Новий підхід до розробки архітектури нейронної мережі на основі метаевристичного підходу протиста
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281986Ключові слова:
нейронна мережа, штучний інтелект, оптимізація прихованого шару, глибока нейронна мережаАнотація
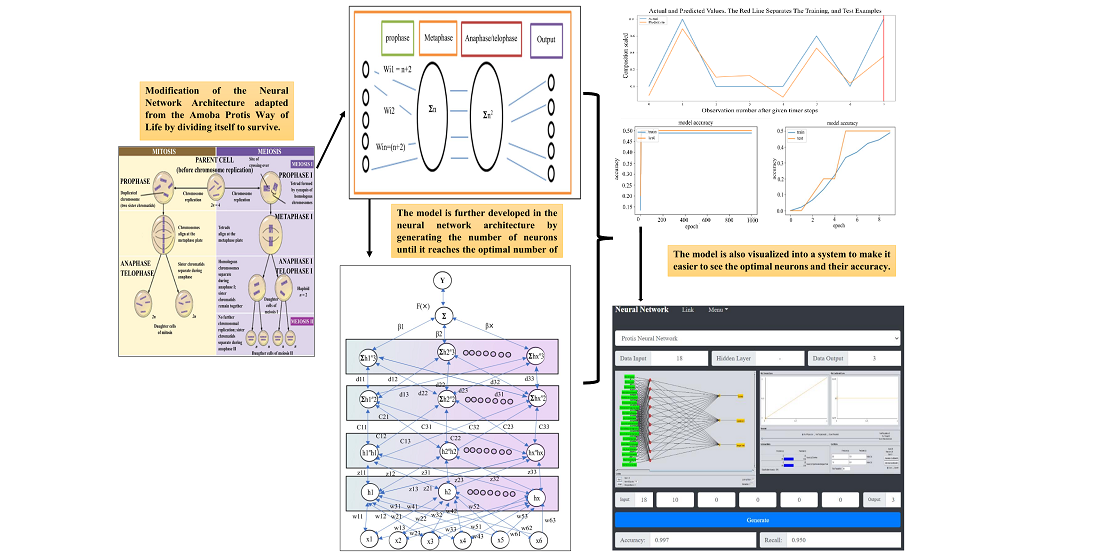
Предметом дослідження є визначення найкращої моделі архітектури нейронної мережі та способів оптимізації архітектури за допомогою метаевристичного підходу протиста. Існує необхідність у всебічному дослідженні і використанні метаевристичних методів. Ці методи спрямовані на вирішення завдань та адаптацію до способу життя протиста амеби. У дослідженні запропонований метод модифікує життєвий цикл амеби, що складається з чотирьох фаз: профази, метафази, анафази та телофази. Ці чотири фази модифіковані в архітектурі нейронної мережі для оптимізації відповідної кількості прихованих шарів та створення ефективної моделі архітектури. Результати показують, що підхід протиста оптимізує архітектуру нейронної мережі, особливо при створенні прихованих шарів для вдосконалення моделі нейронної мережі. Відмінною особливістю отриманих результатів є те, що середній діапазон вироджених нейронів у прихованому шарі становить від 0 до 35 нейронів у кожному шарі. Стандартна кількість нейронів дозволяє вирішити задачу визначення найкращої моделі архітектури нейронної мережі. Алгоритм протиста, вбудований у рекурентну нейронну мережу протиста для вимірювання категоріальних даних, дає середнє значення RMSE, що представляє різницю між фактичними вимірами та прогнозами 0,066.
Отже, розроблена модель перевершує за продуктивністю існуючу класичну модель нейронної мережі. Що стосується точності, алгоритм протиста, вбудований у нейронну мережу для категоріальних даних та даних часових рядів, забезпечує середню точність 0,952 та повноту 0,950. Згорткова нейронна мережа протиста забезпечує точність 95,9 %. Таким чином, із трьох протестованих наборів даних згорткова нейронна мережа протиста демонструє найвище значення точності
Посилання
- Mladenović, N., Brimberg, J., Hansen, P., Moreno-Pérez, J. A. (2007). The p-median problem: A survey of metaheuristic approaches. European Journal of Operational Research, 179 (3), 927–939. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2005.05.034
- Ren, P., Xiao, Y., Chang, X., Huang, P., Li, Z., Chen, X., Wang, X. (2021). A Comprehensive Survey of Neural Architecture Search. ACM Computing Surveys, 54 (4), 1–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3447582
- Alkabbani, H., Ahmadian, A., Zhu, Q., Elkamel, A. (2021). Machine Learning and Metaheuristic Methods for Renewable Power Forecasting: A Recent Review. Frontiers in Chemical Engineering, 3. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fceng.2021.665415
- Joshi, D., Chithaluru, P., Anand, D., Hajjej, F., Aggarwal, K., Torres, V. Y., Thompson, E. B. (2023). An Evolutionary Technique for Building Neural Network Models for Predicting Metal Prices. Mathematics, 11 (7), 1675. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/math11071675
- Panario, D. (2014). Open Problems for Polynomials over Finite Fields and Applications. Open Problems in Mathematics and Computational Science, 111–126. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10683-0_6
- Panchal, G., Ganatra, A., Kosta, Y. P., Panchal, D. (2011). Behaviour Analysis of Multilayer Perceptronswith Multiple Hidden Neurons and Hidden Layers. International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, 3 (2), 332–337. doi: https://doi.org/10.7763/ijcte.2011.v3.328
- Sengupta, S., Basak, S., Saikia, P., Paul, S., Tsalavoutis, V., Atiah, F. et al. (2020). A review of deep learning with special emphasis on architectures, applications and recent trends. Knowledge-Based Systems, 194, 105596. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105596
- Eskandar, H., Sadollah, A., Bahreininejad, A., Hamdi, M. (2012). Water cycle algorithm – A novel metaheuristic optimization method for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Computers & Structures, 110-111, 151–166. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2012.07.010
- Alagoz, B. B., Simsek, O. I., Ari, D., Tepljakov, A., Petlenkov, E., Alimohammadi, H. (2022). An Evolutionary Field Theorem: Evolutionary Field Optimization in Training of Power-Weighted Multiplicative Neurons for Nitrogen Oxides-Sensitive Electronic Nose Applications. Sensors, 22 (10), 3836. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22103836
- Ebenezer M., A., Arya, A. (2022). An Atypical Metaheuristic Approach to Recognize an Optimal Architecture of a Neural Network. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence. doi: https://doi.org/10.5220/0010951600003116
- Castellanos, J. L., Gomez, M. F., Adams, K. D. (2017). Using machine learning based on eye gaze to predict targets: An exploratory study. 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ssci.2017.8285207
- Adhitya, E. K., Satria, R., Subagyo, H. (2015). Komparasi Metode Machine Learning dan Metode Non Machine Learning untuk Estimasi Usaha Perangkat Lunak. Journal of Software Engineering, 1 (2), 109–113. Available at: https://www.neliti.com/publications/90180/komparasi-metode-machine-learning-dan-metode-non-machine-learning-untuk-estimasi#cite
- Demin, S. Yu., Berdieva, M. A., Podlipaeva, Yu. I., Yudin, A. L., Goodkov, A. V. (2017). Karyotyping of Amoeba proteus. Cell and Tissue Biology, 11 (4), 308–313. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/s1990519x17040046
- Harumy, T. H. F., Zarlis, M., Effendi, S., Lidya, M. S. (2021). Prediction Using A Neural Network Algorithm Approach (A Review). 2021 International Conference on Software Engineering & Computer Systems and 4th International Conference on Computational Science and Information Management (ICSECS-ICOCSIM). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icsecs52883.2021.00066
- Harumy, T. H. F., Sitorus, J., Lubis, M. (2018). Sistem Informasi Absensi Pada Pt. Cospar Sentosa Jaya Menggunakan Bahasa Pemprograman Java. Jurnal Teknik dan Informatika, 5 (1), 63–70. Available at: https://jurnal.pancabudi.ac.id/index.php/Juti/article/view/95
- Ergen, T., Pilanci, M. (2021). Convex geometry and duality of over-parameterized neural networks. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 22, 1–63. Available at: https://jmlr.org/papers/volume22/20-1447/20-1447.pdf
- Harumy, T. H. F., Yustika Manik, F., Altaha (2021). Optimization Classification of Diseases Which is Dominant Suffered by Coastal Areas Using Neural Network. 2021 International Conference on Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, and Business Analytics (DATABIA). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/databia53375.2021.9650223
- Pomey, P. (2017). The Protis project (Marseilles, France). Ships And Maritime Landscapes, 484–489. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctt20p56b6.86
- Wagarachchi, N. M., Karunananda, A. S. (2013). Optimization of multi-layer artificial neural networks using delta values of hidden layers. 2013 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence, Cognitive Algorithms, Mind, and Brain (CCMB). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ccmb.2013.6609169
- Musikawan, P., Sunat, K., Kongsorot, Y., Horata, P., Chiewchanwattana, S. (2019). Parallelized Metaheuristic-Ensemble of Heterogeneous Feedforward Neural Networks for Regression Problems. IEEE Access, 7, 26909–26932. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2900563
- Guliyev, N. J., Ismailov, V. E. (2018). On the approximation by single hidden layer feedforward neural networks with fixed weights. Neural Networks, 98, 296–304. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2017.12.007
- Qolomany, B., Maabreh, M., Al-Fuqaha, A., Gupta, A., Benhaddou, D. (2017). Parameters optimization of deep learning models using Particle swarm optimization. 2017 13th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iwcmc.2017.7986470
- Henríquez, P. A., Ruz, G. A. (2018). A non-iterative method for pruning hidden neurons in neural networks with random weights. Applied Soft Computing, 70, 1109–1121. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.03.013
- Balamurugan, P., Amudha, T., Satheeshkumar, J., Somam, M. (2021). Optimizing Neural Network Parameters For Effective Classification of Benign and Malicious Websites. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1998 (1), 012015. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1998/1/012015
- Mohammed, A. J., Al-Majidi, S. D., Al-Nussairi, M. Kh., Abbod, M. F., Al-Raweshidy, H. S. (2022). Design of a Load Frequency Controller based on Artificial Neural Network for Single-Area Power System. 2022 57th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/upec55022.2022.9917853
- Romanuke, V. (2015). Optimal Training Parameters and Hidden Layer Neuron Number of Two-Layer Perceptron for Generalised Scaled Object Classification Problem. Information Technology and Management Science, 18 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/itms-2015-0007
- Hegde, S., Mundada, M. R. (2019). Enhanced Deep Feed Forward Neural Network Model for the Customer Attrition Analysis in Banking Sector. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications, 11 (7), 10–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.5815/ijisa.2019.07.02
- Thomas, A. J., Petridis, M., Walters, S. D., Gheytassi, S. M., Morgan, R. E. (2017). Two Hidden Layers are Usually Better than One. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 279–290. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65172-9_24
- Cardoso, W., Di Felice, R., Dos Santos, B. N., Schitine, A. N., Pires Machado, T. A., Sousa Galdino, A. G. de, Morbach Dixini, P. V. (2022). Modeling of artificial neural networks for silicon prediction in the cast iron production process. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence (IJ-AI), 11 (2), 530. doi: https://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v11.i2.pp530-538
- Zhou, Y., Niu, Y., Luo, Q., Jiang, M. (2020). Teaching learning-based whale optimization algorithm for multi-layer perceptron neural network training. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 17 (5), 5987–6025. doi: https://doi.org/10.3934/mbe.2020319
- Sadollah, A., Eskandar, H., Lee, H. M., Yoo, D. G., Kim, J. H. (2016). Water cycle algorithm: A detailed standard code. SoftwareX, 5, 37–43. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2016.03.001
- Zheng, Y.-J., Lu, X.-Q., Du, Y.-C., Xue, Y., Sheng, W.-G. (2019). Water wave optimization for combinatorial optimization: Design strategies and applications. Applied Soft Computing, 83, 105611. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105611
- Wang, N., Er, M. J., Han,M. (2015). Generalized Single-Hidden Layer Feedforward Networks for Regression Problems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 26 (6), 1161–1176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2014.2334366
- Geurts, A. M., Hackett, C. S., Bell, J. B., Bergemann, T. L., Collier, L. S., Carlson, C. M. et al. (2006). Structure-based prediction of insertion-site preferences of transposons into chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 34 (9), 2803–2811. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl301
- Yang, X.-S. (2011). Metaheuristic Optimization: Algorithm Analysis and Open Problems. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 21–32. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20662-7_2
- Yang, X.-S., He, X. (2014). Swarm Intelligence and Evolutionary Computation: Overview and Analysis. Recent Advances in Swarm Intelligence and Evolutionary Computation, 1–23. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13826-8_1
- Agrawal, P., Abutarboush, H. F., Ganesh, T., Mohamed, A. W. (2021). Metaheuristic Algorithms on Feature Selection: A Survey of One Decade of Research (2009-2019). IEEE Access, 9, 26766–26791. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3056407
- Ge, D. H., Li, H. S., Zhang, L., Liu, R. Y., Shen, P. Y., Miao, Q. G. (2020). Survey of Lightweight Neural Network. Journal of Software. doi: https://doi.org/10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005942
- Hofmann, W., Sedlmeir-Hofmann, C., Ivandic´, M., Ruth, D., Luppa, P. (2010). PROTIS: Use of Combined Biomarkers for Providing Diagnostic Information on Disease States. The Urinary Proteome, 123–142. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-711-2_8
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2023 T. Henny Febriana Harumy, Muhammad Zarlis, Maya Silvi Lydia, Syahril Efendi

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









