Вбудовані моделі на основі DCNN для паралельної діагностики захворювань очей
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281790Ключові слова:
очні захворювання, візуалізація очного дна, оптична когерентна томографія, глибоке навчання, багатозначні вбудовані архітектури, паралельна архітектура, трансферне навчання, ODIR, навчання, перевіркаАнотація
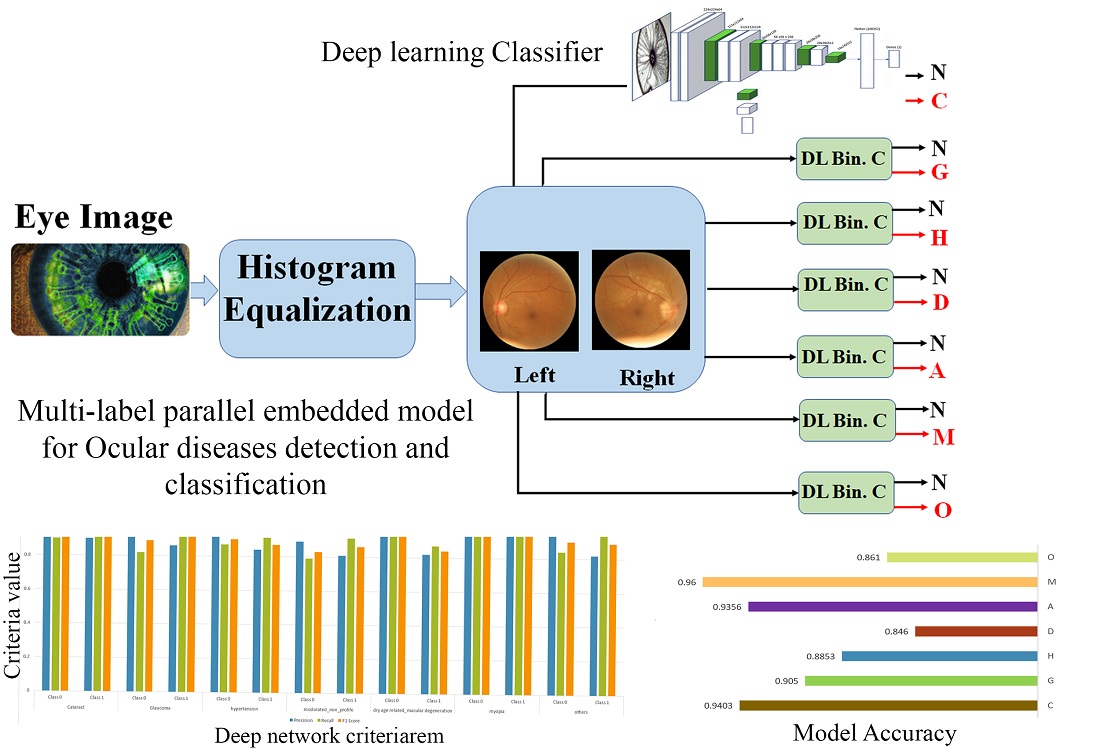
Для виявлення різних захворювань очей за знімками очного дна необхідна автоматизована система виявлення очних захворювань за допомогою комп'ютерних інструментів. Це пов'язано з тим, що діагностика очних захворювань вручну є складним, трудомістким і схильним до помилок процесом. У дослідженні для розпізнавання та класифікації очних захворювань запропоновано дві багатозначні вбудовані архітектури на основі стратегії глибокого навчання. Для цих моделей був використаний набір даних ODIR (інтелектуальне розпізнавання очних захворювань). Запропоновані розробки реалізовані у вигляді паралельних систем. Перша модель була розроблена як паралельна вбудована система, що використовує трансферне навчання для реалізації своїх класифікаторів. При реалізації цих класифікаторів використовувалася мережа глибокого навчання VGG16, тоді як друга модель представлена з паралельною архітектурою, а її класифікатори реалізовані на основі нових запропонованих мереж глибокого навчання. Дані мережі відрізняються невеликим розміром, обмеженою кількістю шарів, швидкодією та точністю. Таким чином, нова запропонована розробка має ряд переваг, таких як невеликий розмір мережі класифікації (20 % VGG16), висока швидкодія та знижене енергоспоживання, а також придатність для IoT-додатків, що підтримують інтелектуальні системи, такі як Raspberry Pi, та автономні компоненти, що мають здатність функціонувати поки заряджений акумулятор. В обох запропонованих моделях для виявлення і класифікації такого очного захворювання як короткозорість була отримана найвища точність 0,9974 і 0,96. У порівнянні з дослідженнями, представленими в тій же області, точність кожної з двох показаних моделей була високою. Для реалізації обох запропонованих вбудованих моделей використовується комплект розробника Jetson Nano P3448-0000
Спонсор дослідження
- The researchers would like to extend their thanks and appreciation to Ninevah University/College of Electronics Engineering/ Computer and Information Engineering department, and Mosul/ College of Engineering/ Computer Engineering department for their support, which has assisted to boost the outcomes of this research paper.
Посилання
- Alwakid, G., Gouda, W., Humayun, M. (2023). Deep Learning-Based Prediction of Diabetic Retinopathy Using CLAHE and ESRGAN for Enhancement. Healthcare, 11 (6), 863. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11060863
- Marouf, A. A., Mottalib, M. M., Alhajj, R., Rokne, J., Jafarullah, O. (2022). An Efficient Approach to Predict Eye Diseases from Symptoms Using Machine Learning and Ranker-Based Feature Selection Methods. Bioengineering, 10 (1), 25. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010025
- Albahli, S., Ahmad Hassan Yar, G. N. (2022). Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using custom convolutional neural network. Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology, 30 (2), 275–291. doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/xst-211073
- Ebri, A. E., Govender, P., Naidoo, K. S. (2019). Prevalence of vision impairment and refractive error in school learners in Calabar, Nigeria. African Vision and Eye Health, 78 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.4102/aveh.v78i1.487
- Pakbin, M., Katibeh, M., Pakravan, M., Yaseri, M., Soleimanizad, R. (2015). Prevalence and causes of visual impairment and blindness in central Iran; The Yazd eye study. Journal of Ophthalmic and Vision Research, 10 (3), 279. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/2008-322x.170362
- Elzean, C., Sakr, E. (2021). Proposed three-dimensional designs for the color wheel to help blind persons understand matching colors of their clothes. International Design Journal, 11 (2), 417–423. doi: https://doi.org/10.21608/idj.2021.153624
- Demir, F., Taşcı, B. (2021). An Effective and Robust Approach Based on R-CNN+LSTM Model and NCAR Feature Selection for Ophthalmological Disease Detection from Fundus Images. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11 (12), 1276. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121276
- Biswas, R. K., Rahman, N., Islam, H., Senserrick, T., Bhowmik, J. (2020). Exposure of mobile phones and mass media in maternal health services use in developing nations: evidence from Urban Health Survey 2013 of Bangladesh. Contemporary South Asia, 29 (3), 460–473. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09584935.2020.1770698
- Alam, K. N., Khan, M. S., Dhruba, A. R., Khan, M. M., Al-Amri, J. F., Masud, M., Rawashdeh, M. (2021). Deep Learning-Based Sentiment Analysis of COVID-19 Vaccination Responses from Twitter Data. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2021, 1–15. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4321131
- He, J., Li, C., Ye, J., Qiao, Y., Gu, L. (2021). Self-speculation of clinical features based on knowledge distillation for accurate ocular disease classification. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 67, 102491. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102491
- Kadhim, Y. A., Khan, M. U., Mishra, A. (2022). Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD): Applications for Medical Image Datasets. Sensors, 22 (22), 8999. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228999
- Roy, A. G., Conjeti, S., Karri, S. P. K., Sheet, D., Katouzian, A., Wachinger, C., Navab, N. (2017). ReLayNet: retinal layer and fluid segmentation of macular optical coherence tomography using fully convolutional networks. Biomedical Optics Express, 8 (8), 3627. doi: https://doi.org/10.1364/boe.8.003627
- Lee, C. S., Tyring, A. J., Deruyter, N. P., Wu, Y., Rokem, A., Lee, A. Y. (2017). Deep-learning based, automated segmentation of macular edema in optical coherence tomography. Biomedical Optics Express, 8 (7), 3440. doi: https://doi.org/10.1364/boe.8.003440
- Oda, M., Yamaguchi, T., Fukuoka, H., Ueno, Y., Mori, K. (2020). Automated eye disease classification method from anterior eye image using anatomical structure focused image classification technique. Medical Imaging 2020: Computer-Aided Diagnosis. doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2549951
- Maaliw, R. R., Alon, A. S., Lagman, A. C., Garcia, M. B., Abante, M. V., Belleza, R. C. et al. (2022). Cataract Detection and Grading Using Ensemble Neural Networks and Transfer Learning. 2022 IEEE 13th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iemcon56893.2022.9946550
- Marrapu, H. K. (2022). Detection of Glaucoma Using Deep Learning Techniques: Literature Survey. Specialusis Ugdymas, 1 (43), 8089–8098. Available at: http://www.sumc.lt/index.php/se/article/view/1182/915
- Kashyap, R., Nair, R., Gangadharan, S. M. P., Botto-Tobar, M., Farooq, S., Rizwan, A. (2022). Glaucoma Detection and Classification Using Improved U-Net Deep Learning Model. Healthcare, 10 (12), 2497. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122497
- Bhimavarapu, U., Battineni, G. (2022). Deep Learning for the Detection and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy with an Improved Activation Function. Healthcare, 11 (1), 97. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11010097
- Fan, R., Bowd, C., Christopher, M., Brye, N., Proudfoot, J. A., Rezapour, J. et al. (2022). Detecting Glaucoma in the Ocular Hypertension Study Using Deep Learning. JAMA Ophthalmology, 140 (4), 383. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.0244
- Lin, M., Hou, B., Liu, L., Gordon, M., Kass, M., Wang, F. et al. (2022). Automated diagnosing primary open-angle glaucoma from fundus image by simulating human’s grading with deep learning. Scientific Reports, 12 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-17753-4
- Santos-Bustos, D. F., Nguyen, B. M., Espitia, H. E. (2022). Towards automated eye cancer classification via VGG and ResNet networks using transfer learning. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 35, 101214. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2022.101214
- Abdelmotaal, H., Hazarbasanov, R., Taneri, S., Al-Timemy, A., Lavric, A., Takahashi, H., Yousefi, S. (2023). Detecting dry eye from ocular surface videos based on deep learning. The Ocular Surface, 28, 90–98. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtos.2023.01.005
- Choudhary, A., Ahlawat, S., Urooj, S., Pathak, N., Lay-Ekuakille, A., Sharma, N. (2023). A Deep Learning-Based Framework for Retinal Disease Classification. Healthcare, 11 (2), 212. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020212
- Park, S.-J., Ko, T., Park, C.-K., Kim, Y.-C., Choi, I.-Y. (2022). Deep Learning Model Based on 3D Optical Coherence Tomography Images for the Automated Detection of Pathologic Myopia. Diagnostics, 12 (3), 742. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12030742
- Seif, G. (2018). Handling imbalanced datasets in deep learning. Available at: https://towardsdatascience.com/handling-imbalanced-datasets-in-deep-learning-f48407a0e758
- Hodge, W. G., Whitcher, J. P., Satariano, W. (1995). Risk Factors for Age-related Cataracts. Epidemiologic Reviews, 17 (2), 336–346. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036197
- Liu, Y.-C., Wilkins, M., Kim, T., Malyugin, B., Mehta, J. S. (2017). Cataracts. The Lancet, 390 (10094), 600–612. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)30544-5
- Al-Jarrah, M. A., Shatnawi, H. (2017). Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy symptoms detection and classification using neural network. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology, 41 (6), 498–505. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/03091902.2017.1358772
- Verkicharla, P. K., Ohno-Matsui, K., Saw, S. M. (2015). Current and predicted demographics of high myopia and an update of its associated pathological changes. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, 35 (5), 465–475. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/opo.12238
- Garcia-Villanueva, C., Milla, E., Bolarin, J. M., García-Medina, J. J., Cruz-Espinosa, J., Benítez-del-Castillo, J. et al. (2022). Impact of Systemic Comorbidities on Ocular Hypertension and Open-Angle Glaucoma, in a Population from Spain and Portugal. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11 (19), 5649. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195649
- Rakhmetulayeva, S., Syrymbet, Z. (2022). Implementation of convolutional neural network for predicting glaucoma from fundus images. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (120)), 70–77. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269229
- Esengönül, M., Cunha, A. (2023). Glaucoma Detection using Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Use. Procedia Computer Science, 219, 1153–1160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2023.01.396
- He, T., Zhou, Q., Zou, Y. (2022). Automatic Detection of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Based on Deep Learning and Local Outlier Factor Algorithm. Diagnostics, 12 (2), 532. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020532
- Fang, H., Li, F., Fu, H., Sun, X., Cao, X., Lin, F. et al. (2022). ADAM Challenge: Detecting Age-Related Macular Degeneration From Fundus Images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 41 (10), 2828–2847. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2022.3172773
- Salih, T. A., Basman Gh., M. (2020). A novel Face Recognition System based on Jetson Nano developer kit. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 928 (3), 032051. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/928/3/032051
- Wang, J., Yang, L., Huo, Z., He, W., Luo, J. (2020). Multi-Label Classification of Fundus Images With EfficientNet. IEEE Access, 8, 212499–212508. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3040275
- Li, C., Ye, J., He, J., Wang, S., Qiao, Y., Gu, L. (2020). Dense Correlation Network for Automated Multi-Label Ocular Disease Detection with Paired Color Fundus Photographs. 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/isbi45749.2020.9098340
- Dipu, N. M., Alam Shohan, S., Salam, K. M. A. (2021). Ocular Disease Detection Using Advanced Neural Network Based Classification Algorithms. ASIAN JOURNAL OF CONVERGENCE IN TECHNOLOGY, 7 (2), 91–99. doi: https://doi.org/10.33130/ajct.2021v07i02.019
- Gour, N., Khanna, P. (2021). Multi-class multi-label ophthalmological disease detection using transfer learning based convolutional neural network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 66, 102329. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102329
- Kumar, E. S., Bindu, C. S. (2021). MDCF: Multi-Disease Classification Framework On Fundus Image Using Ensemble Cnn Models. Journal of Jilin University, 40 (09), 35–45. doi: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/ZHA9C
- He, J., Li, C., Ye, J., Qiao, Y., Gu, L. (2021). Multi-label ocular disease classification with a dense correlation deep neural network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 63, 102167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102167
- Boyina, L., Boddu, K., Tankasala, Y., Vani, K. S. (2022). Classification of Uncertain ImageNet Retinal Diseases using ResNet Model. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, 10 (2s), 35–42. Available at: https://ijisae.org/index.php/IJISAE/article/view/2358
- Bhati, A., Gour, N., Khanna, P., Ojha, A. (2023). Discriminative kernel convolution network for multi-label ophthalmic disease detection on imbalanced fundus image dataset. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 153, 106519. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106519
- Emir, B., Colak, E. (2023). Performance analysis of pretrained convolutional neural network models for ophthalmological disease classification (Version 1). SciELO journals. doi: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.22548323.v1
- Mayya, V., S, S. K., Kulkarni, U., Surya, D. K., Acharya, U. R. (2022). An empirical study of preprocessing techniques with convolutional neural networks for accurate detection of chronic ocular diseases using fundus images. Applied Intelligence, 53 (2), 1548–1566. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03490-8
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2023 Mamoon A Al Jbaar, Shefa A. Dawwd

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









