Розробка методу прогнозування рівня кров’яного тиску за даними сигналів електрокардіограми та фотоплетизмограми
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.265066Ключові слова:
кров’яний тиск, машинне навчання, фотоплетизмограма, біоелектричні сигнали, час розповсюдження пульсової хвиліАнотація
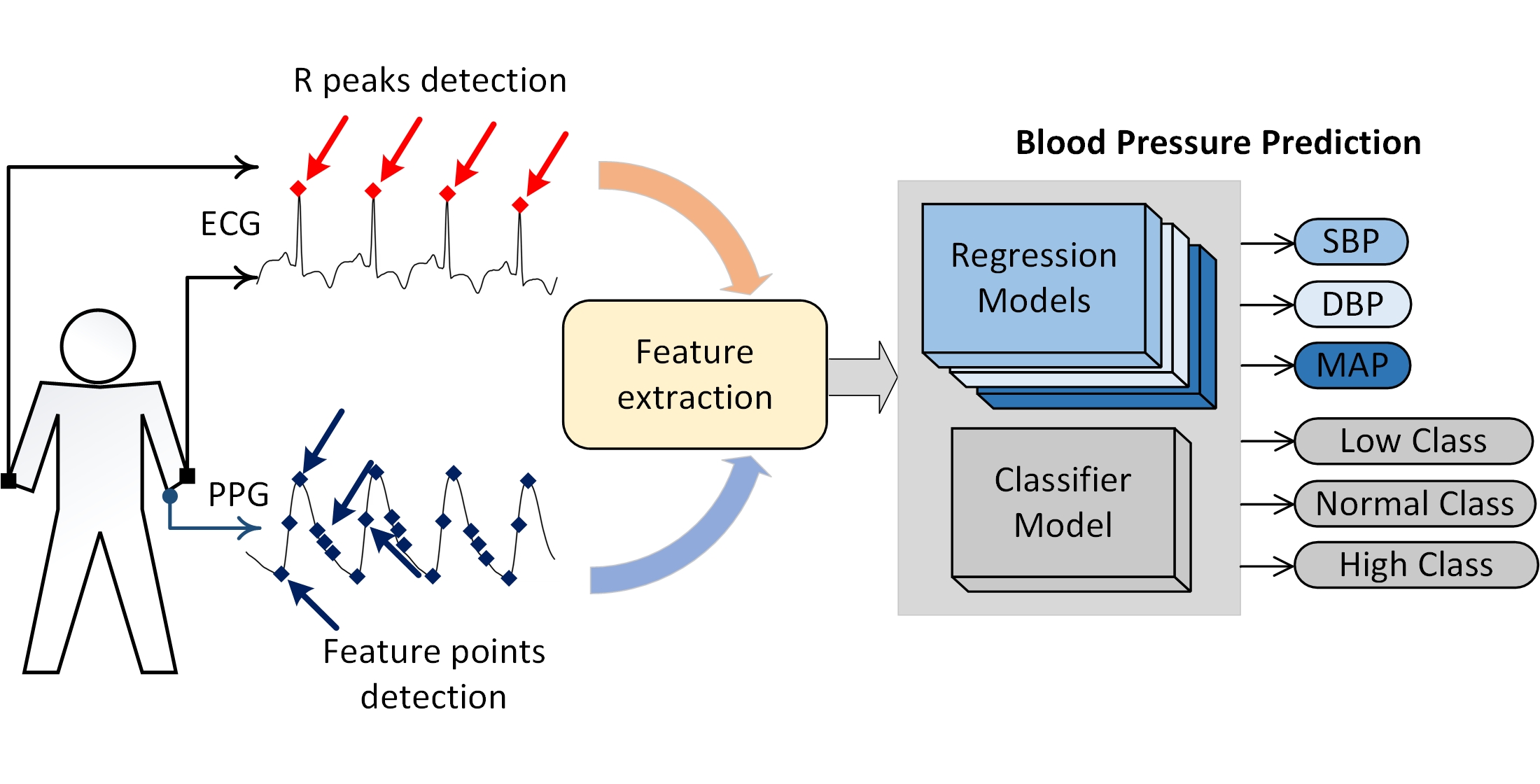
Визначення рівня кров’яного тиску (КТ) неінвазивним способом і без манжети сфігмоманометра має велику актуальність під час проведення безперервного моніторингу або скринінгових досліджень. У зв’язку з цим розроблено метод прогнозування параметрів КТ за даними сигналів фотоплетизмограми (ФПГ) та електрокардіограми (ЕКГ). Як інформативні ознаки пропонується використовувати час поширення пульсової хвилі (PTT) і комплекс розрахованих параметрів імпульсу ФПГ. PTT визначається як часові інтервали між R-зубцем ЕКГ та відповідними характерними точками на ФПГ, що знімається оптичним способом з пальця руки. Як параметри імпульсу ФПГ використовуються відомі характеристики даного сигналу, описані в літературі, а також додаткові інформативні ознаки, відібрані в процесі дослідження.
Відповідно до цього, за допомогою інструментів теорії машинного навчання розроблено модель класифікатора та регресійні моделі. Представлений у роботі підхід визначення КТ дозволяє використовувати 10-ти секундні сигнали ЕКГ у кожному з 12 поширених відведень і сигнали ФПГ з будь-якого оптичного типу датчика.
Розроблена модель класифікатора детектує три рівні КТ: низький, нормальний та високий з метрикою accuracy=0,8494. Регресійні моделі прогнозують параметри систолічного, діастолічного та середнього КТ відповідно до вимог стандарту British Hypertension Society (BHS) за величиною абсолютної помилки.
Запропонований метод оцінки рівня КТ передбачає проведення вимірювань у реальному часі та може бути використаний при побудові вимірювальної апаратури для скринінгових досліджень, а також у безперервному моніторингу в рамках вимог BHS.
Посилання
- Zhou, B., Carrillo-Larco, R. M., Danaei, G., Riley, L. M., Paciorek, C. J., Stevens, G. A. et. al. (2021). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. The Lancet, 398 (10304), 957–980. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(21)01330-1
- Hypertension (2021). World Health Organization (WHO). Available at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
- Williams, B., Mancia, G., Spiering, W., Agabiti Rosei, E., Azizi, M., Burnier, M. et. al. (2018). 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. European Heart Journal, 39 (33), 3021–3104. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339
- Peter, L., Noury, N., Cerny, M. (2014). A review of methods for non-invasive and continuous blood pressure monitoring: Pulse transit time method is promising? IRBM, 35 (5), 271–282. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irbm.2014.07.002
- Pandit, J. A., Lores, E., Batlle, D. (2020). Cuffless Blood Pressure Monitoring. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 15 (10), 1531–1538. doi: https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.03680320
- Mukkamala, R., Stergiou, G. S., Avolio, A. P. (2022). Cuffless Blood Pressure Measurement. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 24 (1), 203–230. doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-110220-014644
- Figini, V., Galici, S., Russo, D., Centonze, I., Visintin, M., Pagana, G. (2022). Improving Cuff-Less Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation with Linear Regression Analysis. Electronics, 11 (9), 1442. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11091442
- Stergiou, G. S., Mukkamala, R., Avolio, A., Kyriakoulis, K. G., Mieke, S., Murray, A. et. al. (2022). Cuffless blood pressure measuring devices: review and statement by the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring and Cardiovascular Variability. Journal of Hypertension, 40 (8), 1449–1460. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000003224
- Nour, M., Polat, K. (2020). Automatic Classification of Hypertension Types Based on Personal Features by Machine Learning Algorithms. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 1–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2742781
- Ibrahim, B., Nathan, V., Jafari, R. (2017). Exploration and validation of alternate sensing methods for wearable continuous pulse transit time measurement using optical and bioimpedance modalities. 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2017.8037256
- Thambiraj, G., Gandhi, U., Mangalanathan, U., Jose, V. J. M., Anand, M. (2020). Investigation on the effect of Womersley number, ECG and PPG features for cuff less blood pressure estimation using machine learning. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 60, 101942. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101942
- Saeed, M., Villarroel, M., Reisner, A. T., Clifford, G., Lehman, L.-W., Moody, G. et. al. (2011). Multiparameter Intelligent Monitoring in Intensive Care II: A public-access intensive care unit database*. Critical Care Medicine, 39 (5), 952–960. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0b013e31820a92c6
- Sanuki, H., Fukui, R., Inajima, T., Warisawa, S. (2017). Cuff-less Calibration-free Blood Pressure Estimation under Ambulatory Environment using Pulse Wave Velocity and Photoplethysmogram Signals. Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies. doi: https://doi.org/10.5220/0006112500420048
- Liang, Y., Chen, Z., Ward, R., Elgendi, M. (2018). Hypertension Assessment via ECG and PPG Signals: An Evaluation Using MIMIC Database. Diagnostics, 8 (3), 65. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8030065
- Miao, F., Liu, Z.-D., Liu, J.-K., Wen, B., He, Q.-Y., Li, Y. (2020). Multi-Sensor Fusion Approach for Cuff-Less Blood Pressure Measurement. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 24 (1), 79–91. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2019.2901724
- Hasanzadeh, N., Ahmadi, M. M., Mohammadzade, H. (2020). Blood Pressure Estimation Using Photoplethysmogram Signal and Its Morphological Features. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20 (8), 4300–4310. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2019.2961411
- Kachuee, M., Kiani, M. M., Mohammadzade, H., Shabany, M. (2015). Cuff-less high-accuracy calibration-free blood pressure estimation using pulse transit time. 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iscas.2015.7168806
- DeMers, D., Wachs, D. (2022). Physiology, Mean Arterial Pressure. StatPearls. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538226/
- Meng, L., Yu, W., Wang, T., Zhang, L., Heerdt, P. M., Gelb, A. W. (2018). Blood Pressure Targets in Perioperative Care. Hypertension, 72 (4), 806–817. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.118.11688
- Guzman, J. C., Melin, P., Prado-Arechiga, G. (2017). Design of an Optimized Fuzzy Classifier for the Diagnosis of Blood Pressure with a New Computational Method for Expert Rule Optimization. Algorithms, 10 (3), 79. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/a10030079
- Elgendi, M. (2012). On the Analysis of Fingertip Photoplethysmogram Signals. Current Cardiology Reviews, 8 (1), 14–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/157340312801215782
- Scholkmann, F., Boss, J., Wolf, M. (2012). An Efficient Algorithm for Automatic Peak Detection in Noisy Periodic and Quasi-Periodic Signals. Algorithms, 5 (4), 588–603. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/a5040588
- Kachuee, M., Kiani, M. M., Mohammadzade, H., Shabany, M. (2017). Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Algorithms for Continuous Health-Care Monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 64 (4), 859–869. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2016.2580904
- Hasan, O. S., Saleh, I. A. (2021). Development of heart attack prediction model based on ensemble learning. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (2 (112)), 26–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.238528
- Geurts, P., Ernst, D., Wehenkel, L. (2006). Extremely randomized trees. Machine Learning, 63 (1), 3–42. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-006-6226-1
- Pedregosa, F. et. al. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825–2830. Available at: https://www.jmlr.org/papers/volume12/pedregosa11a/pedregosa11a.pdf
- Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., Kegelmeyer, W. P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 16, 321–357. doi: https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953
- Chen, T., Guestrin, C. (2016). XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
- Wolpert, D. H. (1992). Stacked generalization. Neural Networks, 5 (2), 241–259. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0893-6080(05)80023-1
- O'Brien, E., Petrie, J., Littler, W., de Swiet, M., Padfield, P. L., O'Malley, K. et. al. (1990). The British Hypertension Society protocol for the evaluation of automated and semi-automated blood pressure measuring devices with special reference to ambulatory systems. Journal of Hypertension, 8 (7), 607–619. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00004872-199007000-00004
- ANSI/AAMI SP10:2002/(R)2008 & ANSI/AAMI SP10:2002/A1:2003/(R)2008 & ANSI/AAMI SP10:2002/A2:2006/(R)2008. Manual, electronic, or automated sphygmomanometers. Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation.
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2022 Alexey Savostin, Amandyk Tuleshov, Kayrat Koshekov, Galina Savostina, Alexandr Largin

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









