Developing a model of smart home usage among it specialists: the role of machine learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.265657Keywords:
GCC, Internet of Things, relative advantage, smart home, technology acceptance modelAbstract
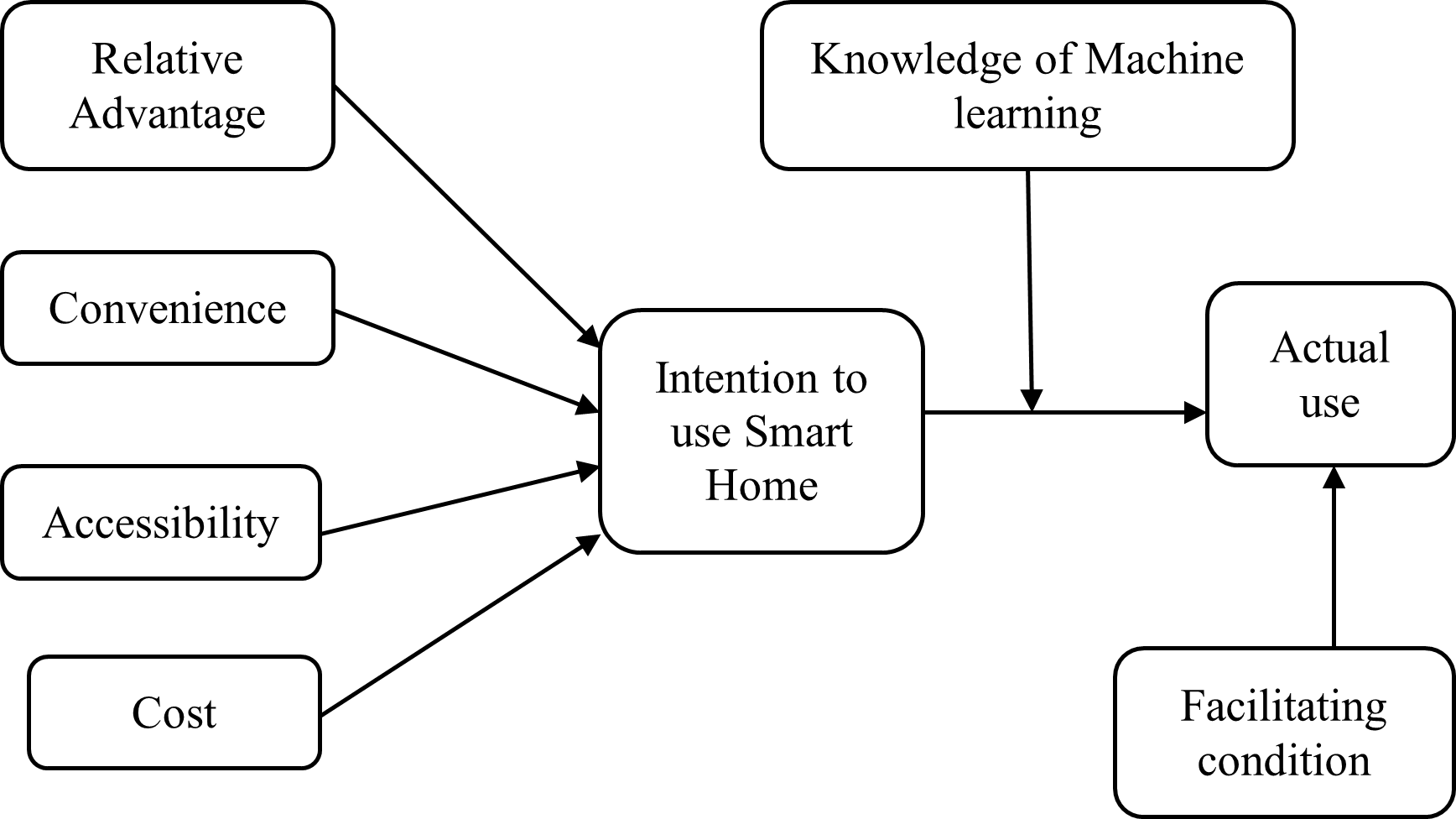
Models of smart home usage dominate in developed countries, while in developing countries, they are still lacking. Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is widely used in the context of smart home, and few studies examined other technology acceptance theories. The purpose of this study is to examine the experience of using smart home by Information Technology (IT) specialists in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). The study deploys existence theories and proposes that the effect of relative advantage, convenience, accessibility, and cost on the intention to use smart home is positive. In addition, it was suggested that intention to use, as well as facilitating condition, directly affects the actual use of smart home. The knowledge of machine learning was proposed as a moderator between intention to use and actual use. The data were collected from IT specialists in the GCC using purposive sampling. The analysis was conducted using the Analysis of moment structures (AMOS). The findings showed that convenience, accessibility, and relative advantage have a positive effect, while cost has a negative effect on the intention to use smart home. The intention to use and facilitating condition affected positively the actual use. Knowledge in machine learning moderated positively the effect of intention to use on actual use. Decision makers are recommended to enhance the benefits of using the Internet of Things smart home and create a customized plan to enable using smart home at all levels. The knowledge of machine learning is critical for smart home usage, and customized courses in this regard are critical to boost the usage of smart home.
References
- Marikyan, D., Papagiannidis, S., Alamanos, E. (2019). A systematic review of the smart home literature: A user perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 138, 139–154. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.08.015
- Sovacool, B. K., Furszyfer Del Rio, D. D. (2020). Smart home technologies in Europe: A critical review of concepts, benefits, risks and policies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 120, 109663. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109663
- Almusaylim, Z. A., Zaman, N. (2018). A review on smart home present state and challenges: linked to context-awareness internet of things (IoT). Wireless Networks, 25 (6), 3193–3204. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1712-5
- Awad, S. R., Sharef, B. T., Salih, A. M., Malallah, F. L. (2022). Deep learning-based iraqi banknotes classification system for blind people. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (2 (115)), 31–38. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.248642
- Liang, T., Zeng, B., Liu, J., Ye, L., Zou, C. (2018). An Unsupervised User Behavior Prediction Algorithm Based on Machine Learning and Neural Network For Smart Home. IEEE Access, 6, 49237–49247. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2868984
- Hargreaves, T., Wilson, C., Hauxwell-Baldwin, R. (2017). Learning to live in a smart home. Building Research & Information, 46 (1), 127–139. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09613218.2017.1286882
- Maleki, M., Manshouri, N., Kayikcioglu, T. (2021). Brain-computer Interface Systems for Smart Homes - A Review Study. Recent Advances in Electrical & Electronic Engineering (Formerly Recent Patents on Electrical & Electronic Engineering), 14 (2), 144–155. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/2352096513999200727175948
- Miandashti, F. J., Izadi, M., Shirehjini, A. A. N., Shirmohammadi, S. (2020). An Empirical Approach to Modeling User-System Interaction Conflicts in Smart Homes. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 50 (6), 573–583. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/thms.2020.3017784
- Ousghir, S., Daoud, M. (2022). Exploratory study on innovation management in startups, an attempt to design it through the business model. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (13 (115)), 20–26. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.251845
- Marufuzzaman, M., Tumbraegel, T., Rahman, L. F., Sidek, L. M. (2021). A machine learning approach to predict the activity of smart home inhabitant. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments, 13 (4), 271–283. doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/ais-210604
- Machorro-Cano, I., Alor-Hernández, G., Paredes-Valverde, M. A., Rodríguez-Mazahua, L., Sánchez-Cervantes, J. L., Olmedo-Aguirre, J. O. (2020). HEMS-IoT: A Big Data and Machine Learning-Based Smart Home System for Energy Saving. Energies, 13 (5), 1097. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en13051097
- Babichenko, A., Kravchenko, Y., Babichenko, J., Lysachenko, I., Krasnikov, I., Velma, V. (2022). Design of an intelligent system to control the technological system of ammonia production secondary condensation. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (2 (115)), 105–115. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.252383
- Khudov, H., Makoveichuk, O., Misiuk, D., Pievtsov, H., Khizhnyak, I., Solomonenko, Y. et. al. (2022). Devising a method for processing the image of a vehicle’s license plate when shooting with a smartphone camera. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (2 (115)), 6–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.252310
- Galchonkov, O., Nevrev, A., Shevchuk, B., Baranov, N. (2022). Determination of the influence of the choice of the pruning procedure parameters on the learning quality of a multilayer perceptron. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (9 (115)), 75–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.253103
- Dong, X., Chang, Y., Wang, Y., Yan, J. (2017). Understanding usage of Internet of Things (IOT) systems in China. Information Technology & People, 30 (1), 117–138. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/itp-11-2015-0272
- Park, E., Cho, Y., Han, J., Kwon, S. J. (2017). Comprehensive Approaches to User Acceptance of Internet of Things in a Smart Home Environment. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4 (6), 2342–2350. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2017.2750765
- Mital, M., Chang, V., Choudhary, P., Papa, A., Pani, A. K. (2018). Adoption of Internet of Things in India: A test of competing models using a structured equation modeling approach. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 136, 339–346. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.03.001
- de Boer, P. S., van Deursen, A. J. A. M., van Rompay, T. J. L. (2019). Accepting the Internet-of-Things in our homes: The role of user skills. Telematics and Informatics, 36, 147–156. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2018.12.004
- Nakashydze, L., Gil’orme, T. (2015). Energy security assessment when introducing renewable energy technologies. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (8 (76)), 54–59. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2015.46577
- Pronoza, P., Kuzenko, T., Sablina, N. (2022). Implementation of strategic tools in the process of financial security management of industrial enterprises in Ukraine. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (13 (116)), 15–23. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.254234
- Poltorak, A., Khrystenko, O., Sukhorukova, A., Moroz, T., Sharin, O. (2022). Development of an integrated approach to assessing the impact of innovative development on the level of financial security of households. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (13 (115)), 103–112. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.253062
- Shachak, A., Kuziemsky, C., Petersen, C. (2019). Beyond TAM and UTAUT: Future directions for HIT implementation research. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 100, 103315. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103315
- Hong, A., Nam, C., Kim, S. (2020). What will be the possible barriers to consumers’ adoption of smart home services? Telecommunications Policy, 44 (2), 101867. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2019.101867
- Arthanat, S., Chang, H., Wilcox, J. (2020). Determinants of information communication and smart home automation technology adoption for aging-in-place. Journal of Enabling Technologies, 14 (2), 73–86. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/jet-11-2019-0050
- Balta-Ozkan, N., Davidson, R., Bicket, M., Whitmarsh, L. (2013). Social barriers to the adoption of smart homes. Energy Policy, 63, 363–374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.08.043
- Pal, D., Funilkul, S., Charoenkitkarn, N., Kanthamanon, P. (2018). Internet-of-Things and Smart Homes for Elderly Healthcare: An End User Perspective. IEEE Access, 6, 10483–10496. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2808472
- Cvitić, I., Peraković, D., Periša, M., Gupta, B. (2021). Ensemble machine learning approach for classification of IoT devices in smart home. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 12 (11), 3179–3202. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01241-0
- Lytvyn, V., Vysotska, V., Demchuk, A., Demkiv, I., Ukhanska, O., Hladun, V. et. al. (2019). Design of the architecture of an intelligent system for distributing commercial content in the internet space based on SEO-technologies, neural networks, and Machine Learning. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (2 (98)), 15–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.164441
- Tsoy, A., Titlov, O., Granovskiy, A., Koretskiy, D., Vorobyova, O., Tsoy, D., Jamasheva, R. (2022). Improvement of refrigerating machine energy efficiency through radiative removal of condensation heat. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (8 (115)), 35–45. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.251834
- Huang, H., Yu, H. (2019). Compact and Fast Machine Learning Accelerator for IoT Devices. Springer, 149. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3323-1
- Aliiev, E., Paliy, A., Kis, V., Paliy, A., Petrov, R., Plyuta, L. et. al. (2022). Establishing the influence of technical and technological parameters of milking equipment on the efficiency of machine milking. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (1 (115)), 44–55. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.251172
- Nykyforov, А., Antoshchenkov, R., Halych, I., Kis, V., Polyansky, P., Koshulko, V. et. al. (2022). Construction of a regression model for assessing the efficiency of separation of lightweight seeds on vibratory machines involving measures to reduce the harmful influence of the aerodynamic factor. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (1 (116)), 24–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.253657
- Zahorulko, A., Zagorulko, A., Kasabova, K., Liashenko, B., Postadzhiev, A., Sashnova, M. (2022). Improving a tempering machine for confectionery masses. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (11 (116)), 6–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.254873
- Petrakov, Y., Korenkov, V., Myhovych, A. (2022). Technology for programming contour milling on a CNC machine. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (1 (116)), 55–61. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.255389
- Alarifi, A., Tolba, A. (2019). Optimizing the network energy of cloud assisted internet of things by using the adaptive neural learning approach in wireless sensor networks. Computers in Industry, 106, 133–141. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2019.01.004
- Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Quarterly, 13 (3), 319. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
- Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., Davis, F. D. (2003). User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Quarterly, 27 (3), 425. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/30036540
- Shin, D.-H., Jin Park, Y. (2017). Understanding the Internet of Things ecosystem: multi-level analysis of users, society, and ecology. Digital Policy, Regulation and Governance, 19 (1), 77–100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/dprg-07-2016-0035
- Khayer, A., Talukder, Md. S., Bao, Y., Hossain, Md. N. (2020). Cloud computing adoption and its impact on SMEs’ performance for cloud supported operations: A dual-stage analytical approach. Technology in Society, 60, 101225. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.101225
- Sivathanu, B. (2018). Adoption of internet of things (IOT) based wearables for healthcare of older adults – a behavioural reasoning theory (BRT) approach. Journal of Enabling Technologies, 12 (4), 169–185. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/jet-12-2017-0048
- Pinochet, L. H. C., Lopes, E. L., Srulzon, C. H. F., Onusic, L. M. (2018). The influence of the attributes of “Internet of Things” products on functional and emotional experiences of purchase intention. Innovation & Management Review, 15 (3), 303–320. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/inmr-05-2018-0028
- de Oliveira, G. A. A., de Bettio, R. W., Freire, A. P. (2016). Accessibility of the smart home for users with visual disabilities: an evaluation of open source mobile applications for home automation. Proceedings of the 15th Brazilian Symposium on Human Factors in Computing Systems. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3033701.3033730
- Agustina, R., Suprianto, D., Ariyanto, R. (2021). Technology Acceptance Model Analysis of User Behavioral Intentions on IoT Smart Board Devices. 2021 1st Conference on Online Teaching for Mobile Education (OT4ME). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ot4me53559.2021.9638937
- Sivarethinamohan, R., Sujatha, S. (2021). Upskilling and Curating the Potentials of IoT Enabled Smart Cities: Use Cases and Implementation Strategies. Artificial Intelligence in Industrial Applications, 67–78. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85383-9_5
- Al-Momani, A. M., Mahmoud, M. A., Ahmad, M. S. (2018). Factors that Influence the Acceptance of Internet of Things Services by Customers of Telecommunication Companies in Jordan. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing, 30 (4), 51–63. doi: https://doi.org/10.4018/joeuc.2018100104
- Karahoca, A., Karahoca, D., Aksöz, M. (2017). Examining intention to adopt to internet of things in healthcare technology products. Kybernetes, 47 (4), 742–770. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/k-02-2017-0045
- Shuhaiber, A., Mashal, I. (2019). Understanding users’ acceptance of smart homes. Technology in Society, 58, 101110. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.01.003
- Solangi, Z. A., Solangi, Y. A., Aziz, M. S. Abd., Asadullah. (2017). An empirical study of Internet of Things (IoT) – Based healthcare acceptance in Pakistan: PILOT study. 2017 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Social Sciences (ICETSS). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icetss.2017.8324135
- Sohn, K., Kwon, O. (2020). Technology acceptance theories and factors influencing artificial Intelligence-based intelligent products. Telematics and Informatics, 47, 101324. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2019.101324
- Chakraborty, S., Khayer, N., Ahmed, T. (2020). Assessing Critical Factors Affecting the Mass Adoption of IoT in Bangladesh. International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial and Energy Engineering. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/347889988_Assessing_Critical_Factors_Affecting_the_Mass_Adoption_of_IoT_in_Bangladesh
- Roma, P., Monaro, M., Muzi, L., Colasanti, M., Ricci, E., Biondi, S. et. al. (2020). How to Improve Compliance with Protective Health Measures during the COVID-19 Outbreak: Testing a Moderated Mediation Model and Machine Learning Algorithms. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17 (19), 7252. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197252
- Hwang, J., Park, S., Kim, I. (2020). Understanding motivated consumer innovativeness in the context of a robotic restaurant: The moderating role of product knowledge. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 44, 272–282. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.06.003
- Rogers, E. (1995). Diffusion of innovations. Available at: https://web.stanford.edu/class/symbsys205/Diffusion%20of%20Innovations.htm
- Kayali, M., Alaaraj, S. (2020). Adoption of Cloud Based E-learning in Developing Countries: A Combination of DOI, TAM and UTAUT. International Journal of Contemporary Management and Information Technology, 1 (1), 1–7. Available at: https://ijcmit.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Kayali-Alaaraj-2020-1d59ab79.pdf
- Lian, J.-W. (2015). Critical factors for cloud based e-invoice service adoption in Taiwan: An empirical study. International Journal of Information Management, 35 (1), 98–109. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2014.10.005
- Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Babin, B. J., Black, W. C. (2010). Multivariate data analysis: A global perspective. Upper Saddle River (N.J.) : Pearson education, 800.
- Lowry, P. B., Gaskin, J. (2014). Partial Least Squares (PLS) Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) for Building and Testing Behavioral Causal Theory: When to Choose It and How to Use It. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication, 57 (2), 123–146. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tpc.2014.2312452
- Awang, Z. (2014). A Handbook on Structural Equation Modeling for Academicians and Practitioner. Bandar Baru Bangi, kuala lumpur, Malaysia: MPWS Rich Resources.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Baraa Sharef

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








