SIMD-реалізація глибоких CNN для виявлення короткозорості в одноплатній комп'ютерній системі
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289007Ключові слова:
CNN, багатоядерний, економічно ефективний, платформа, прогнозування, короткозорість, очний, ODIR, AIoT, SIMDАнотація
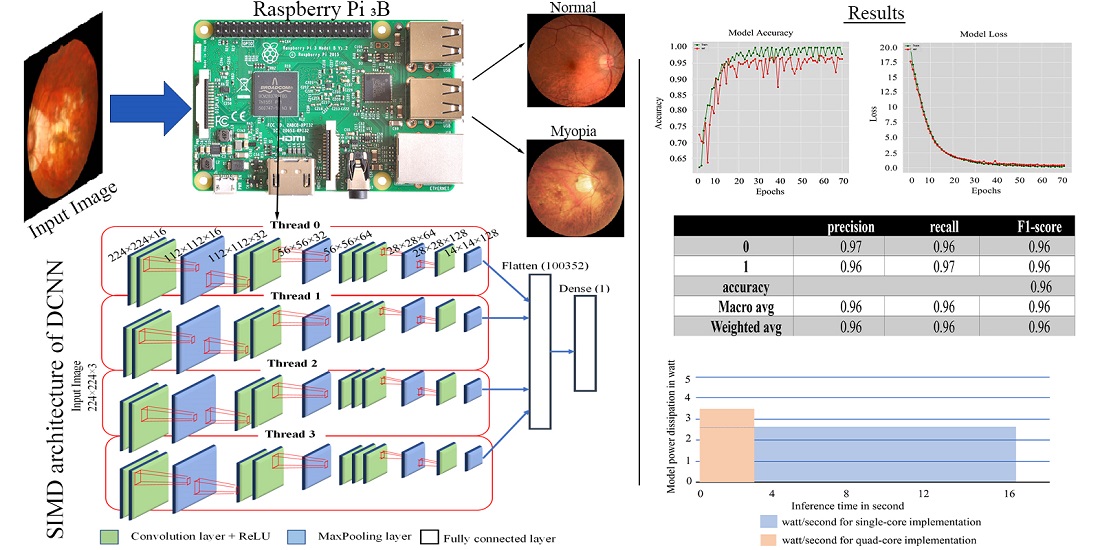
Алгоритми глибокого навчання, особливо згорткові нейронні мережі (CNN), набули швидкого розвитку завдяки своїй гнучкості та масштабованості для використання в декількох областях для моделювання реальних застосувань, таких як виявлення об’єктів, класифікація зображень тощо. Однак їх висока точність вимагає інтенсивних обчислень. Тому надзвичайно важливо ретельно обирати відповідну комп’ютерну платформу та методологію реалізації мережевих архітектур CNN із забезпеченням підвищеної ефективності. У реалізації CNN переважають паралельні архітектури. В даному дослідженні представлено нову паралельну реалізацію Single Instruction Multi Data (SIMD) запропонованої CNN з метою прискорити процес виконання та зробити її придатною для розгортання на недорогих платформах з низьким енергоспоживанням. Запропонована реалізація дозволяє отримати вдосконалену модель глибокої CNN для реалізації на економічно ефективній платформі і забезпечує портативність для автономної роботи з багатоядерними процесорами при збереженні точності роботи. Для реалізації нашої моделі використовувався малопотужний цільовий пристрій Raspberry Pi 3 B. Запропонований підхід характеризується високою точністю діагностики до 96,35 % при енергоспоживанні 3,65 Вт, досягаючи зниження енергоспоживання на 19,17–68,45 % порівняно з попередньою роботою. У той же час, він забезпечує гарний час висновку для обраної платформи. Видатні результати даного дослідження відображають успіх застосування паралельних архітектур для використання чотирьох ядер процесора ARM на цільовій платформі. Представлена модель може бути ефективним медичним помічником для автоматизованого виявлення та діагностики короткозорості очей. Таким чином, це може стати перспективним медичним інструментарієм, що дозволяє зменшити зусилля медичного персоналу та підвищити якість наданих медичних послуг для пацієнтів з короткозорістю.
Посилання
- Suzen, A. A., Duman, B., Sen, B. (2020). Benchmark Analysis of Jetson TX2, Jetson Nano and Raspberry PI using Deep-CNN. 2020 International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications (HORA). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/hora49412.2020.9152915
- Choi, K., Sobelman, G. E. (2022). An Efficient CNN Accelerator for Low-Cost Edge Systems. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 21 (4), 1–20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3539224
- Fernández-Cerero, D., Fernández-Rodríguez, J. Y., Álvarez-García, J. A., Soria-Morillo, L. M., Fernández-Montes, A. (2019). Single-Board-Computer Clusters for Cloudlet Computing in Internet of Things. Sensors, 19 (13), 3026. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s19133026
- Saranya, V., Carmel Mary Belinda, M. J., Kanagachidambaresan, G. R. (2020). An Evolution of Innovations Protocols and Recent Technology in Industrial IoT. Internet of Things for Industry 4.0, 161–175. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32530-5_11
- Srinivasan, V., Meudt, S., Schwenker, F. (2019). Deep Learning Algorithms for Emotion Recognition on Low Power Single Board Computers. Multimodal Pattern Recognition of Social Signals in Human-Computer-Interaction, 59–70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20984-1_6
- Dubovečak, M., Dumić, E., Bernik, A. (2023). Face Detection and Recognition Using Raspberry PI Computer. Tehnički Glasnik, 17 (3), 346–352. doi: https://doi.org/10.31803/tg-20220321232047
- Zamir, M., Ali, N., Naseem, A., Ahmed Frasteen, A., Zafar, B., Assam, M., Othman, M., Attia, E.-A. (2022). Face Detection & Recognition from Images & Videos Based on CNN & Raspberry Pi. Computation, 10 (9), 148. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10090148
- Huang, Z., Yang, S., Zhou, M., Gong, Z., Abusorrah, A., Lin, C., Huang, Z. (2021). Making accurate object detection at the edge: review and new approach. Artificial Intelligence Review, 55 (3), 2245–2274. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10059-3
- Sonkar, S., Kumar, P., George, R. C., Yuvaraj, T. P., Philip, D., Ghosh, A. K. (2022). Real-Time Object Detection and Recognition Using Fixed-Wing LALE VTOL UAV. IEEE Sensors Journal, 22 (21), 20738–20747. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2022.3206345
- Didi, Z., El Azami, I., Boumait, E. M. (2022). Design of a Security System Based on Raspberry Pi with Motion Detection. Digital Technologies and Applications, 427–434. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-02447-4_44
- Hammad, M., Abd El-Latif, A. A., Hussain, A., Abd El-Samie, F. E., Gupta, B. B., Ugail, H., Sedik, A. (2022). Deep Learning Models for Arrhythmia Detection in IoT Healthcare Applications. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 100, 108011. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108011
- Dhar, T., Dey, N., Borra, S., Sherratt, R. S. (2023). Challenges of Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis—Improving Explainability and Trust. IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society, 4 (1), 68–75. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tts.2023.3234203
- Vayadande, K., Ingale, V., Verma, V., Yeole, A., Zawar, S., Jamadar, Z. (2022). Ocular Disease Recognition using Deep Learning. 2022 International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (IConSIP). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iconsip49665.2022.10007470
- Albahli, S., Ahmad Hassan Yar, G. N. (2022). Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using custom convolutional neural network. Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology, 30 (2), 275–291. doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/xst-211073
- Ebri, A. E., Govender, P., Naidoo, K. S. (2019). Prevalence of vision impairment and refractive error in school learners in Calabar, Nigeria. African Vision and Eye Health, 78 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.4102/aveh.v78i1.487
- Pakbin, M., Katibeh, M., Pakravan, M., Yaseri, M., Soleimanizad, R. (2015). Prevalence and causes of visual impairment and blindness in central Iran; The Yazd eye study. Journal of Ophthalmic and Vision Research, 10 (3), 279. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/2008-322x.170362
- Gibertoni, G., Borghi, G., Rovati, L. (2022). Vision-Based Eye Image Classification for Ophthalmic Measurement Systems. Sensors, 23 (1), 386. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010386
- da Rocha, D. A., Ferreira, F. M. F., Peixoto, Z. M. A. (2022). Diabetic retinopathy classification using VGG16 neural network. Research on Biomedical Engineering, 38 (2), 761–772. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-022-00200-8
- Pan, Y., Liu, J., Cai, Y., Yang, X., Zhang, Z., Long, H. et al. (2023). Fundus image classification using Inception V3 and ResNet-50 for the early diagnostics of fundus diseases. Frontiers in Physiology, 14. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2023.1126780
- Menghani, G. (2023). Efficient Deep Learning: A Survey on Making Deep Learning Models Smaller, Faster, and Better. ACM Computing Surveys, 55 (12), 1–37. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3578938
- Islam, S., Deng, J., Zhou, S., Pan, C., Ding, C., Xie, M. (2022). Enabling Fast Deep Learning on Tiny Energy-Harvesting IoT Devices. 2022 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE). doi: https://doi.org/10.23919/date54114.2022.9774756
- Dai, S., Chen, L., Lei, T., Zhou, C., Wen, Y. (2020). Automatic Detection Of Pathological Myopia And High Myopia On Fundus Images. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icme46284.2020.9102787
- Gour, N., Khanna, P. (2021). Multi-class multi-label ophthalmological disease detection using transfer learning based convolutional neural network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 66, 102329. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102329
- Topaloglu, I. (2022). Deep Learning Based Convolutional Neural Network Structured New Image Classification Approach for Eye Disease Identification. Scientia Iranica, 30 (5), 1731–1742. doi: https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2022.58049.5537
- Rakhmetulayeva, S., Syrymbet, Z. (2022). Implementation of convolutional neural network for predicting glaucoma from fundus images. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (120)), 70–77. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269229
- David, S. A., Mahesh, C., Kumar, V. D., Polat, K., Alhudhaif, A., Nour, M. (2022). Retinal Blood Vessels and Optic Disc Segmentation Using U-Net. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2022, 1–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8030954
- Wang, K., Xu, C., Li, G., Zhang, Y., Zheng, Y., Sun, C. (2023). Combining convolutional neural networks and self-attention for fundus diseases identification. Scientific Reports, 13 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-27358-6
- Maqsood, Z., Gupta, M. K. (2022). Automatic Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy on the Edge. Cyber Security, Privacy and Networking, 129–139. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8664-1_12
- Karamihan, K. C., Agustino, I. D. F., Bionesta, R. B. B., Tuason, F. C., Arellano, S. V. E., Esguerra, P. A. M. (2019). SBC-Based Cataract Detection System using Deep Convolutional Neural Network with Transfer Learning Algorithm. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE), 9(2), 4605–4613. doi: https://doi.org/10.35940/ijrte.b3368.078219
- Civit-Masot, J., Luna-Perejón, F., Corral, J. M. R., Domínguez-Morales, M., Morgado-Estévez, A., Civit, A. (2021). A study on the use of Edge TPUs for eye fundus image segmentation. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 104, 104384. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104384
- Lee, S.-J., Park, S.-S., Chung, K.-S. (2018). Efficient SIMD implementation for accelerating convolutional neural network. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Communication and Information Processing. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3290420.3290444
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B. Available at: https://www.raspberrypi.com/products/raspberry-pi-3-model-b/
- Raspberry Pi Power Consumption Guide. Available at: https://www.ecoenergygeek.com/raspberry-pi-power-consumption/
- Wang, J., Yang, L., Huo, Z., He, W., Luo, J. (2020). Multi-Label Classification of Fundus Images With EfficientNet. IEEE Access, 8, 212499–212508. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3040275
- He, J., Li, C., Ye, J., Qiao, Y., Gu, L. (2021). Multi-label ocular disease classification with a dense correlation deep neural network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 63, 102167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102167
- Bhati, A., Gour, N., Khanna, P., Ojha, A. (2023). Discriminative kernel convolution network for multi-label ophthalmic disease detection on imbalanced fundus image dataset. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 153, 106519. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106519
- Jeny, A. A., Junayed, M. S., Islam, M. B. (2023). Deep Neural Network-Based Ensemble Model for Eye Diseases Detection and Classification. Image Analysis & Stereology, 42 (2), 77–91. doi: https://doi.org/10.5566/ias.2857
- Kristiani, E., Yang, C.-T., Huang, C.-Y. (2020). iSEC: An Optimized Deep Learning Model for Image Classification on Edge Computing. IEEE Access, 8, 27267–27276. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2971566
- Goel, A., Aghajanzadeh, S., Tung, C., Chen, S.-H., Thiruvathukal, G. K., Lu, Y.-H. (2020). Modular Neural Networks for Low-Power Image Classification on Embedded Devices. ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems, 26 (1), 1–35. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3408062
- Dong, Z., Li, N., Iosifidis, A., Zhang, Q. (2022). Design and Prototyping Distributed CNN Inference Acceleration in Edge Computing. arXiv. doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2211.13778
- James, N., Ong, L.-Y., Leow, M.-C. (2022). Exploring Distributed Deep Learning Inference Using Raspberry Pi Spark Cluster. Future Internet, 14 (8), 220. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/fi14080220
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2023 Mamoon A Al Jbaar, Shefa A. Dawwd

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









