Improving empirical models of complex technological objects under conditions of uncertainty
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.276586Keywords:
empirical model, membership function, function approximation, fuzzy numbers, genetic algorithmAbstract
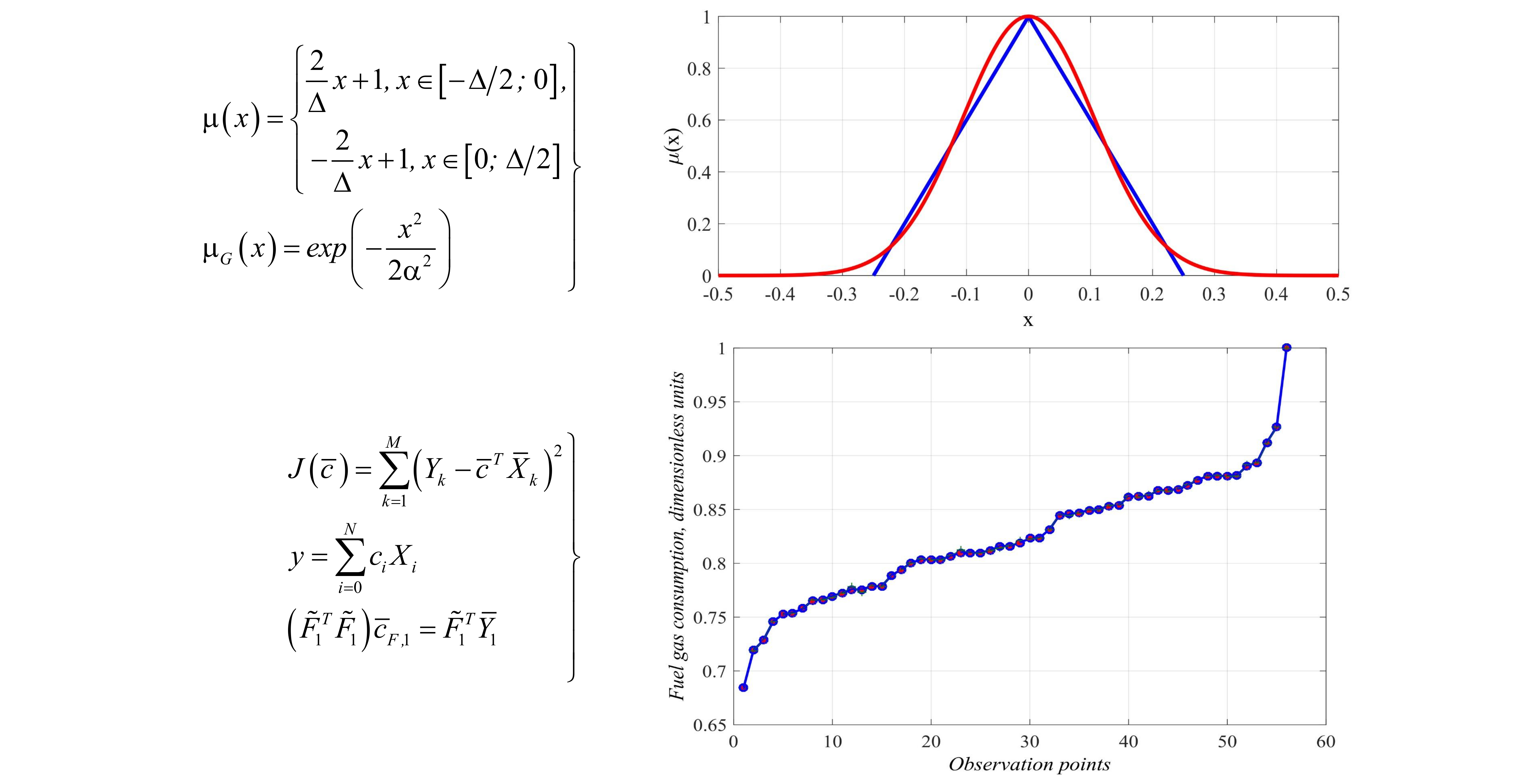
This paper proposes a method for improving empirical models of complex technological objects with insufficient information about the input and output values of an object's parameters. It has been established that most methods for constructing empirical models require knowledge of the statistical characteristics of the input and output values of an object. When modeling complex non-reproducible stochastic processes that evolve over time, information about the parameters and structure of an object is usually not available. A method has been proposed where input and output values are treated as fuzzy quantities with a triangular membership function. Since at some points in the region, the triangular membership function is undifferentiated, it is inconvenient to use it in its typical form to solve the problem of optimal control. Therefore, it is proposed to approximate it with the Gaussian membership function. It is shown that such an approximation is reduced to finding one parameter, which is determined by the least squares method. Its value practically does not depend on the magnitude of the uncertainty interval while the value characterizing the accuracy of approximation is a monotonously increasing function that has a linear character. This makes it possible to define the main operations on fuzzy numbers and derive an empirical model for the case of a polynomial "base" model. The resulting model is linear in its parameters, so a genetic algorithm can be used to find them. It is shown that genetic algorithms can be used in the construction of empirical polynomial models when input parameters are interpreted as fuzzy numbers.
Thus, it can be argued that when constructing an empirical model of an object that is affected by external disturbances that cannot be measured, it is advisable to approximate all input quantities with a triangular Gaussian membership function
References
- Syniehlazov, V. M., Silvestrov, A. M. (2015). Teoriya identyfikatsiyi. Kyiv: NAU, 471.
- Bidiuk, P. I., Kalinina, I. O., Hozhyi, O. P. (2021). Baiesivskyi analiz danykh. Kherson: Knyzhkove vydavnytstvo FOP Vyshemyrskyi V. S., 208.
- Čížek, P., Sadıkoğlu, S. (2020). Robust nonparametric regression: A review. WIREs Computational Statistics, 12 (3), e1492. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/wics.1492
- Hable, R., Christmann, A. (2011). On qualitative robustness of support vector machines. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 102 (6), 993–1007. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmva.2011.01.009
- Draper, N., Smith, H. (1998). Applied Regression Analysis. Wiley. 2016. 736.
- Chen, F., Chen, Y., Zhou, J., Liu, Y. (2016). Optimizing h value for fuzzy linear regression with asymmetric triangular fuzzy coefficients. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 47, 16–24. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2015.02.011
- Raskin, L., Sira, O., Ivanchykhin, Y. (2017). Models and methods of regression analysis under conditions of fuzzy initial data. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (88), 12–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.107536
- Muzzioli, S., Ruggieri, A., De Baets, B. (2015). A comparison of fuzzy regression methods for the estimation of the implied volatility smile function. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 266, 131–143. doi: doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2014.11.015
- Seraya, O. V., Demin, D. A. (2012). Linear Regression Analysis of a Small Sample of Fuzzy Input Data. Journal of Automation and Information Sciences, 44 (7), 34–48. doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/jautomatinfscien.v44.i7.40
- Domin, D. (2013). Application of artificial orthogonalization in search for optimal control of technological processes under uncertainty. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (9 (65)), 45–53. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2013.18452
- Ivakhnenko, A. G. (1981). Induktivniy metod samoorganizatsii modeley slozhnykh sistem. Kyiv: Naukova dumka, 286.
- Gorbiychuk, M., Medvedchuk, V., Pashkovskyi, B. (2014). The parallelism in the algorithm of the synthesis of models of optimal complexity based on the genetic algorithms. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (2 (70)), 42–48. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2014.26305
- Raskin, L. G., Seraya, O. V., Volovschikov, V. Yu. (2016). Nechetkaya matematika. Kharki: NTU «KhPI», 203.
- Ihnatkin, V. U. et al. (2019). Matematychne zabezpechennia tekhnichnykh zasobiv vymiriuvannia i kontroliu. Dnipro: TOV «Favor LTD», 339.
- Verzhbitskiy, V. M. (2021). Osnovy chislennykh metodov. Moscow-Berlin: Direkt-Media. doi: https://doi.org/10.18720/SPBPU/2/ek21-2
- Yaroshenko, O. I., Hryhorkiv, M. V. (2018). Chyslovi metody. Chernivtsi: Chernivetskyi nats. un-t, 172.
- Dykha, M. V., Moroz, V. S. (2016). Ekonometriya. Kyiv: Tsentr navchalnoi literatury, 206.
- Horbiychuk, M. I., Skripka, O. A., Pashkovskyi, B. V. (2016). Optymalnyi rozpodil kilkosti hazoperekachuvalnykh ahrehativ v umovakh nevyznachenosti pry zadanykh obsiahakh na perekachku pryrodnoho hazu. East European Scientific Journal, 2 (3 (7)), 53–58.
- Gorbiychuk, M., Pashkovskyi, B., Moyseenko, O., Sabat, N. (2017). Solution of the optimization problem on the control over operation of gas pumping units under fuzzy conditions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (2 (89)), 65–71. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.111349
- Dranyshnykov, L. V. (2018). Intelektualni metody v upravlinni. Kamianske: DDTU, 416.
- Gorbiychuk, M. I., Humenyuk, T. V. (2016). Synthesis Method of Empirical Models Optimal by Complexity under Uncertainty Conditions. Journal of Automation and Information Sciences, 48 (9), 64–74. doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/jautomatinfscien.v48.i9.50
- Oliynyk, A. P., Subbotin, S. O., Oliynyk, O. O. (2012). Intelektualnyi analikh danykh. Zaporizhzhia: ZNTU, 277.
- SOU 60.3-30019801-011:2004. Kompresorni stantsiyi. Kontrol teplotekhnichnykh ta ekolohichnykh kharakterystyk hazoperekachuvalnykh ahrehativ. Kyiv: DK Ukrtranshaz, 117.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Mykhail Gorbiychuk, Dmytro Kropyvnytskyi, Vitalia Kropyvnytska

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








