Визначення впливу втрат на нежорсткий дорожній одяг внаслідок перевантаження транспортних засобів
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.299653Ключові слова:
нежорсткий дорожній одяг, механістичноемпіричне проектування дорожнього покриття, перевантаження, коефіцієнт вантажного автомобіля, перевитрата паливаАнотація
Перевантаження дорожнього покриття стало серйозною проблемою в Індонезії через руйнівний вплив на систему дорожнього покриття, де більшість доріг використовують нежорстке покриття. Між тим, перевантаження також характерне для інших країн, що розвиваються, завдаючи шкоди учасникам та операторам дорожнього руху, починаючи від пошкоджень і закінчуючи дорожньотранспортними пригодами. Поточна проблема полягає у відсутності певних знань про поводження з перевантаженими транспортними засобами, що призводить до негативних наслідків. Тому метою даного дослідження є визначення впливу втрат, спричинених перевантаженими транспортними засобами, на нежорстке дорожнє покриття.
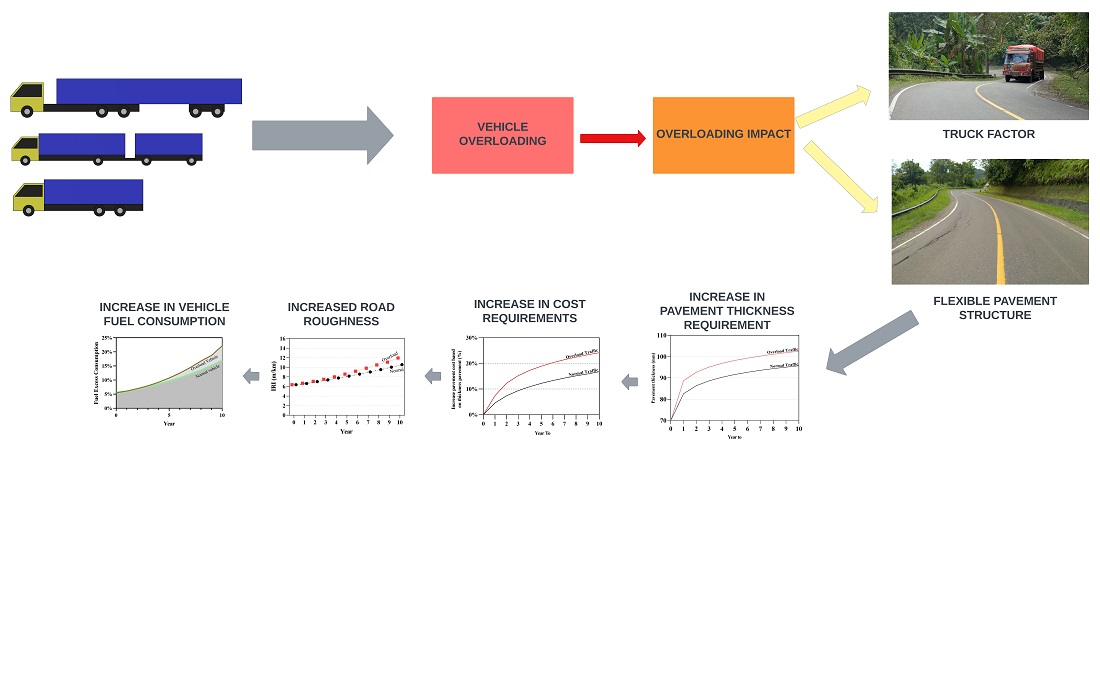
У дослідженні використовуються дані про навантаження транспортних засобів для вивчення фактичних умов на місці, які перетворюються у значення навантаження на вісь для кожного транспортного засобу та використовуються для визначення стану дорожнього покриття з використанням підходу з урахуванням коефіцієнта вантажного автомобіля, механістичноемпіричного проектування, рівності дорожнього покриття та впливу перевантаження через споживання палива транспортними засобами на нежорсткому дорожньому покритті.
Результати показують, що перевантажені транспортні засоби завдають шкоди нежорсткому дорожньому покриттю. Збільшення значень коефіцієнта вантажного автомобіля для всіх перевантажених транспортних засобів понад максимально допустиме навантаження призводить до більшого пошкодження нежорсткого дорожнього покриття зі збільшенням значень коефіцієнта вантажного автомобіля до 83 %. Вплив перевантаження може бути зменшений за рахунок збільшення товщини шару асфальту та модуля пружності асфальту, тому важливо звертати увагу на якість асфальту з урахуванням перевантаження. Для запобігання перевантаження було виявлено, що товщина верхнього шару асфальту в діапазоні 170–205 мм дозволяє пом’якшити цей негативний вплив. Крім того, перевантаження впливає на рівність нежорсткого дорожнього покриття та витрату палива транспортними засобами. Збільшення рівності та витрати палива призводить до збільшення витрат на утримання доріг, а також впливає на комфорт і безпеку руху. Крім того, перевитрата палива може призвести до забруднення навколишнього середовища
Посилання
- Zhou, Y., Tong, C., Wang, Y. (2022). Road construction, economic growth, and poverty alleviation in China. Growth and Change, 53 (3), 1306–1332. https://doi.org/10.1111/grow.12617
- Idei, R., Kato, H. (2018). Changes in Individual Economic Activities and Regional Market Structures Caused by Rural Road Improvements in Cambodia. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2672 (3), 26–36. https://doi.org/10.1177/0361198118783863
- Syadullah, M., Setyawan, D. (2021). The Impact of Infrastructure Spending on Economic Growth: A Case Study of Indonesia. Communications - Scientific Letters of the University of Zilina, 23 (3), A184–A192. https://doi.org/10.26552/com.c.2021.3.a184-a192
- Rifai, A. I., Hadiwardoyo, S. P., Correia, A. G., Pereira, P., Cortez, P. (2015). The Data Mining Applied for the Prediction of Highway Roughness due to Overloaded Trucks. International Journal of Technology, 6 (5), 751. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v6i5.1186
- Azis, A., Krisbiantoro, D., R. (2023). Internet of Things (IoT) Innovation and Application to Intelligent Governance Systems: A Case Study on DISHUB for Transport Vehicles. JOIV : International Journal on Informatics Visualization, 7 (1), 193. https://doi.org/10.30630/joiv.7.1.1282
- Wang, B., De Backer, H., Zhou, X.-Y., Chen, A. (2020). Two-stage crack growth-based fatigue damage evaluation of orthotropic steel decks considering vehicle overload. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 17 (5), 591–604. https://doi.org/10.1080/15732479.2020.1759657
- Prastyanto, C. A., Hidayat, A. S. (2023). The Evaluation of Equivalent Axle Load Equation Based on Deflection Value before and after Overlay Flexible Pavement. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1209 (1), 012002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1209/1/012002
- Yulfadli, Z., Arifin, M. Z., Djakfar, L., Wicaksono, A., Nafis, Moch. A. (2023). Analysis of the impact of the railway allowance policy and the increase in fines for loaded trucks on the transfer of modes to rail transportation types. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (3 (124)), 54–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.285861
- Budiharjo, A., Fauzi, A., Masrukhin, Prasetyo, B. (2021). The Relationship between Overloading and Over Dimension of Freight Vehicle. International Journal on Advanced Science, Engineering and Information Technology, 11 (4), 1588. https://doi.org/10.18517/ijaseit.11.4.11430
- Ryguła, A., Brzozowski, K., Maczyński, A. (2020). Limitations of the effectiveness of Weigh in Motion systems. Open Engineering, 10 (1), 183–196. https://doi.org/10.1515/eng-2020-0020
- Liu, Z., Gu, X., Dong, Q. (2024). Permanent Deformation Evaluation and Instability Prediction of Semi-rigid Pavement Structure Using Accelerated Pavement Testing and Finite Element Method. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 52 (1). https://doi.org/10.1520/jte20230209
- The Manual of Pavement Design Guide No. 02/M/BM/2017 (2017). Directorate General of Highway.
- Li, Q., Xiao, D. X., Wang, K. C. P., Hall, K. D., Qiu, Y. (2011). Mechanistic-empirical pavement design guide (MEPDG): a bird’s-eye view. Journal of Modern Transportation, 19 (2), 114–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03325749
- Hatoum, A., Khatib, J., Elkordi, A. (2023). Comparison of Flexible Pavement Designs: Mechanistic-Empirical (NCHRP1-37A) Versus Empirical (AASHTO 1993) Flexible Pavement Design Using Available Local Calibration Models. Transportation Infrastructure Geotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-023-00305-2
- Rys, D., Judycki, J., Jaskula, P. (2015). Analysis of effect of overloaded vehicles on fatigue life of flexible pavements based on weigh in motion (WIM) data. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 17 (8), 716–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2015.1019493
- Rys, D., Jaskula, P. (2018). Effect of Overloaded Vehicles on Whole Life Cycle Cost of Flexible Pavements. Sustainable Civil Infrastructures, 104–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95789-0_10
- Jihanny, J. (2021). The overload impact on design life of flexible pavement. International Journal of GEOMATE, 20 (78). https://doi.org/10.21660/2021.78.j2020
- Jihanny, J., Subagio, B. S., Hariyadi, E. S. (2018). The analysis of overloaded trucks in indonesia based on weigh in motion data (east of sumatera national road case study). MATEC Web of Conferences, 147, 02006. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201814702006
- Kinasih, R. K., Ratna Putri, M. D., Nabila, N. (2020). Modified Zero Overloading Policy Impact to Pavement’s Service Life. Engineering, MAthematics and Computer Science (EMACS) Journal, 2 (2), 41–46. https://doi.org/10.21512/emacsjournal.v2i2.6333
- Wang, H., Al-Saadi, I., Lu, P., Jasim, A. (2019). Quantifying greenhouse gas emission of asphalt pavement preservation at construction and use stages using life-cycle assessment. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 14 (1), 25–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/15568318.2018.1519086
- Kabongo Booto, G., Run Vignisdottir, H., Marinelli, G., Brattebø, H., Bohne, R. A. (2020). Optimizing Road Gradients Regarding Earthwork Cost, Fuel Cost, and Tank-to-Wheel Emissions. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 146 (3). https://doi.org/10.1061/jtepbs.0000289
- Amorim, S. I. R., Pais, J. C., Vale, A. C., Minhoto, M. J. C. (2014). A model for equivalent axle load factors. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 16 (10), 881–893. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2014.968570
- Pais, J., Pereira, P. (2016). The Effect of Traffic Overloads on Road Pavements. Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Maintenance and Rehabilitation of Pavements. https://doi.org/10.3850/978-981-11-0449-7-046-cd
- Nunn, M. E., Brown, A., Weston, D., Nicholls, J. C. (1997). Design of long-life flexible pavements for heavy traffic. Prepared for Highways Agency, British Aggregate Construction. Transport Research Laboratory. Available at: https://www.trl.co.uk/Uploads/TRL/Documents/TRL250---Design-of-long-life-flexible-pavements-for-heavy-traffic.pdf
- Mechanistic-empirical pavement design guide: A manual of practice (MEPDG-2). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials.
- Liu, X., Al-Qadi, I. L. (2021). Development of a Simulated Three-Dimensional Truck Model to Predict Excess Fuel Consumption Resulting from Pavement Roughness. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2675 (9), 1444–1456. https://doi.org/10.1177/03611981211007849
- Zhou, H., Wang, G., Wang, Y. (2018). Wide-Base Tire-Building Process and Design Optimization Using Finite Element Analysis. Tire Science and Technology, 46 (4), 242–259. https://doi.org/10.2346/tire.18.460405
- Xue, W., Weaver, E. (2014). Influence of tyre configuration on pavement response and predicted distress. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 16 (6), 538–548. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2014.943206
- Pais, J. C., Amorim, S. I. R., Minhoto, M. J. C. (2013). Impact of Traffic Overload on Road Pavement Performance. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 139 (9), 873–879. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)te.1943-5436.0000571
- Alavi, S. A. K., Tanzadeh, J., Tahami, S. A., Mirhosseini, A. F. (2020). Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Fibers and Nano-zeolite Modified Asphalt Micro-surfacing. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 48 (3), 2412–2431. https://doi.org/10.1520/jte20190732
- Mashaan, N., Karim, M., Khodary, F., Saboo, N., Milad, A. (2021). Bituminous Pavement Reinforcement with Fiber: A Review. CivilEng, 2 (3), 599–611. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng2030033
- Mugume, R. B., Musumba, S. (2020). Contribution of reactive aggregates towards the performance of in-service asphalt pavements. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 14 (5), 530–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42947-020-0109-x
- Subagio, B. S., Prayoga, A. B., Fadilah, S. R. (2022). Implementation of Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide against Indonesian Conditions using Arizona Calibration. The Open Civil Engineering Journal, 16 (1). https://doi.org/10.2174/18741495-v16-e221026-2022-45
- Rahmawati, A., Adly, E., Lutfiyanto, I., A Syifa, M. (2019). The Overloading Effect on the Design Life of Road and Thickness of Pavement Layer. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 650 (1), 012051. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/650/1/012051
- Zhang, G., Li, Y., King, M. J., Zhong, Q. (2018). Overloading among crash-involved vehicles in China: identification of factors associated with overloading and crash severity. Injury Prevention, 25 (1), 36–46. https://doi.org/10.1136/injuryprev-2017-042599
- Jereb, B., Kumperščak, S., Bratina, T. (2018). The impact of traffic flow on fuel consumption increase in the urban environment. FME Transaction, 46 (3), 278–284. https://doi.org/10.5937/fmet1802278j
- Hyks, O., Neubergova, K., Pribyl, P. (2018). Influence of Driving Fluency on Economic and Ecological Aspects of Transport. Communications - Scientific Letters of the University of Zilina, 20 (3), 9–14. https://doi.org/10.26552/com.c.2018.3.9-14
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Muh Miftahulkhair, Muhammad Zainul Arifin, Fauzul Rizal Sutikno

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









