Anomaly detection in internet of medical things with artificial intillegence
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.274575Keywords:
anomaly detection, outlier score, anomaly score, fuzzy logic, hybrid systemAbstract
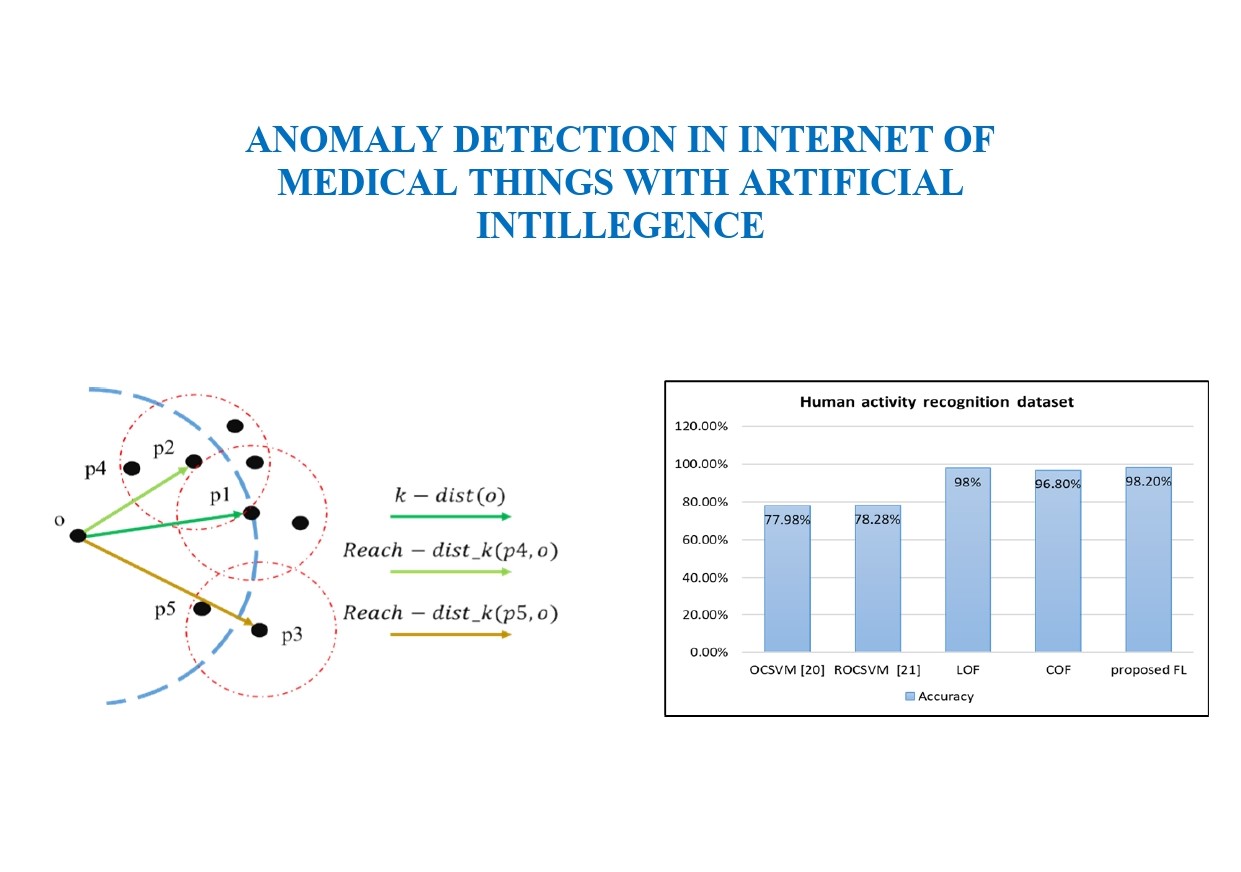
Internet of things (IoT) becomes the most popular term in the recent advances in Healthcare devices. The healthcare data in the IoT process and structure is very sensitive and critical in terms of healthy and technical considerations. Outlier detection approaches are considered as principal tool or stage of any IoT system and are mainly categorized in statistical and probabilistic, clustering and classification-based outlier detection. Recently, fuzzy logic (FL) system is used in ensemble and cascade systems with other ML-based tools to enhance outlier detection performance but its limitation involves the false detection of outliers. In this paper, we propose a fuzzy logic system that uses the anomaly score of each point using local outlier factor (LOF), connectivity-based outlier factor (COF) and generalized LOF to eliminate the confusion in classifying points as outliers or inliers. Regarding human activity recognition (HAR) dataset, the FL achieved a value of 98.2 %. Compared to the performance of LOF, COF, and GLOF individually, the accuracy increased slightly, but the increase in precision and recall indicates an increase in correctly classified data and that neither true nor abnormal data is classified wrongly. The results show the increase in precision and recall which indicates an increase in correctly classified data. Thus, it can be confirmed that fuzzy logic with input of scores achieved the desired goal in terms of mitigating cases of false detection of anomalous data. By comparing the proposed ensemble of fuzzy logic and different types of local density scores in this study, the outcomes of fuzzy logic presents a new way of elaborating or fusing the different tools of the same purpose to enhance detection performance
References
- Alsaydia, O. M., Saadallah, N. R., Malallah, F. L., AL-Adwany, M. A. S. (2021). Limiting COVID-19 infection by automatic remote face mask monitoring and detection using deep learning with IoT. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (2 (113)), 29–36. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.238359
- Kadhim, K. T., Alsahlany, A. M., Wadi, S. M., Kadhum, H. T. (2020). An Overview of Patient’s Health Status Monitoring System Based on Internet of Things (IoT). Wireless Personal Communications, 114 (3), 2235–2262. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07474-0
- Samara, M. A., Bennis, I., Abouaissa, A., Lorenz, P. (2022). A Survey of Outlier Detection Techniques in IoT: Review and Classification. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 11 (1), 4. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan11010004
- Alghushairy, O., Alsini, R., Soule, T., Ma, X. (2020). A Review of Local Outlier Factor Algorithms for Outlier Detection in Big Data Streams. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 5 (1), 1. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc5010001
- Bzai, J., Alam, F., Dhafer, A., Bojović, M., Altowaijri, S. M., Niazi, I. K., Mehmood, R. (2022). Machine Learning-Enabled Internet of Things (IoT): Data, Applications, and Industry Perspective. Electronics, 11 (17), 2676. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172676
- Razzak, I., Zafar, K., Imran, M., Xu, G. (2020). Randomized nonlinear one-class support vector machines with bounded loss function to detect of outliers for large scale IoT data. Future Generation Computer Systems, 112, 715–723. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.05.045
- Vani, K., Neeralagi, R. R. (2017). IoT based health monitoring using fuzzy logic. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Research, 13 (10), 2419–2429. Available at: https://www.ripublication.com/ijcir17/ijcirv13n10_11.pdf
- Bharathy, A. V., Basha, A. M. (2016). A hybrid intrusion detection system cascading support vector machine and fuzzy logic. World Applied Sciences Journal, 35 (1), 104–109.
- Cateni, S., Colla, V., Vannucci, M. (2009). A fuzzy system for combining different outliers detection methods. 9th IASTED International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Applications AIA 2009. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235351913_A_Fuzzy_System_for_Combining_Different_Outliers_Detection_Methods
- Tan, F. H. S., Park, J. R., Jung, K., Lee, J. S., Kang, D.-K. (2020). Cascade of One Class Classifiers for Water Level Anomaly Detection. Electronics, 9 (6), 1012. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9061012
- Muniyandi, A. P., Rajeswari, R., Rajaram, R. (2012). Network Anomaly Detection by Cascading K-Means Clustering and C4.5 Decision Tree algorithm. Procedia Engineering, 30, 174–182. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.01.849
- Breunig, M. M., Kriegel, H.-P., Ng, R. T., Sander, J. (2000). LOF. ACM SIGMOD Record, 29 (2), 93–104. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/335191.335388
- Alshawabkeh, M., Jang, B., Kaeli, D. (2010). Accelerating the local outlier factor algorithm on a GPU for intrusion detection systems. Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on General-Purpose Computation on Graphics Processing Units. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/1735688.1735707
- Wang, Y., Li, K., Gan, S. (2018). A Kernel Connectivity-based Outlier Factor Algorithm for Rare Data Detection in a Baking Process. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 51 (18), 297–302. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.09.316
- Anguita, D., Ghio, A., Oneto, L., Parra, X., Reyes-Ortiz, J. L. (2013). A public domain dataset for human activity recognition using smartphones. In Proceedings of the 21th international European symposium on artificial neural networks, computational intelligence and machine learning. Bruges. Available at: https://web.archive.org/web/20210506171341id_/https://www.elen.ucl.ac.be/Proceedings/esann/esannpdf/es2013-84.pdf
- Reiss, A., Stricker, D. (2012). Introducing a New Benchmarked Dataset for Activity Monitoring. 2012 16th International Symposium on Wearable Computers. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iswc.2012.13
- Pokrajac, D., Reljin, N., Pejcic, N., Lazarevic, A. (2008). Incremental Connectivity-Based Outlier Factor Algorithm. Electronic Workshops in Computing. doi: https://doi.org/10.14236/ewic/vocs2008.18
- Jiang, S.-Y., Li, Q.-H., Li, K.-L., Wang, H., Meng, Z.-L. (2003). GLOF: a new approach for mining local outlier. Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No.03EX693). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icmlc.2003.1264462
- Fuzzy Logic Toolbox. The MathWorks. Available at: https://www.mathworks.com/products/fuzzy-logic.html
- Li, K.-L., Huang, H.-K., Tian, S.-F., Xu, W. (2003). Improving one-class SVM for anomaly detection. Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No.03EX693). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/icmlc.2003.1260106
- Xiao, Y., Wang, H., Xu, W. (2017). Ramp Loss based robust one-class SVM. Pattern Recognition Letters, 85, 15–20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2016.11.016
- Anderez, D. O., Lotfi, A., Pourabdollah, A. (2020). Eating and drinking gesture spotting and recognition using a novel adaptive segmentation technique and a gesture discrepancy measure. Expert Systems with Applications, 140, 112888. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112888
- Yahaya, S. W., Lotfi, A., Mahmud, M. (2019). A Consensus Novelty Detection Ensemble Approach for Anomaly Detection in Activities of Daily Living. Applied Soft Computing, 83, 105613. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105613
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Shalau Farhad Hussein, Zena Ez. Dallalbashi, Ahmed Burhan Mohammed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








