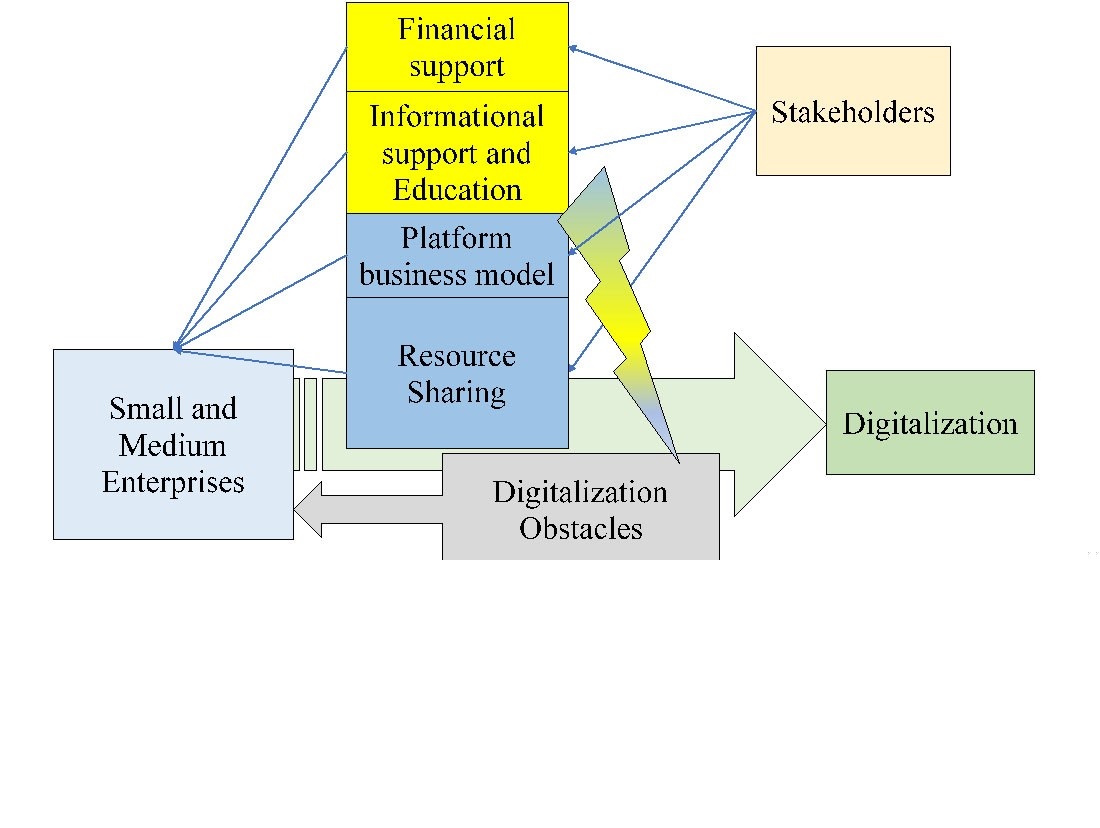
The object of this study was the digitalization of small and medium-sized enterprises under martial law. The problem being solved was to overcome obstacles that slow down the introduction of digital technologies into the business processes of small and medium-sized enterprises during periods of conflict or war. During the period of martial law, the consequences for small and medium-sized enterprises are instability, material losses, resource limitations, and security threats. Despite the reduction in the number of small and medium-sized enterprises in Ukraine during the military invasion by 29.39 %, most of them continued to function, adapting to the new conditions of the crisis situation. However, neither the crisis conditions nor the increase in Internet users prompted these enterprises to make significant changes in the use of digital technologies. This was due to a number of barriers, including the following. The lack of liquidity and financing, the forced nature of implementation, the need to constantly adapt business processes to external changes are more related to the crisis situation. Inappropriate digital tools, lack of package solutions, lack of sufficient knowledge and skills, low trust in the state, small size of the enterprise, lack of understanding of the need or direction of reformatting business processes do not depend on the state of war. Overcoming the barriers to digitization of small and medium-sized enterprises under martial law is envisaged through interaction and partnership with other stakeholders. Cooperation and partnership are based on financial and informational support, training, platform model, and shared use of resources. The necessity and possibility of applying the developed proposals to overcome the barriers of digitalization of small and medium-sized enterprises under the conditions of martial law predetermines the practical significance of reported results
References
- Di Bella, L., Katsinis, A., Lagüera-González, J., Odenthal, L., Hell, M., Lozar, B. (2023). Annual Report on European SMEs 2022/2023. European Commission. https://doi.org/10.2760/028705
- SME digitalisation to “Build Back Better” (2021). OECD SME and Entrepreneurship Papers. https://doi.org/10.1787/50193089-en
- Indicators activity of large, medium, small and micro-entrepreneurship entities in 2010-2022. Derzhavna sluzhba statystyky Ukrainy. Available at: https://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/operativ/operativ2022/fin/pssg/pds_vsmm_2010-2021.xlsx
- Beyond COVID-19 Advancing Digital Business Transformation in the Eastern Partner Countries (2021). OECD. Available at: https://t4.oecd.org/eurasia/Beyond%20COVID-19%20Advancing%20Digital%20Transformation%20in%20the%20Eastern%20Partner%20Countries%20.pdf
- Türkeș, M., Oncioiu, I., Aslam, H., Marin-Pantelescu, A., Topor, D., Căpușneanu, S. (2019). Drivers and Barriers in Using Industry 4.0: A Perspective of SMEs in Romania. Processes, 7 (3), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7030153
- Reim, W., Yli-Viitala, P., Arrasvuori, J., Parida, V. (2022). Tackling business model challenges in SME internationalization through digitalization. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 7 (3), 100199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2022.100199
- Hassan, S. S., Meisner, K., Krause, K., Bzhalava, L., Moog, P. (2023). Is digitalization a source of innovation? Exploring the role of digital diffusion in SME innovation performance. Small Business Economics, 62 (4), 1469–1491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-023-00826-7
- Kádárová, J., Lachvajderová, L., Sukopová, D. (2023). Impact of Digitalization on SME Performance of the EU27: Panel Data Analysis. Sustainability, 15 (13), 9973. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15139973
- Horváth, D., Szabó, R. Zs. (2019). Driving forces and barriers of Industry 4.0: Do multinational and small and medium-sized companies have equal opportunities? Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 146, 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.05.021
- Papadopoulos, T., Baltas, K. N., Balta, M. E. (2020). The use of digital technologies by small and medium enterprises during COVID-19: Implications for theory and practice. International Journal of Information Management, 55, 102192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102192
- Cenamor, J., Parida, V., Wincent, J. (2019). How entrepreneurial SMEs compete through digital platforms: The roles of digital platform capability, network capability and ambidexterity. Journal of Business Research, 100, 196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.03.035
- Priyono, A., Moin, A., Putri, V. N. A. O. (2020). Identifying Digital Transformation Paths in the Business Model of SMEs during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6 (4), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6040104
- Pfister, P., Lehmann, C. (2023). Measuring the Success of Digital Transformation in German SMEs. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 33 (1). https://doi.org/10.53703/001c.39679
- Vuță, D. R., Nichifor, E., Chițu, I. B., Brătucu, G. (2022). Digital Transformation – Top Priority in Difficult Times: The Case Study of Romanian Micro-Enterprises and SMEs. Sustainability, 14 (17), 10741. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710741
- Guo, H., Yang, Z., Huang, R., Guo, A. (2020). The digitalization and public crisis responses of small and medium enterprises: Implications from a COVID-19 survey. Frontiers of Business Research in China, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11782-020-00087-1
- Hrabovetskyi, B. Ye. (2010). Metody ekspertnykh otsinok: teoriya, metodolohiya, napriamky vykorystannia. Vinnytsia. Available at: https://press.vntu.edu.ua/index.php/vntu/catalog/download/324/612/651-1?inline=1
- Pro pravovyi rezhym voiennoho stanu (2015). Zakon No. 389-VIII. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/389-19
- Pro vvedennia voiennoho stanu v Ukraini (2022). Ukaz Prezydenta Ukrainy No. 64/2022. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/64/2022#Text
- United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (1980). Vienna. Available at: https://treaties.un.org/doc/Treaties/1988/01/19880101%2003-03%20AM/Ch_X_10p.pdf
- Pro torhovo-promyslovi palaty v Ukraini (1997). Zakon No. 671/97-VR. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/671/97-вр#Text
- Diyalnist vitchyznianykh pidpryiemstv pid chas viyny v Ukrayini: doslidzhennia realnoho stanu ta potreb (2022). Tsentr resursoefektyvnoho ta chystoho vyrobnytstva. Available at: http://www.recpc.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/National_businesses_during-war_2022.pdf
- Doslidzhennia stanu ukrainskoho biznesu pid chas viyny: yak sebe pochuvaiut seredni, mali ta velyki kompaniyi (2022). Kyivstar Business Hub. Available at: https://hub.kyivstar.ua/articles/doslidzhennya-stanu-ukrayinskogo-biznesu-pid-chas-vijny-yak-sebe-pochuvayut-seredni-mali-ta-velyki-kompaniyi
- Doslidzhennia stanu biznesu v Ukrayini. Berezen-kviten 2023. Available at: https://business.diia.gov.ua/uploads/6/30910-doslidzenna_stanu_ta_potreb_biznesu_za_rik_povnomasstabnoi_vijni.pdf
- Ekspres-otsinka vplyvu viyny na mikro-, mali ta seredni pidpryiemstva v Ukraini (2022). Prohrama rozvytku OON v Ukraini. Available at: https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/2022-10/UA_Rapid_Assessment_of_War_on_MSMEs_in_Ukraine_0.pdf
- Measuring Digital Development – Facts and Figures 2023. Available at: https://www.itu.int/hub/publication/d-ind-ict_mdd-2023-1/
- Kilkist abonentiv zviazku na 1 sichnia 2019 roku. Available at: https://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/operativ/operativ2019/zv/az/xls/az0119_u.xlsx
- Dostup domohospodarstv Ukrainy do Internetu (za danymy vybirkovoho opytuvannia domohospodarstv, provedenoho u sichni 2022 roku) (2022). Kyiv. Available at: https://ukrstat.gov.ua/druk/publicat/kat_u/2022/zb/07/zb_dd_internet_21.pdf
- gemiusAudience: June summary for Ukraine (2023). Gemius. Available at: https://gemius.com/blog/gemiusaudience-june-summary-for-ukraine/
- Number of enterprises which have made e-commerce and value of the turnover of e-commerce sales by type of economic activity, with a breakdown by number of employed in 2018-2021. Available at: https://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/operativ/operativ2021/zv/ikt/vikpt_3D_18-22.xlsx
- Use of information and communication technologies at enterprises: use of internet network, social media, cloud calculation. Available at: https://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/operativ/operativ2021/zv/ikt/vikpt_18-22.xlsx
- Akpan, I. J., Udoh, E. A. P., Adebisi, B. (2020). Small business awareness and adoption of state-of-the-art technologies in emerging and developing markets, and lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 34 (2), 123–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/08276331.2020.1820185
- Laudon, K. C., Laudon, J. P. (2019). Management Information Systems: Managing the Digital Firm. Pearson. Available at: https://www.pearson.com/en-gb/subject-catalog/p/management-information-systems-managing-the-digital-firm-global-edition/P200000008841/9781292296708
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Svitlana Semenіuk, Vitalii Levytskyi, Olena Fomina, Kostiantyn Fedorchenko, Nataliya Yudina, Vadym Ratynskiy, Olena Shcherbatiuk, Vladyslav Bendiuh, Yuliia Zhurakivska

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









