Performance evaluation of the cloud computing application for IoT-based public transport systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.285514Keywords:
internet of things, cloud computing, system architecture, public transport systems, scalabilityAbstract
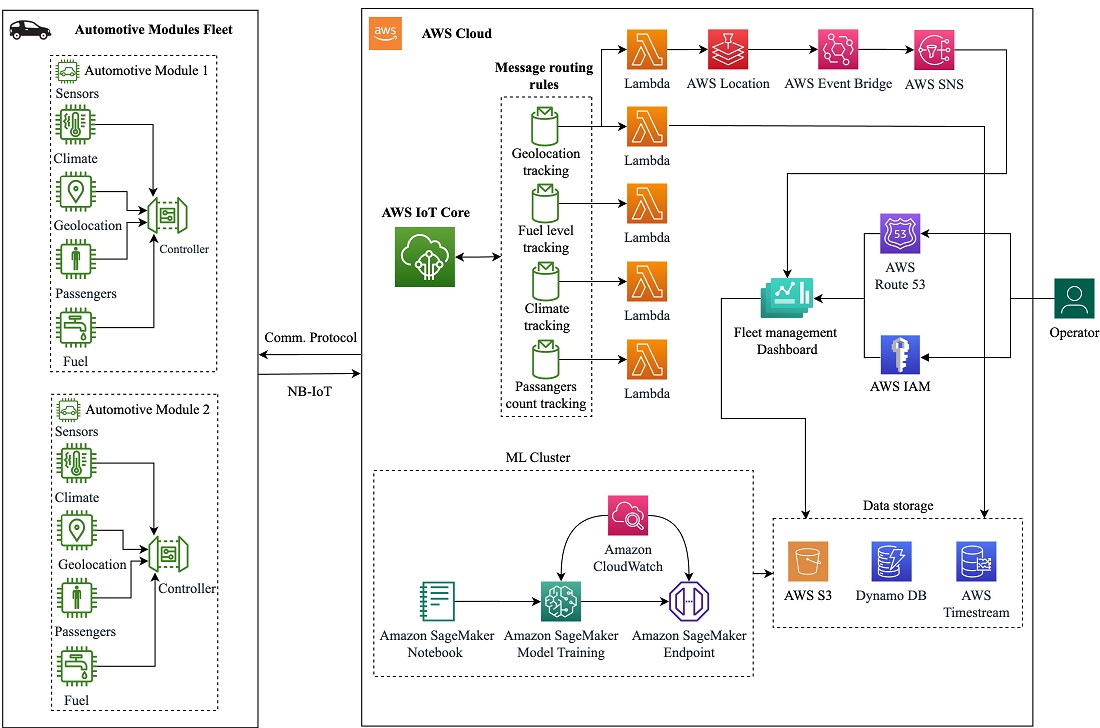
The object of research is cloud computing as an element of the server infrastructure for intelligent public transport systems. Given the increasing complexity and requirements for modern transportation, the application of the Internet of Things concept has a high potential to improve efficiency and passenger comfort. Since the load generated in IoT systems is dynamic and difficult to predict, the use of traditional infrastructure with dedicated servers is suboptimal. This study considers the use of cloud computing as the main server infrastructure for the above systems. The paper investigates the main cloud platforms that can be used to develop such systems and evaluates their advantages and disadvantages. The authors developed the overall architecture of the system and evaluated the performance and scalability of individual components of the server infrastructure. To test the system, a software emulator was developed that simulates the controller module installed in vehicles. Using the developed emulator, stress tests were conducted to analyze and confirm the ability to scale and process input data by the proposed architecture. The test scenarios were developed and conducted on the basis of the existing public transportation system in Kyiv, Ukraine. The experimental results showed that the proposed IoT architecture is able to scale efficiently according to the load generated by the connected devices. It has been found that when the number of incoming messages increases from 40 to 6000, the average message processing time remains unchanged, and the error rate does not increase, which is an indicator of stable system operation. The obtained results can be used in the development of modern public transport systems, as well as for the modernization of existing ones
References
- Future Of Industry Ecosystems: Shared Data And Insights. IDC. Available at: https://blogs.idc.com/2021/01/06/future-of-industry-ecosystems-shared-data-and-insights/
- Mchergui, A., Hajlaoui, R., Moulahi, T., Alabdulatif, A., Lorenz, P. (2023). Steam computing paradigm: Cross‐layer solutions over cloud, fog, and edge computing. IET Wireless Sensor Systems. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/wss2.12051
- Porru, S., Misso, F. E., Pani, F. E., Repetto, C. (2020). Smart mobility and public transport: Opportunities and challenges in rural and urban areas. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 7 (1), 88–97. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtte.2019.10.002
- Farkas, K., Feher, G., Benczur, A., Sidlo, C. (2015). Crowdsending based public transport information service in smart cities. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53 (8), 158–165. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/mcom.2015.7180523
- Vieira, E., Almeida, J., Ferreira, J., Dias, T., Vieira Silva, A., Moura, L. (2023). A Roadside and Cloud-Based Vehicular Communications Framework for the Provision of C-ITS Services. Information, 14 (3), 153. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/info14030153
- Metzger, F., Hobfeld, T., Bauer, A., Kounev, S., Heegaard, P. E. (2019). Modeling of Aggregated IoT Traffic and Its Application to an IoT Cloud. Proceedings of the IEEE, 107 (4), 679–694. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jproc.2019.2901578
- Khan, M. A., Nawaz, T., Khan, U. S., Hamza, A., Rashid, N. (2023). IoT-Based Non-Intrusive Automated Driver Drowsiness Monitoring Framework for Logistics and Public Transport Applications to Enhance Road Safety. IEEE Access, 11, 14385–14397. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3244008
- Hind, M., Noura, O., Sanae, M., Abraham, A. (2023). A Comparative Study for Modeling IoT Security Systems. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, 258–269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35510-3_25
- Ahmad, W., Rasool, A., Javed, A. R., Baker, T., Jalil, Z. (2021). Cyber Security in IoT-Based Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Survey. Electronics, 11 (1), 16. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11010016
- Siwakoti, Y. R., Bhurtel, M., Rawat, D. B., Oest, A., Johnson, R. C. (2023). Advances in IoT Security: Vulnerabilities, Enabled Criminal Services, Attacks, and Countermeasures. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 10 (13), 11224–11239. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2023.3252594
- Zakutynskyi, I., Sibruk, L., Kokarieva, A. (2023). IoT System for Monitoring and Managing Public Transport Data. WSEAS TRANSACTIONS ON SYSTEMS, 22, 242–248. doi: https://doi.org/10.37394/23202.2023.22.25
- Kyivpastrans. Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kyivpastrans
- Availability. Amazon. Available at: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/reliability-pillar/availability.html
- Image "RaspberryPi B3 +". Available at: https://media.distrelec.com/Web/WebShopImages/landscape_large/8-/01/RaspberryPi_B3_plus_30109158-01.jpg
- Image "Teltonika TRM 250". Available at: https://wiki.teltonika-networks.com/images/3/3f/Trm250_hd_1.png
- Data modeling. Amazon. Available at: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/timestream/latest/developerguide/data-modeling.html
- Massaro, A., Selicato, S., Galiano, A. (2020). Predictive Maintenance of Bus Fleet by Intelligent Smart Electronic Board Implementing Artificial Intelligence. IoT, 1 (2), 180–197. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/iot1020012
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ihor Zakutynskyi, Leonid Sibruk, Ihor Rabodzei

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








