Визначення впливу полімерної композиції при модифікації гарячої асфальтової суміші
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.299189Ключові слова:
гаряча асфальтова суміш, синтетичний каучук, випробування за Маршаллом, оптимальний вміст асфальтуАнотація
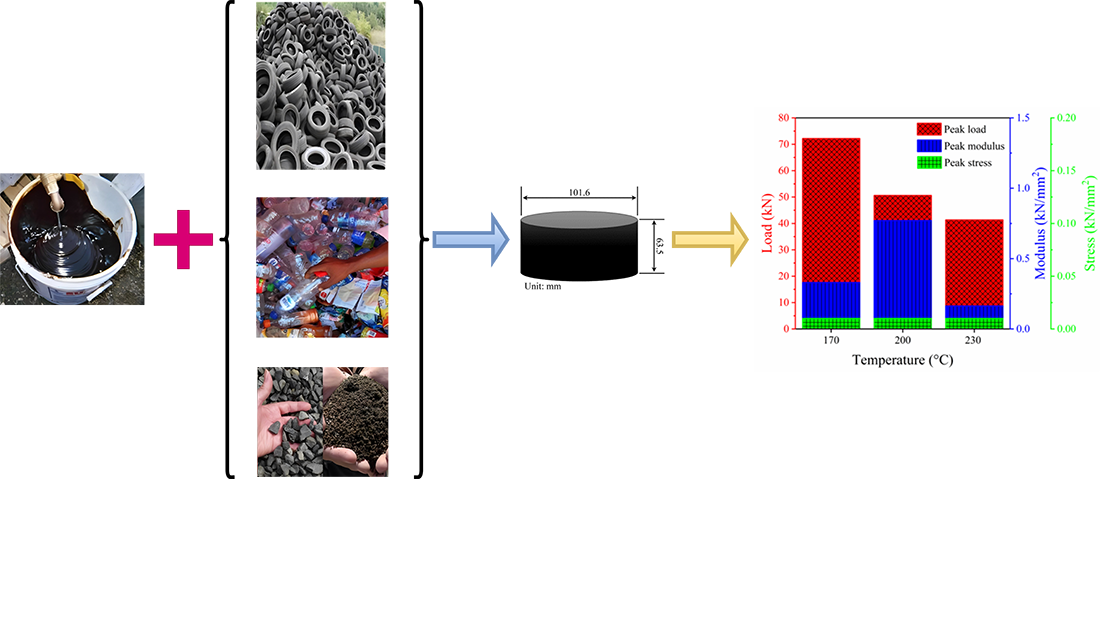
У дослідженні основна увага приділяється впливу полімерної композиції на гарячу асфальтову суміш (HMA). Основною метою є вивчення впливу температури на механічні та експлуатаційні характеристики HMA, особливо щодо концентрації полімеру. Об'єктом дослідження є полімерна композиція та модифікації HMA, включаючи синтетичний каучук та поліетилен високої щільності (HDPE). Ключовим завданням дослідження є оптимізація полімерної суміші HMA для підвищення довговічності, несучої здатності та структурної цілісності. Дослідження також спрямоване на розуміння складного взаємозв'язку між концентрацією полімеру та параметрами HMA, такими як міцність на стиск, модуль пружності та напруження. Результати досліджень показують, що максимальне навантаження в 68,169 кН було досягнуто при використанні суміші, що містить 5 % синтетичного каучуку, за температури 200 °C. Матеріал продемонстрував жорсткість та стійкість до деформації із середнім розміром тріщин 0,01 кН/мм2 та значенням модуля пружності 0,309 кН/мм2. Згідно з функцією Маршалла, оптимальна суміш складається з 5 % асфальту, змішаного за температури 175 °C. Результати показують, що полімерна суміш істотно впливає на механічні властивості HMA, зокрема на несучу здатність та опір деформації. Для оптимізації експлуатаційних характеристик HMA необхідна оптимізація вмісту полімеру і температури. Результати показали, що HMA, що містить 5 % синтетичного каучуку, при певних температурних режимах має кращі механічні властивості, включаючи несучу здатність і жорсткість. Ці результати дозволяють оптимізувати полімерну композицію для забезпечення експлуатаційних характеристик HMA. Дані результати можуть бути використані для створення більш довговічних та екологічних дорожніх покриттів. Дорожні інженери та проектувальники можуть продовжити термін служби асфальтового покриття та зменшити вплив на навколишнє середовище шляхом регулювання складу полімерної суміші HMA та температури
Посилання
- Caputo, P., Porto, M., Angelico, R., Loise, V., Calandra, P., Oliviero Rossi, C. (2020). Bitumen and asphalt concrete modified by nanometer-sized particles: Basic concepts, the state of the art and future perspectives of the nanoscale approach. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 285, 102283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102283
- Al-Gurah, E. R., Al-Humeidawi, B. H. (2023). Assessment of performance of hot mix asphalt contained various types of mineral fillers and newly polymer modified bitumen. Materials Today: Proceedings, 80, 3877–3886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.07.406
- Menapace, I., Yiming, W., Masad, E. (2018). Effects of Environmental Factors on the Chemical Composition of Asphalt Binders. Energy & Fuels, 33 (4), 2614–2624. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b03273
- Ekejiuba, A. I. B. (2021). Natural Petroleum: Chemistry and Valuable Products Fractions. Inter- World Journal Of Science And Technology, 4 (2), 300–337. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350790219_Natural_Petroleum_Chemistry_and_Valuable_Products_Fractions
- Li, R., Xiao, F., Amirkhanian, S., You, Z., Huang, J. (2017). Developments of nano materials and technologies on asphalt materials – A review. Construction and Building Materials, 143, 633–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.158
- Behnood, A., Modiri Gharehveran, M. (2019). Morphology, rheology, and physical properties of polymer-modified asphalt binders. European Polymer Journal, 112, 766–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.10.049
- Sun, D., Lu, T., Xiao, F., Zhu, X., Sun, G. (2017). Formulation and aging resistance of modified bio-asphalt containing high percentage of waste cooking oil residues. Journal of Cleaner Production, 161, 1203–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.155
- Revelo, C. F., Correa, M., Aguilar, C., Colorado, H. A. (2021). Composite materials made of waste tires and polyurethane resin: A case study of flexible tiles successfully applied in industry. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 15, e00681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00681
- Al-Sabaeei, A., Yussof, N. I. Md., Napiah, M., Sutanto, M. (2019). A review of using natural rubber in the modification of bitumen and asphalt mixtures used for road construction. Jurnal Teknologi, 81 (6). https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v81.13487
- Wu, X., Lu, C., Han, Y., Zhou, Z., Yuan, G., Zhang, X. (2016). Cellulose nanowhisker modulated 3D hierarchical conductive structure of carbon black/natural rubber nanocomposites for liquid and strain sensing application. Composites Science and Technology, 124, 44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.01.012
- Gogoi, R., Biligiri, K. P., Das, N. C. (2015). Performance prediction analyses of styrene-butadiene rubber and crumb rubber materials in asphalt road applications. Materials and Structures, 49 (9), 3479–3493. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-015-0733-0
- Yu, H., Leng, Z., Zhou, Z., Shih, K., Xiao, F., Gao, Z. (2017). Optimization of preparation procedure of liquid warm mix additive modified asphalt rubber. Journal of Cleaner Production, 141, 336–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.043
- Nciri, N., Kim, N., Cho, N. (2017). New insights into the effects of styrene-butadiene-styrene polymer modifier on the structure, properties, and performance of asphalt binder: The case of AP-5 asphalt and solvent deasphalting pitch. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 193, 477–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.03.014
- Raza, A., Khan, I., Tufail, R., Frankovska, J., Mushtaq, M., Salmi, A. et al. (2022). Evaluation of Moisture Damage Potential in Hot Mix Asphalt Using Polymeric Aggregate Treatment. Materials, 15 (15), 5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155437
- Hossein Hamedi, G., Ghalandari Shamami, K., Mazhari Pakenari, M. (2020). Effect of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene on the performance characteristics of hot mix asphalt. Construction and Building Materials, 258, 119729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119729
- Tahmoorian, F., Liyanapathirana, S., Yeaman, J., Egwurube, J. (2023). Performance of Hot-Mix Asphalt and Modified Binders Containing Polyethylene. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: Pavements, 149 (1). https://doi.org/10.1061/jpeodx.pveng-502
- Wu, W., Cavalli, M. C., Jiang, W., Kringos, N. (2024). Differing perspectives on the use of high-content SBS polymer-modified bitumen. Construction and Building Materials, 411, 134433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134433
- Masad, E., Roja, K. L., Rehman, A., Abdala, A. (2020). A review of asphalt modification using plastics: a focus on polyethylene. Qatar. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.36633.77920
- Jitsangiam, P., Nusit, K., Teeratitayangkul, P., Ping Ong, G., Thienchai, C. (2023). Development of a modified Marshall mix design for Hot-mix asphalt concrete mixed with recycled plastic based on dry mixing processes. Construction and Building Materials, 404, 133127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133127
- Zhdaniuk, V., Volovyk, O., Kostin, D., Lisovin, S. (2021). An investigation of the effect of thermoplastic additives in asphalt concrete mixtures on the properties of different types of asphalt concrete. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (6 (110)), 61–70. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.227806
- Aliha, M. R. M., Razmi, A., Mansourian, A. (2017). The influence of natural and synthetic fibers on low temperature mixed mode I + II fracture behavior of warm mix asphalt (WMA) materials. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 182, 322–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.06.003
- Kodur, V. (2014). Properties of Concrete at Elevated Temperatures. ISRN Civil Engineering, 2014, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/468510
- Wang, T., Xiao, F., Amirkhanian, S., Huang, W., Zheng, M. (2017). A review on low temperature performances of rubberized asphalt materials. Construction and Building Materials, 145, 483–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.031
- Han, L., Zheng, M., Wang, C. (2016). Current status and development of terminal blend tyre rubber modified asphalt. Construction and Building Materials, 128, 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.10.080
- Ruellan, B., Le Cam, J.-B., Jeanneau, I., Canévet, F., Mortier, F., Robin, E. (2019). Fatigue of natural rubber under different temperatures. International Journal of Fatigue, 124, 544–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.10.009
- Fatemi, S., Zarei, M., Ziaee, S. A., Shad, R., Amir Saadatjoo, S., Tabasi, E. (2023). Low and intermediate temperatures fracture behavior of amorphous poly alpha olefin (APAO)-modified hot mix asphalt subjected to constant and variable temperatures. Construction and Building Materials, 364, 129840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129840
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Stella Junus, Ilyas Renreng, Muhamad Syahid, Azwar Hayat

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









