Determining the efficiency of installing fixed solar photovoltaic modules and modules with different tracking options
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286464Keywords:
photovoltaic module, angle of incidence of solar rays, angle of inclination, angle of inclination to the horizon, efficiency of module installationAbstract
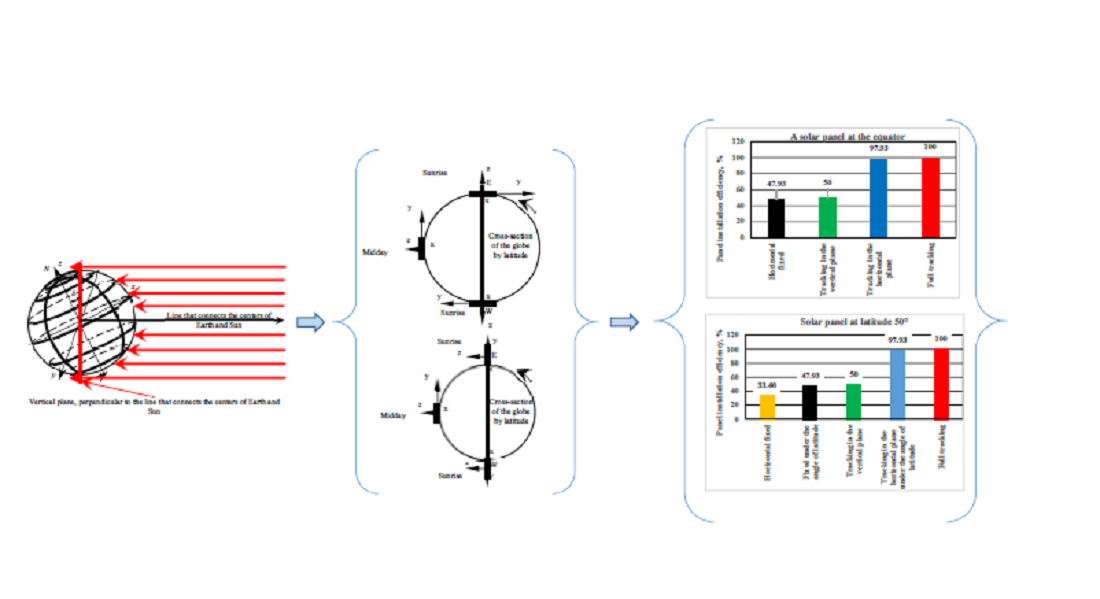
The object of this study is photovoltaic modules in various installation options. The physical model of the Earth's illumination by a parallel flow of solar rays has been refined. The dependence of the cosine of the angle of incidence of the Sun's rays on the angular length of the day, as well as the average annual efficiency of the installation of photovoltaic modules, both fixed and with various tracking options, was determined. Refinement of the physical model implies determining the angle of inclination as the angle between the inclined axis of the Earth and its projection on a vertical plane, perpendicular to the line connecting the centers of the Earth and the Sun. This line passes through the center of the Earth. The concept of the average annual efficiency of the installation of photovoltaic modules is introduced as the annual weighted average value of the cosine of the angle of incidence of solar rays on the plane of the photovoltaic module. Various options for installing photovoltaic modules were analyzed: fixed horizontal on the equator; stationary, installed at an angle to the horizon; one that performs tracking in horizontal (vertical) planes; with full tracking. The efficiency of installing a photovoltaic module at each latitude can be equal to the efficiency of installing this module at the equator, that is, 47.93 % when installing the module at an angle of inclination to the horizon equal to the latitude. Tracking in the vertical plane makes it possible to increase the efficiency of the photovoltaic module installation by up to 50 %. Compared to full tracking, tracking in the horizontal plane at an angle of latitude makes it possible to obtain the efficiency of the installation of the photovoltaic module at the level of 97.93 %.
The results could be used as a basis for evaluating the efficiency of the installation of photovoltaic modules at different latitudes with different techniques of their installation, as well as for the subsequent generation of electricity
References
- Dib, M., Nejmi, A., Ramzi, M. (2020). New auxiliary services system in a transmission substation in the presence of a renewable energy source PV. Materials Today: Proceedings, 27, 3151–3156. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.820
- Satpathy, R., Pamuru, V. (2020). Solar PV Power: Design, Manufacturing and Applications from Sand to Systems. Academic Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/c2018-0-02530-x
- Umar, S., Waqas, A., Tanveer, W., Shahzad, N., Janjua, A. K., Dehghan, M. et al. (2023). A building integrated solar PV surface-cleaning setup to optimize the electricity output of PV modules in a polluted atmosphere. Renewable Energy, 216, 119122. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.119122
- Lu, Y., Li, G. (2023). Potential application of electrical performance enhancement methods in PV/T module. Energy, 281, 128253. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.128253
- Jha, V. (2023). Generalized modelling of PV module and different PV array configurations under partial shading condition. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 56, 103021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2023.103021
- Barbosa de Melo, K., Kitayama da Silva, M., Lucas de Souza Silva, J., Costa, T. S., Villalva, M. G. (2022). Study of energy improvement with the insertion of bifacial modules and solar trackers in photovoltaic installations in Brazil. Renewable Energy Focus, 41, 179–187. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ref.2022.02.005
- Dhimish, M., Ahmad, A., Tyrrell, A. M. (2022). Inequalities in photovoltaics modules reliability: From packaging to PV installation site. Renewable Energy, 192, 805–814. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.04.156
- Peters, I. M., Hauch, J. A., Brabec, C. J. (2022). The role of innovation for economy and sustainability of photovoltaic modules. IScience, 25 (10), 105208. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105208
- Duffie, J. A., Beckman, W. A. (2013). Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes. John Wiley & Sons. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118671603
- Wald, L. (2021). Fundamentals of Solar Radiation. CRC Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003155454
- Grygiel, P., Tarłowski, J., Prześniak-Welenc, M., Łapiński, M., Łubiński, J., Mielewczyk-Gryń, A. et al. (2021). Prototype design and development of low-load-roof photovoltaic modules for applications in on-grid systems. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 233, 111384. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2021.111384
- Winter, C.-J., Sizmann, R. L., Vant-Hull, L. L. (Eds.) (1991). Solar Power Plants. Springer Berlin, 425. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-61245-9
- Cooper, P. I. (1969). The absorption of radiation in solar stills. Solar Energy, 12 (3), 333–346. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092x(69)90047-4
- Barbón, A., Ghodbane, M., Bayón, L., Said, Z. (2022). A general algorithm for the optimization of photovoltaic modules layout on irregular rooftop shapes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 365, 132774. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132774
- Konovalov, Y. V., Khaziev, A. N. (2022). Computer technology applications to calculate the insolation of photoelectric power plant. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 990 (1), 012048. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/990/1/012048
- Yassir, A. (2019). Genetic Algorithm as a Solutions Optimization of Tilt Angles for Monthly Periods of Photovoltaic Installation. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 536 (1), 012100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/536/1/012100
- Khadidja, B., Dris, K., Boubeker, A., Noureddine, S. (2014). Optimisation of a Solar Tracker System for Photovoltaic Power Plants in Saharian Region, Example of Ouargla. Energy Procedia, 50, 610–618. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.06.075
- Jin, Z., Xu, K., Zhang, Y., Xiao, X., Zhou, J., Long, E. (2017). Installation Optimization on the Tilt and Azimuth Angles of the Solar Heating Collectors for High Altitude Towns in Western Sichuan. Procedia Engineering, 205, 2995–3002. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.225
- Pan, D., Bai, Y., Chang, M., Wang, X., Wang, W. (2022). The technical and economic potential of urban rooftop photovoltaic systems for power generation in Guangzhou, China. Energy and Buildings, 277, 112591. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.112591
- N’Tsoukpoe, K. E. (2022). Effect of orientation and tilt angles of solar collectors on their performance: Analysis of the relevance of general recommendations in the West and Central African context. Scientific African, 15, e01069. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e01069
- Shu, N., Kameda, N., Kishida, Y., Sonoda, H. (2006). Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Optimal Tilt Angle of Photovoltaic Panels. Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering, 5 (2), 399–405. doi: https://doi.org/10.3130/jaabe.5.399
- Buzra, U., Mitrushi, D., Serdari, E., Halili, D., Muda, V. (2022). Fixed and adjusted optimal tilt angle of solar panels in three cities in Albania. Journal of Energy Systems, 6 (2), 153–164. doi: https://doi.org/10.30521/jes.952260
- Nikitenko, G. V., Konoplev, E. V., Salpagarov, V. K., Danchenko, I. V., Masyutina, G. V. (2020). Improving the energy efficiency of using solar panels. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 613 (1), 012092. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/613/1/012092
- Kuttybay, N., Saymbetov, A., Mekhilef, S., Nurgaliyev, M., Tukymbekov, D., Dosymbetova, G. et al. (2020). Optimized Single-Axis Schedule Solar Tracker in Different Weather Conditions. Energies, 13 (19), 5226. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en13195226
- Jäger, K., Isabella, O., Smets, A. H. M., Swaaij, R. A., Zeman, M. (2014). Solar Energy, Fundamentals, Technology, and Systems. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 408. Available at: http://web.kpi.kharkov.ua/ief/wp-content/uploads/sites/39/2020/05/solar_energy_1.pdf
- Renewable Energy. Solar Power (2009). Courseware Sample by the staff of Lab-Volt Ltd., 115.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Gennadii Golub, Nataliya Tsyvenkova, Oksana Yaremenko, Oleh Marus, Ivan Omarov, Anna Нolubenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








