Development of biotechnologically transesterified three-component fat systems stable to oxidation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.287326Keywords:
biotechnological transesterification, fat systems, fat peroxide value, oxidation induction periodAbstract
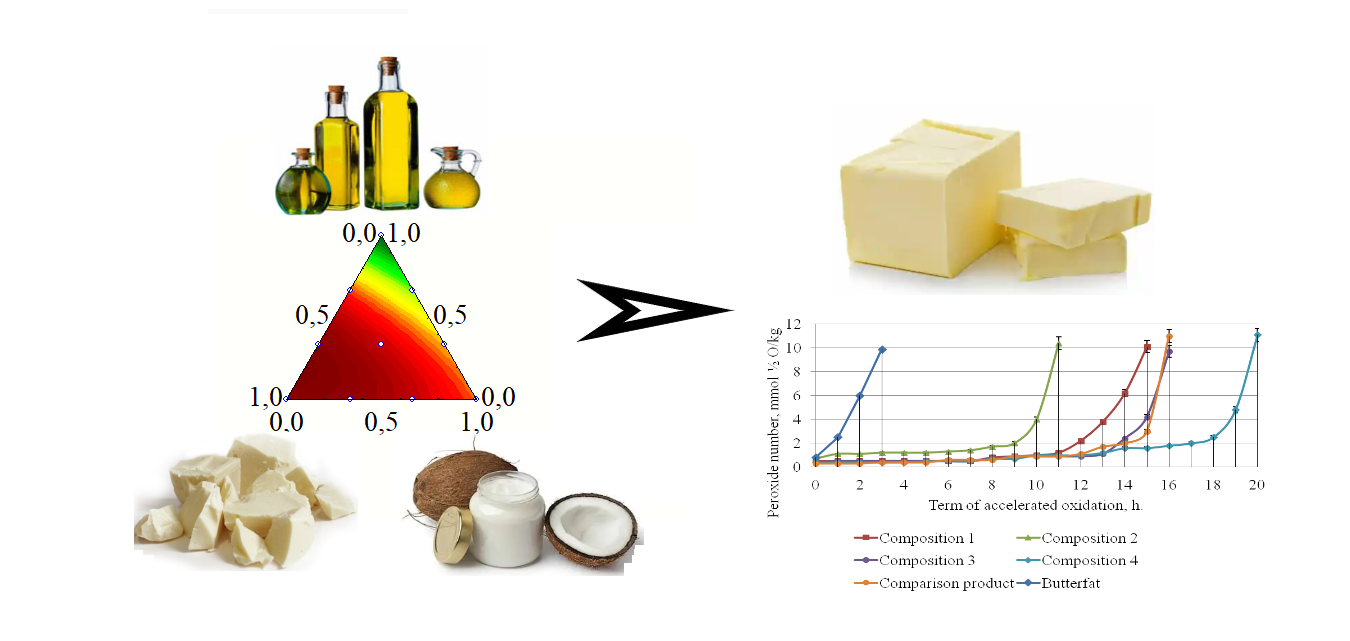
The object of the research is the period of induction of accelerated oxidation of biotechnologically transesterified fatty systems that do not contain trans isomers of fatty acids. The paper defines the rational ratio of fatty raw materials in mixtures for biotechnological transesterification. The results obtained make it possible to develop biotechnologically transesterified three-component fat systems (palm stearin, coconut and sunflower, or soybean, or corn, or sesame oil) to obtain substitutes for milk fat. The proposed calculation of melting points of transesterified fat systems of a wide range of ratios of raw components allows us to justify such rational ratios of components that allow obtaining finished products with a melting point of 33.0...33.5 °С. It is effective to use the products of the developed composition in view of the technological requirements of consumers for their oxidizing capacity. The data obtained in the work are explained by the fatty acid and antioxidant composition of low-melting components of fat systems in a different range of their ratios, which determines different technological properties, in particular, the melting point and stability to oxidation of finished products. A feature of the obtained results is the competitiveness of the obtained fat systems, which are characterized by the absence of atherogenic components and the presence of biologically valuable polyunsaturated fatty acids in the composition. The results of the research make it possible to minimize the cost of raw components while preserving the nutritional value and technological characteristics. An applied aspect of using the scientific result is the possibility of expanding the range of milk fat substitutes with high nutritional value
References
- Norazlina, M. R., Jahurul, M. H. A., Hasmadi, M., Mansoor, A. H., Norliza, J., Patricia, M. et al. (2021). Trends in blending vegetable fats and oils for cocoa butter alternative application: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 116, 102–114. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.07.016
- Sivakanthan, S., Madhujith, T. (2020). Current trends in applications of enzymatic interesterification of fats and oils: A review. LWT, 132, 109880. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109880
- Oteng, A.-B., Kersten, S. (2020). Mechanisms of Action of trans Fatty Acids. Advances in Nutrition, 11 (3), 697–708. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz125
- Lai, O. M., Ghazali, H. M., Cho, F., Chong, C. L. (2000). Enzymatic transesterification of palm stearin: anhydrous milk fat mixtures using 1,3-specific and non-specific lipases. Food Chemistry, 70 (2), 221–225. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0308-8146(00)00085-6
- Esonye, C., Onukwuli, O. D., Ofoefule, A. U. (2019). Chemical kinetics of a two-step transesterification of dyacrodes edulis seed oil using acid-alkali catalyst. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 145, 245–257. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.03.010
- Tang, W., Wang, X., Huang, J., Jin, Q., Wang, X. (2015). A novel method for the synthesis of symmetrical triacylglycerols by enzymatic transesterification. Bioresource Technology, 196, 559–565. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.024
- Kovaliova, O., Tchoursinov, Y., Kalyna, V., Koshulko, V., Kunitsia, E., Chernukha, A. et al. (2020). Identification of patterns in the production of a biologically-active component for food products. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (11 (104)), 61–68. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.200026
- de Oliveira, P. D., da Silva, D. A., Pires, W. P., Bezerra, C. V., da Silva, L. H. M., da Cruz Rodrigues, A. M. (2021). Enzymatic interesterification effect on the physicochemical and technological properties of cupuassu seed fat and inaja pulp oil blends. Food Research International, 145, 110384. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110384
- Zhang, Z., Ye, J., Lee, W. J., Akoh, C. C., Li, A., Wang, Y. (2021). Modification of palm-based oil blend via interesterification: Physicochemical properties, crystallization behaviors and oxidative stabilities. Food Chemistry, 347, 129070. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129070
- Sytnik, N., Kunitsa, E., Mazaeva, V., Chernukha, A., Bezuglov, O., Bogatov, O. et al. (2020). Determination of the influence of natural antioxidant concentrations on the shelf life of sunflower oil. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (11 (106)), 55–62. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.209000
- Gruczynska-Sekowska, E., Aladedunye, F., Anwar, F., Koczon, P., Kowalska, D., Kozlowska, M. et al. (2020). Development of zero-trans shortenings with high thermo-oxidative stability by enzymatic transesterification. Grasas y Aceites, 71 (4), 375. doi: https://doi.org/10.3989/gya.0564191
- Belinska, A., Bliznjuk, O., Shcherbak, O., Masalitina, N., Myronenko, L., Varankina, O. et al. (2022). Improvement of fatty systems biotechnological interesterification with immobilized enzyme preparation usage. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (6 (120)), 6–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.268373
- Gruczyńska, E., Majewska, E., Tarnowska, K. (2018). Development of zero trans baking shortenings by enzymatic interesterification. Zeszyty Problemowe Postępów Nauk Rolniczych, 592, 27–35. doi: https://doi.org/10.22630/zppnr.2018.592.3
- Kowalska, D., Gruczynska, E., Kowalska, M. (2014). The effect of enzymatic interesterification on the physico-chemical properties and thermo-oxidative stabilities of beef tallow stearin and rapeseed oil blends. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 120 (1), 507–517. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3869-1
- Kowalska, D., Kostecka, M., Tarnowska, K., Kowalski, B. (2013). Oxidative stabilities of enzymatically interesterified goose fat and rapeseed oil blend by rancimat and PDSC. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 115 (3), 2063–2070. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3125-0
- Jeyakumar, N., Huang, Z., Balasubramanian, D., Le, A. T., Nguyen, X. P., Pandian, P. L., Hoang, A. T. (2022). Experimental evaluation over the effects of natural antioxidants on oxidation stability of binary biodiesel blend. International Journal of Energy Research, 46 (14), 20437–20461. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7956
- Manzoor, S., Masoodi, F. A., Akhtar, G., Rashid, R. (2022). Production of trans-free shortening by lipase catalysed interesterification using mustard oil and palm stearin: optimisation and characterisation. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03315-1
- Zaminnyk molochnoho zhyru Akomiks. Available at: https://organicoil.com.ua/zmzh-akomiks
- Maslo vershkove natural'ne toplene DSTU 99%. Available at: https://prom.ua/ua/p1491578709-maslo-slivochnoe-naturalnoe.html
- Belinska, A., Bochkarev, S., Varankina, O., Rudniev, V., Zviahintseva, O., Rudnieva, K. et al. (2019). Research on oxidative stability of protein-fat mixture based on sesame and flax seeds for use in halva technology. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (11 (101)), 6–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.178908
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Anna Belinska, Olga Bliznjuk, Nataliia Masalitina, Iryna Bielykh, Oksana Zviahintseva, Tatyana Gontar, Serhii Stankevych, Inna Zabrodina, Oleksandra Mandych, Galyna Stepankova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








