Planning trajectories of a manipulation robot with a spherical coordinate system for removing oxide film in the production of commercial lead, zinc
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286463Keywords:
oxide film, manipulation robot, trajectory planning, program trajectory, quadratic interpolationAbstract
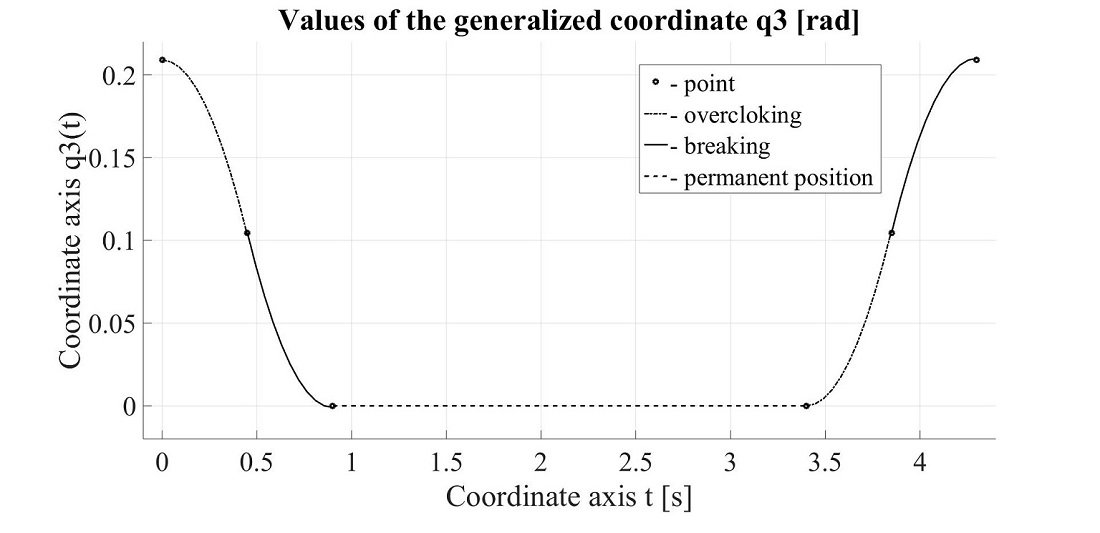
The object of this study is the technological operation of removing the oxide film from the surface of the metal melt, foundry production of commercial lead, zinc. To carry out the robotization of this technological operation, it is proposed to use a manipulation robot with a spherical coordinate system. A kinematic structure of a manipulation robot with six degrees of mobility and two arms is proposed. On the first arm of the manipulation robot, a movable blade is fixed, and on the second arm, a rotary blade is fixed. With the translational movement of the first hand, the movable blade rakes the oxide film onto the rotary blade. Further, the oxide film collected on the rotary blade is thrown into a special container with a rotational movement. Restrictions are introduced on the values of generalized coordinates, velocities, and accelerations for each degree of mobility of the manipulation robot. Taking into account these limitations, for the implementation of this process, software trajectories have been developed for the degrees of mobility of the manipulation robot, which are approximated by quadratic polynomials. Each program movement is divided into three sections, in the first section acceleration with a given acceleration is carried out, in the second section movement with a given speed, in the third section braking with a given acceleration. To assess the reliability of the developed software trajectories, simulations were carried out in the MatLab software environment, version R2015b. The resulting graphs of program trajectories coincide with the calculated values of the generalized coordinates, time intervals, speeds, and accelerations of change in the generalized coordinates in terms of the degrees of mobility of the manipulation robot. The period of time required to remove the oxide film is 15.88 s. On the basis of the results obtained, a cyclogram for controlling a manipulation robot was built to perform the technological operation of removing the oxide film in the production of commercial lead, zinc
References
- Belov, V. D. et al.; Belov, V. D. (Ed.) (2015). Liteynoe proizvodstvo. Moscow: Izd. dom MISiS, 487.
- Romanteev, Yu. P., Bystrov, V. P. (2010). Metallurgiya tyazhelykh tsvetnykh metallov. Svinets. Tsink. Kadmiy. Moscow: MISiS, 576.
- Әсембай, А. Ә. (2017). Razrabotka modeley i algoritmov postroeniya robototekhnicheskikh sistem pri robotizatsii liteynykh proizvodstv tsvetnykh metallov. Almaty: KazNITU, 170.
- Beisembayev, A., Yerbossynova, A., Pavlenko, P., Baybatshaev, M. (2023). Development of a software trajectory of a manipulation robot for removing oxide film in the production of commercial magnesium. KazATC Bulletin, 127 (4). Available at: https://vestnik.alt.edu.kz/index.php/journal/article/view/1322
- Arkhipov, M. V. (2020). Promyshlennye roboty: upravlenie manipulyatsionnymi robotami. Moscow: Yurayt, 170.
- Ruiz-Celada, O., Verma, P., Diab, M., Rosell, J. (2022). Automating Adaptive Execution Behaviors for Robot Manipulation. IEEE Access, 10, 123489–123497. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3223995
- Akbari, A., Lagriffoul, F., Rosell, J. (2018). Combined heuristic task and motion planning for bi-manual robots. Autonomous Robots, 43 (6), 1575–1590. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-018-9817-3
- Dai, H., Lu, Z., He, M., Yang, C. (2023). A Gripper-like Exoskeleton Design for Robot Grasping Demonstration. Actuators, 12 (1), 39. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/act12010039
- Xu, S., Ou, Y., Duan, J., Wu, X., Feng, W., Liu, M. (2019). Robot trajectory tracking control using learning from demonstration method. Neurocomputing, 338, 249–261. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.01.052
- Kazim, I. J., Tan, Y., Qaseer, L. (2021). Integration of DE Algorithm with PDC-APF for Enhancement of Contour Path Planning of a Universal Robot. Applied Sciences, 11 (14), 6532. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146532
- Wu, G., Zhao, W., Zhang, X. (2020). Optimum time-energy-jerk trajectory planning for serial robotic manipulators by reparameterized quintic NURBS curves. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 235 (19), 4382–4393. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406220969734
- Biagiotti, L., Melchiorri, C. (2019). Trajectory generation via FIR filters: A procedure for time-optimization under kinematic and frequency constraints. Control Engineering Practice, 87, 43–58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2019.03.017
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Akambay Beisembayev, Anargul Yerbossynova, Petro Pavlenko, Mukhit Baibatshayev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








