Devising a comprehensive method to manage digital competencies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281933Keywords:
cyber business management, personal data, digital literacy, integrated method, efficiency, competenceAbstract
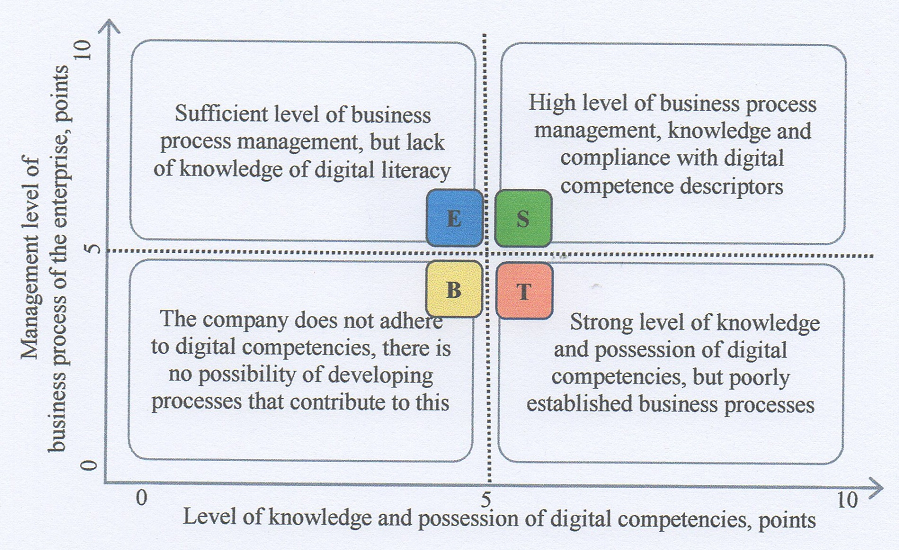
Researching the changes that are taking place in the era of digitalization makes it possible to track the digital footprint of consumers and form new trends and models in business management. The object of this study is the digital literacy of citizens. The vast majority of society cannot imagine their life without online activity, viewing web pages, sites, and social networks. That is why there is an increasing need to expand knowledge of digital literacy. The purpose of this research is the formation of the "BEST" matrix, which makes it possible to determine the level of knowledge and possession of digital competencies of the staff. For diagnosis, 10 criteria were selected, and the specific weight of each of them was calculated, which was summarized in the survey form. Determination of the importance of each factor is carried out by the method of expert assessment, taking into account that the overall coefficient of importance=1 for each group of factors. Achieving maximum efficiency (5‒10 points) will ensure a stay in the "S" segment of the matrix, which indicates a high level of business process management, knowledge and compliance with the descriptors of digital competencies by the staff. This contributes to the solution of the problem of knowledge of the descriptors of digital literacy and makes it possible to improve the efficiency of the enterprise, as well as to repulse cyber attacks in a timely manner. The application of defined digital competencies will allow making optimal decisions in the process of applying digital skills, while ensuring the uniqueness of digital literacy in business management. The results can be used by enterprise managers to analyze and build countermeasures against data leaks or cyber attacks. This will contribute to the establishment of cooperation between enterprises and stakeholders and the formation of consumer trust
References
- Yerina, A., Honchar, I., Zaiets, S. (2021). Statistical Indicators of Cybersecurity Development in the Context of Digital Transformation of Economy and Society. Science and Innovation, 17 (3), 3–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.15407/scine17.03.003
- Yakymova, L., Novotná, A., Kuz, V., Tamándl, L. (2022). Measuring industry digital transformation with a composite indicator: A case study of the utility industry. JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL STUDIES, 15 (1), 168–180. doi: https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-8330.2022/15-1/11
- Biliavska, Y., Mykytenko, N., Romat, Y., Biliavskyi, V. (2023). Category management: Industry vs trade. Scientific Horizons, 26 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.48077/scihor.26(1).2023.129-150
- Mariano, E. B., Ferraz, D., de Oliveira Gobbo, S. C. (2021). The Human Development Index with Multiple Data Envelopment Analysis Approaches: A Comparative Evaluation Using Social Network Analysis. Social Indicators Research, 157 (2), 443–500. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-021-02660-4
- Remeikiene, R., Gaspareniene, L., Fedajev, A., Vebraite, V. (2021). The role of ICT development in boosting economic growth in transition economies. Journal of International Studies, 14 (4), 9–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-8330.2021/14-4/1
- Cioacă, S.-I., Cristache, S.-E., Vuță, M., Marin, E., Vuță, M. (2020). Assessing the Impact of ICT Sector on Sustainable Development in the European Union: An Empirical Analysis Using Panel Data. Sustainability, 12 (2), 592. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020592
- Osiyevskyy, O., Shevchenko, L., Marchenko, O., Umantsiv, Y. (2022). Hybrid Firm: The Future of Organizing for Industry 4.0. Rutgers Business Review, 7 (3), 289–308. Available at: https://rbr.business.rutgers.edu/sites/default/files/documents/rbr-070306.pdf
- Strange, R., Zucchella, A. (2017). Industry 4.0, global value chains and international business. Multinational Business Review, 25 (3), 174–184. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/mbr-05-2017-0028
- Ghauri, P., Strange, R., Cooke, F. L. (2021). Research on international business: The new realities. International Business Review, 30 (2), 101794. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101794
- Chaudhary, S., Gkioulos, V., Katsikas, S. (2022). Developing metrics to assess the effectiveness of cybersecurity awareness program. Journal of Cybersecurity, 8 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/cybsec/tyac006
- Ziniuk, M., Dyeyeva, N., Bogatyrova, K., Melnychenko, S., Fayvishenko, D., Shevchun, M. (2022). Digital transformation of corporate governance. Financial and Credit Activity Problems of Theory and Practice, 5 (46), 300–310. doi: https://doi.org/10.55643/fcaptp.5.46.2022.3807
- Waladali, E., Rabaiah, A. (2022). Impact of e-government maturity on public servants’ job satisfaction. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 20 (3), 501–515. doi: https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.20(3).2022.40
- Ninh Nguyen, H., Dung Tran, M. (2022). Stimuli to adopt e-government services during Covid-19: Evidence from Vietnam. Innovative Marketing, 18 (1), 12–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.21511/im.18(1).2022.02
- Bhargava, A., Bester, M., Bolton, L. (2020). Employees’ Perceptions of the Implementation of Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, and Automation (RAIA) on Job Satisfaction, Job Security, and Employability. Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science, 6 (1), 106–113. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00153-8
- Rachmawati, Aswar, K., Sumardjo, M., Wiguna, M., Hariyani, E. (2022). Personal and reliability factors affecting adoption and utilization of e-government: An effect of intention to use. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 20 (2), 281–290. doi: https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.20(2).2022.23
- Vuorikari, R., Kluzer, S., Punie, Y. (2022). DigComp 2.2: The Digital Competence Framework for Citizens - With new examples of knowledge, skills and attitudes. Publications Office of the European Union. doi: https://doi.org/10.2760/490274
- Hatisaru, V., Falloon, G., Seen, A., Fraser, S., Powling, M., Beswick, K. (2023). Educational leaders’ perceptions of STEM education revealed by their drawings and texts. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 1, 1–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739x.2023.2170290
- Mishra, P., Koehler, M. J. (2006). Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge: A Framework for Teacher Knowledge. Teachers College Record: The Voice of Scholarship in Education, 108 (6), 1017–1054. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9620.2006.00684.x
- Janssen, J., Stoyanov, S., Ferrari, A., Punie, Y., Pannekeet, K., Sloep, P. (2013). Experts’ views on digital competence: Commonalities and differences. Computers & Education, 68, 473–481. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.06.008
- Hope, A., Yemm, N., Nguyen, G., Raza, M. A., Sparke, E., Buhagier,C., Neumann, R. (2022). Digital skills in the Australian and International economies. National Skills Commission. Available at: https://www.nationalskillscommission.gov.au/sites/default/files/2022-03/ABS%20Paper%20-%20Digital%20Skills.pdf
- Derzhavni posluhy onlain. Available at: https://diia.gov.ua/
- Opys ramky tsyfrovoi kompetentnosti dlia hromadian Ukrainy (2021). Available at: https://thedigital.gov.ua/storage/uploads/files/news_post/2021/3/mintsifra-oprilyudnyue-ramku-tsifrovoi-kompetentnosti-dlya-gromadyan/%D0%9E%D0%A0%20%D0%A6%D0%9A.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Yaroslav Shestak, Yuliia Biliavska, Valerii Osetskyi, Nelya Mykytenko, Yurii Umantsiv

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








