Obtaining and investigation of the chemical composition of powdered malt and polymalt extracts for application in the production of non-alcoholic functional beverages
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.265762Keywords:
buckwheat, peas, barley, corn, non-alcoholic beverages, malt, polymalt, extract, powder, glutenAbstract
The group of consumer goods used in regular and daily nutrition, as well as the group of products that have a positive effect on the physiological functions of the body and have a certain chemical composition, should include processed beverages.
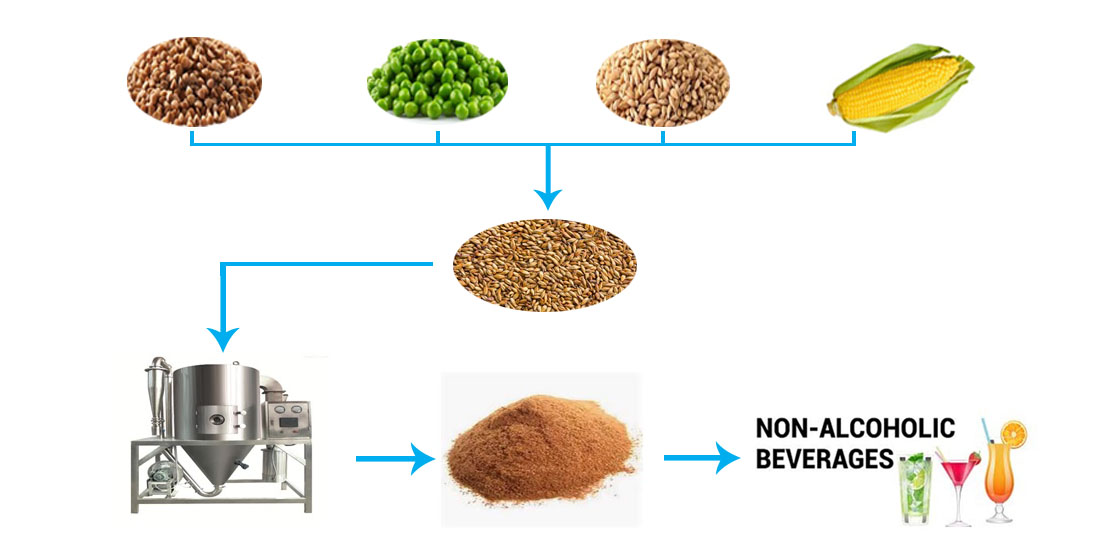
It is extremely important to expand the use of malt extracts in the creation of new non-alcoholic beverages, including functional ones. These extracts must come from sources other than typical malt forms, such as food grains and legumes (horse beans, buckwheat, peas, etc.). Buckwheat is a promising raw material for the production of beverages, especially without barley, wheat and rye gluten. To find the optimal parameters of primary mechanical, heat and moisture exchange processes by computer tests, it is required to develop a physical and mathematical method for grinding malt and mixed malt extracts. The aim of the study is to evaluate new malt extracts used in non-alcoholic beverages.
Beverages made from powdered malt and polymalt do not increase the intake of vitamins (B4) and minerals (potassium, calcium and magnesium) in the body, do not cure the deficiency of the nutrient dextrin. They have also not been shown to have a positive effect on physiological processes. The answer to this question lies in increasing the nutritional value of beverages by eliminating gluten, which has a negative effect on some physiological processes in the body. The studied powdered malt and polymalt extracts for functional beverages were evaluated theoretically and practically. The presented results showed that buckwheat extract powder can be used as an ingredient in beverages, as an independent product, and also as a product recommended for people with gluten intolerance
References
- Stanisavljevic, D. M., Dordevic, S. M., Milenkovic, M. T., Zlatkovic, B. P., Nikolova, M. T., Velickovic, D. T. (2019). Wild mint (Mentha longifolia) extracts in the production of non-alcoholic beverages. Progress in Nutrition, 21 (1), 202–209. Available at: https://mattioli1885journals.com/index.php/progressinnutrition/article/view/7256
- Basinskiene, L., Cizeikiene, D. (2020). Cereal-Based Nonalcoholic Beverages. Trends in Non-Alcoholic Beverages, 63–99. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-816938-4.00003-3
- Srikaeo, K. (2020). Biotechnological Tools in the Production of Functional Cereal-Based Beverages. Biotechnological Progress and Beverage Consumption, 149–193. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-816678-9.00005-9
- Xiong, Y., Zhang, P., Warner, R. D., Shen, S., Fang, Z. (2020). Cereal grain-based functional beverages: from cereal grain bioactive phytochemicals to beverage processing technologies, health benefits and product features. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 62 (9), 2404–2431. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1853037
- Gurbanov, N. H., Gadimova, N. S., Gurbanova, R. I., Akhundova, N. A., Babashli, A. A. (2020). Substantiation and development of technology for a new assortment of combined sour-milk drinks based on bio modified bean raw materials. Food Science and Technology, 40 (2), 517–522. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.04219
- Serikbaeva, A., Tnymbaeva, B., Mardar, M., Tkachenko, N., Ibraimova, S., Uazhanova, R. (2021). Determining optimal process parameters for sprouting buckwheat as a base for a food seasoning of improved quality. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (11 (112)), 6–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.237369
- Peñaranda, J. D., Bueno, M., Álvarez, F., Pérez, P. D., Perezábad, L. (2021). Sprouted grains in product development. Case studies of sprouted wheat for baking flours and fermented beverages. International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, 25, 100375. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgfs.2021.100375
- Novikova, I. V., Korotkikh, E. A., Korostelev, A. V., Agafonov, G. V., Penkina, A. A. (2017). The study of powdered extracts from grain raw materials by using the X-ray crystallography. Proceedings of the Voronezh State University of Engineering Technologies, 79 (2), 143–147. doi: https://doi.org/10.20914/2310-1202-2017-2-143-147
- Jnawali, P., Kumar, V., Tanwar, B. (2016). Celiac disease: Overview and considerations for development of gluten-free foods. Food Science and Human Wellness, 5 (4), 169–176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2016.09.003
- Dulka, O. S., Prybylskiy, V. L., Kuts, A. M., Oliinyk, S. I., Dong, N. P., Vitriak, O. P. (2020). The use of rice in the technology of gluten-free fermented non-alcoholic beverages. Food Science and Technology, 14 (4). doi: https://doi.org/10.15673/fst.v14i4.1892
- Koehler, P., Wieser, H., Konitzer, K. (2014). Gluten-Free Products. Celiac Disease and Gluten, 173–223. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-420220-7.00004-3
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Natavan Gadimova, Hasil Fataliyev, Zulfiyya Allahverdiyeva, Teymur Musayev, Nazilya Akhundova, Aynur Babashli

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








