Forming an elliptical directional diagram of the sectoral horn antenna for flow irradiation of sugar beet seeds by electromagnetic field
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.273972Keywords:
low-energy electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic field emitter, horn antenna, H-sectoral antenna, directional diagram, sugar beet seeds, presowing treatmentAbstract
The object of research is the process that forms an elliptical directional diagram of the H-sector horn antenna for flow irradiation of seeds with the electromagnetic field.
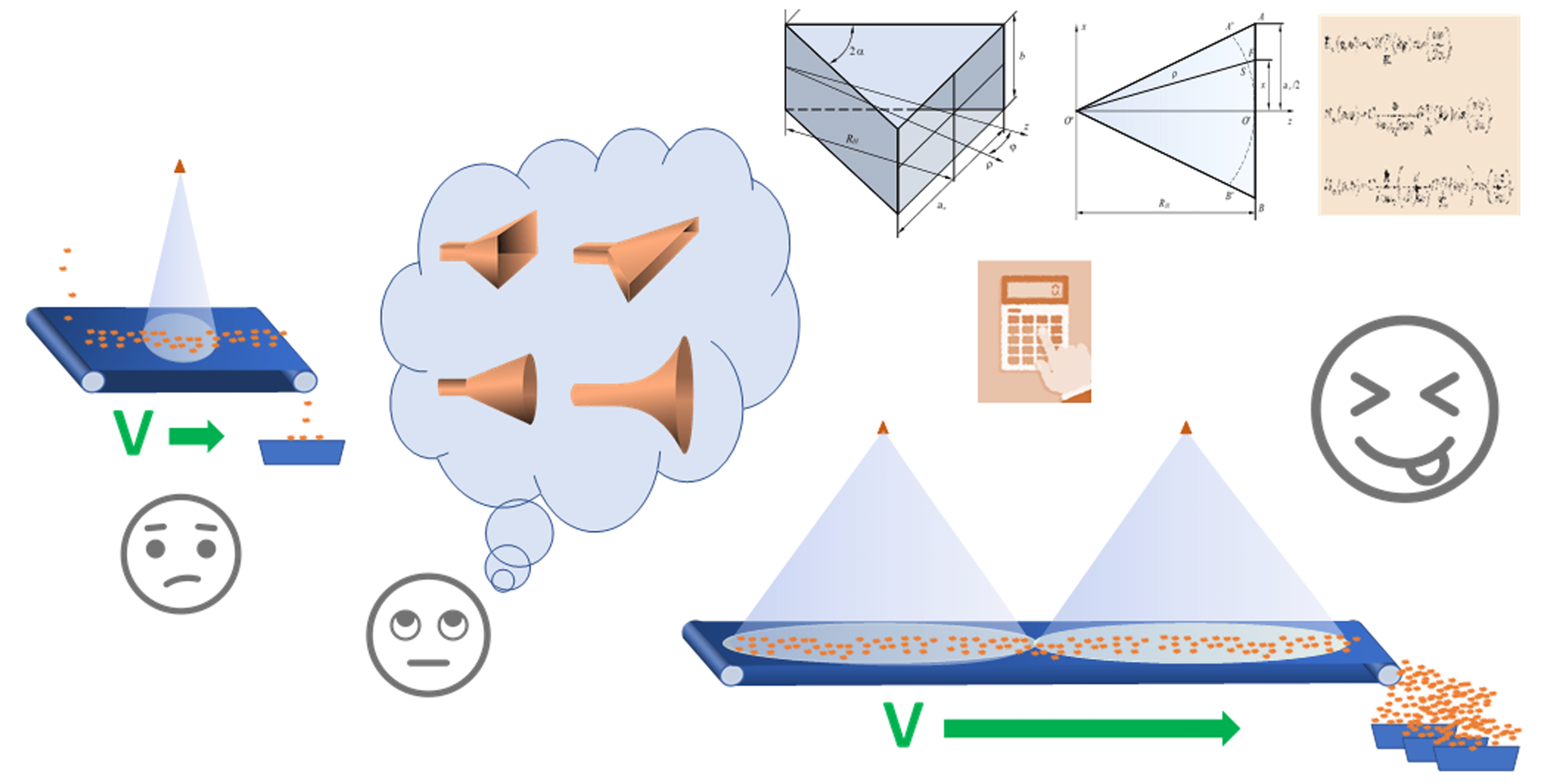
The emitter of electromagnetic energy is presented as one of the main elements of installations for irradiating seeds with an electromagnetic field before sowing. This parameter was investigated by taking into account the values of the biotropic parameters of the low-energy electromagnetic field under the conditions of flow processing.
This paper reports a study into the parameters of the H-sector horn emitter for irradiation of sugar beet seeds with a low-energy electromagnetic field at a frequency of 73...75 GHz in continuous flow. Thus, one should use the H-sectoral horn emitter with the following parameters: aperture width aa=20 mm; horn length RH=35 mm; b=1.8 mm. It is determined that in order to irradiate sugar beet seeds on the conveyor plane with a power flow density of P=100 μW/cm2, it is necessary to place two horns 1200 mm above the conveyor at a distance of 2540 mm from each other. It was checked that the treatment of sugar beet seeds with electromagnetic radiation in a continuous flow with a capacity of 300 kg/h is possible with a power of up to 2 W supplied to two horn antennas; the speed of the conveyor is 15 cm/s.
The parameters of the sectoral horn for an elliptical directional diagram were studied by dividing the main task into internal and external.
According to the results of the research, it is possible to build a base of geometric presets for adjusting installations for different types of seeds, the desired performance, the structural features of installations, as well as existing emitters
References
- Huyghe, C., Desprez, B., Laudinat, V. (2020). Sugar beet. Quae. doi: https://doi.org/10.35690/978-2-7592-3185-0
- Hruzynska, I., Smahina, A., Airapetov, M., Zhyhadlo, V. (2018). Zelena knyha "Rehuliuvannia rynku tsukru". Ofis efektyvnoho rehuliuvannia. Available at: https://issuu.com/office_brdo/docs/_______________________?utm_medium=referral&utm_source=regulation.gov.ua
- Abbott, G. C. (2020). Sugar. Routledge, 414. doi: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003292203
- Fyliuk, G., Sytenko, D. (2014). Causes of crisis situation in Ukraine sugar industry enterprises and their solutions. Bulletin of Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv. Economics, 158, 6–11. Available at: http://bulletin-econom.univ.kiev.ua/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/158_6-11.pdf
- Smit, A. B., Jongeneel, R. A., Prins, H., Jager, J. H., Hennen, W. H. G. J. (2017). Impact of coupled EU support for sugar beet growing: more production, lower prices. Wageningen Economic Research. doi: https://doi.org/10.18174/430039
- Mitchell, D. (2004). Sugar Policies: Opportunity for Change. Washington.
- Kosulina, N. G., Cherenkov, A. D. (2008). Low-energy electromagnetic technologies are in plantgrower. Svitlotekhnika ta elektroenerhetyka, 4, 80–85. Available at: http://eprints.kname.edu.ua/8430/1/80-85.pdf
- Chernaya, M. A., Kosulina, N. G., Avrunin, O. G. (2013). Analiz problem predposevnoy obrabotki semyan na osnove elektromagnitnykh tekhnologiy. Visnyk Kharkivskoho natsionalnoho tekhnichnoho universytetu silskoho hospodarstva im. Petra Vasylenka, 141, 93–94.
- Tanaś, J., Cherenkov, A. D., Kosulina, N. G., Yaroslavskyy, Y. I., Titova, N. V., Aizhanova, A. (2018). Justification of the electromagnetic impulse method destruction of insect pests in gardens. Photonics Applications in Astronomy, Communications, Industry, and High-Energy Physics Experiments 2018. doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2501665
- Mуkhaylova, L., Ryd, A., Potapski, P., Kosulina, N., Cherenkov, A. (2018). Determining the electromagnetic field parameters to kill flies at livestock facilities. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (5 (94)), 53–60. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2018.137600
- Kosulina, N., Kosulin, S. (2022). Determination of biotropic parameters of a pulsed electric field for increasing i mmunoglobulins in cow coloster. Sciences of Europe, 103, 90–93.
- Kosulina, N., Kosulin, S. (2022). Аpplication of low-energy radio-wave emissions in medicine and animal husbandry. The scientific heritage, 99, 22–25. Available at: https://ru.calameo.com/read/00505976992f912ada90e
- Uğurlu, B. T. (2022). On the wave nature of particles. Physics Essays, 35 (2), 171–174. doi: https://doi.org/10.4006/0836-1398-35.2.171
- Rossing, T. D., Chiaverina, C. J. (2019). The Wave Nature of Light. Light Science, 25–49. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27103-9_2
- Kuchin, L. F., Cherenkov, A. D., Kosulina, N. G. (2002). Znachenie strukturnoy organizatsii bioobektov pri vzaimodeystvii s nizkoenergeticheskimi polyarizovannymi elektromagnitnymi polyami. Pratsi. Tavriyska derzhavna ahrotekhnichna akademiya, 6, 26–29.
- Kosulina, N. H. (2003). Vykorystannia mikrokhvylovykh tekhnolohiy u silskomu hospodarstvi. Pratsi. Tavriyska derzhavna ahrotekhnichna akademiya, 15, 141–148.
- Cherenkov, A. D., Kosulina, N. G. (2005). Primenenie informatsionnykh elektromagnitnykh poley v tekhnologicheskikh protsessakh sel'skogo khozyaystva. Svitlotekhnika ta elektroenerhetyka, 5, 77–80.
- Kosulina, N. H., Cherenkov, O. D. (2005). Doslidzhennia vplyvu elektromahnitnoho polia na nasinnia soi. Visnyk Kharkivskoho derzhavnoho tekhnichnoho universytetu silskoho hospodarstva, 37 (1), 152–160.
- Kosulina, N. G. (2006). Opredelenie diapazona izmeneniy parametrov elektromagnitnogo polya, vozdeystvuyuschikh na semena soi. Tavriyska derzhavna ahrotekhnichna akademiya. Pratsi, 35, 102–105.
- Popriadukhin, V., Popova, I., Kosulina, N., Cherenkov, A., Chorna, M. (2017). Analysis of the electromagnetic field of multilayered biological objects for their irradiation in a waveguide system. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (5 (90)), 58–65. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.118159
- Konstantinov, I. S., Mamatov, A. V., Sapryka, V. A., Sapryka, A. V., Kosulina, N. G. (2015). Theoretical analysis of electromagnetic field electric tension distribution in the seeds of cereals. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences, 6 (6), 1686–1694.
- Olenyuk, A. A. (2013). Calculation of EMF resonance frequency for presowing processing of sugar beet seeds. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (9 (61)), 13–16. Available at: http://journals.uran.ua/eejet/article/view/9494
- Olenyuk, A. A. (2012). Opredelenie rezonansnoy chastoty EMP dlya vozdeystviya na semena sfericheskoy formy. Visnyk natsionalnoho tekhnichnoho universytetu «KhPI», 66 (972), 173–177.
- Cherenkov, A. D., Kosulina, N. G., Sereda, A. I. (2004). Analiz rozpodilu elektromahnitnoho polia formovanoho antennymy prystroiamy dlia vplyvu na biolohichni obiekty. Visnyk Kharkivskoho derzhavnoho tekhnichnoho universytetu silskoho hospodarstva, 27 (1), 238–245.
- Josefsson, L., Rengarajan, S. (Eds.) (2018). Slotted waveguide array antennas: theory, analysis and design. The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 400.
- Yang, F., Rahmat-Samii, Y. (2008). Surface wave antennas. Electromagnetic Band Gap Structures in Antenna Engineering, 203–237. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511754531.008
- Kobayashi, H. (2020). Horn Antenna. Analyzing the Physics of Radio Telescopes and Radio Astronomy, 144–177. doi: https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-2381-0.ch008
- Kosulina, N. G., Korshunov, K. S. (2021). Calculation of a specialized antenna for biological research. Engineering of nature management, 22, 99–103. Available at: https://repo.btu.kharkov.ua/bitstream/123456789/1211/1/16.pdf
- Volakis, J. L. (2019). Antenna engineering handbook. McGraw Hill, 1424.
- Waterhouse, R. B. (2005). Traveling Wave Antennas. Encyclopedia of RF and Microwave Engineering. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/0471654507.eme466
- Chand, R. K., Raghavendra, M. V., Sathyavathi, K. (2013). Radiation Analysis and Design of Pyramidal Horn Antenna. International Journal Of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), 2 (10). Available at: https://www.ijert.org/research/radiation-analysis-and-design-of-pyramidal-horn-antenna-IJERTV2IS100033.pdf
- Hirokawa, J., Zhang, M. (2015). Waveguide Slot Array Antennas. Handbook of Antenna Technologies, 1–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-4560-75-7_51-1
- Balanis, C. A. (2016). Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design. Hoboken. John Wiley and Sons, 1104.
- Kildal, P.-S. (2015). Foundations of antenna engineering: a unified approach for line-of-sight and multipath. Artech.
- Olver, A. D. (1992). Microwave and Optical Transmission. Wiley, 400.
- Kong, J. A. (1994). Electromagnetic Wave Theory. Wiley.
- Towne, D. H. (1998). Wave Phenomena. Dover Publications.
- Elmore, W. C., Heald, M. A. (1995). Physics of Waves. Dover Publications.
- Wieglhofer, W. S., Lakhtakia, A. (Eds.) (2003). Introduction to Complex Mediums for Optics and Electromagnetics. SPIE. doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/3.504610
- Yanke, E. (1994). Spetsial'nye funktsii (Formuly, grafiki, tablitsy). Kyiv: Naukova dumka, 344.
- Dass, H. K. (2007). Advanced Engineering Mathematics. S Chand & Co Ltd, 1136.
- Godon Webster, A. (2016). Partial Differential Equations of Mathematical Physics. Dover Publications, 464.
- Riley, K. F., Hobson, M., P. Bence, S. J. (2012). Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering. Cambridge University Press, 1333. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9781139164979
- Freeden, W., Gutting, M. (2013). Special Functions of Mathematical (Geo-)Physics. Springer, 501. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-0563-6
- Kalinin, L. H., Moiseev, V. F., Malinovskyi, V. V. (2006). Pat. No. 19550 UA. Microwave device for presowing seed treatment. No. u200607446; declareted: 04.07.2006; published: 15.12.2006. Available at: https://uapatents.com/2-19550-mikrokhvilovijj-pristrijj-peredposivno-obrobki-nasinnya.html
- Dziuba, V. P., Kalinin, L. H., Tuchnyi, V. P., Tokovenko, O. M. (2003). Pat. No. 53954 UA. Microwave device for presowing seed treatment. No. 2002032451; declareted: 28.03.2002; published: 17.02.2003. Available at: https://uapatents.com/2-53954-mikrokhvilovijj-pristrijj-doposivno-obrobki-nasinnya.html
- Sydoruk, Y. K. (2011). Pat. No. 65629 UA. Microwave device for presowing seed treatment, drying grain and other loose materials. No. u201106351; declareted: 20.05.2011; published: 12.12.2011. Available at: https://uapatents.com/4-65629-mikrokhvilovijj-pristrijj-dlya-peredposivno-obrobki-nasinnya-sushinnya-zerna-ta-inshikh-sipuchikh-materialiv.html
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Natalia Kosulina, Maksym Sorokin, Yuri Handola, Stanislav Kosulin, Kostiantyn Korshunov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








