Optimization of the method of hydrothermal treatment of mogar grain for production of food concentrate "Talkan"
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.289235Keywords:
hydrothermal treatment, grain quality, roasting, drying, mogar, TalkanAbstract
The possibility of using mogar grain for the production of food concentrates based on the traditional national dish "Talkan" is considered. "Talkan" is a national food concentrate for Republic of Kazakhstan, which has been used as a staple food in long-distance trekking by various cultures for centuries. Traditionally, talkan is prepared from various cereals, particularly millet, wheat and barley. When boiling water and oil are added, it turns into a hearty porridge, and when oil and sugar are added, it becomes a delicious dessert.
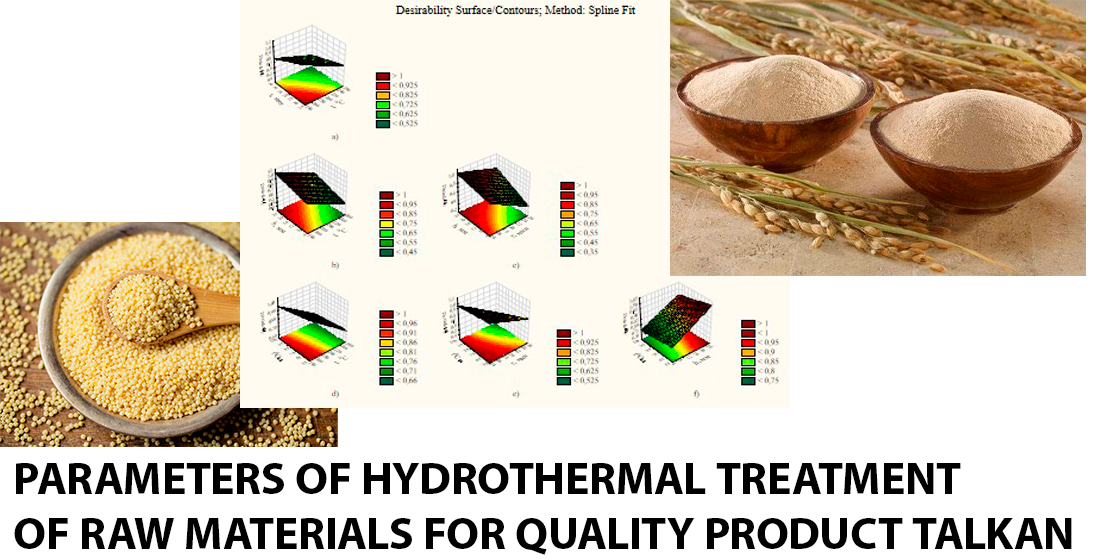
The difficulty lies in the careful handling and preparation of the mogar grain. During intensive cooking, the grain can easily overcook, resulting in all the valuable nutrients being leached into the broth. In addition, improperly prepared mogar can burn during further roasting. To determine the optimal parameters of mogar hydrothermal treatment and to create a high-quality food concentrate based on the national dish "Talkan", a complex experiment was conducted using modern methods of experiment planning.
A number of variables were tested during the experiment, including temperature limits and duration of cooking, as well as temperature, duration and intensity of stirring during drying and roasting of mogar. The study showed that the most favourable conditions for mogar grain involve cooking at an initial temperature of between 15–20 °C for about 60 minutes, gradually reaching 100 °C. The drying and roasting processes are best carried out for 25 minutes, with a layer thickness of 25 mm and a surface temperature of 250 °C.
The determined of hydrothermal treatment serve as a basis for the design of specialised equipment for preparation of mogar grain for the purpose of making Talkan
References
- Alcázar-Alay, S. C., Meireles, M. A. A. (2015). Physicochemical properties, modifications and applications of starches from different botanical sources. Food Science and Technology (Campinas), 35 (2), 215–236. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-457x.6749
- Saleh, A. S. M., Zhang, Q., Chen, J., Shen, Q. (2013). Millet Grains: Nutritional Quality, Processing, and Potential Health Benefits. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 12 (3), 281–295. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12012
- Annor, G. A., Tyl, C., Marcone, M., Ragaee, S., Marti, A. (2017). Why do millets have slower starch and protein digestibility than other cereals? Trends in Food Science & Technology, 66, 73–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.05.012
- Shahidi, F., Chandrasekara, A. (2013). Millet grain phenolics and their role in disease risk reduction and health promotion: A review. Journal of Functional Foods, 5 (2), 570–581. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2013.02.004
- Kam, J., Puranik, S., Yadav, R., Manwaring, H. R., Pierre, S., Srivastava, R. K., Yadav, R. S. (2016). Dietary Interventions for Type 2 Diabetes: How Millet Comes to Help. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01454
- Michaelraj, P. S. J., Shanmugam, A. (2013). A study on millets based cultivation and consumption in India. International Journal of Marketing, Financial Services and Management Research, 2 (4), 49–58.
- Vanga, S. K., Singh, A., Orsat, V., Raghavan, V. (2018). Annex 2.5: Nutritional Comparison of Millets With Other Super Foods. Available at: https://idl-bnc-idrc.dspacedirect.org/items/25fa3a1b-5400-45d9-8bb4-3d48bc88667a
- Ambati, K., Sucharitha, K. V. (2019). Millets-review on nutritional profiles and health benefits. International Journal of Recent Scientific Research, 10 (7), 33943–33948. Available at: https://www.recentscientific.com/sites/default/files/14234-A-2019.pdf?fbclid=IwAR2AMaT7nEr1ulo5rvKKptHDm77O84ZUwOJJom-Lx4YV1i_Y2RGKt71p4lU
- Kumar, A., Metwal, M., Kaur, S., Gupta, A. K., Puranik, S., Singh, S. et al. (2016). Nutraceutical value of finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.), and their improvement using omics approaches. Front. Plant Sci., 7, 934. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00934
- Kaur, A., Bhise, S., Kaur, M. (2021). Hydrothermal treatments for paddy to improve physicochemical quality of brown rice. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences, 9 (5), 913–926. doi: https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.2020.9.5.913-926
- Venkatachalapathy, N., Udhayakumar, R. (2013). Effects of Continuous Steaming on Milling Characteristics of Two Indica Rice Varieties. Rice Science, 20 (4), 309–312. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1672-6308(13)60141-9
- Bello, M. O., Tolaba, M. P., Suarez, C. (2007). Water absorption and starch gelatinization in whole rice grain during soaking. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 40 (2), 313–318. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.09.017
- Oli, P., Ward, R., Adhikari, B., Torley, P. (2014). Parboiled rice: Understanding from a materials science approach. Journal of Food Engineering, 124, 173–183. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.09.010
- Sarangapani, C., Thirumdas, R., Devi, Y., Trimukhe, A., Deshmukh, R. R., Annapure, U. S. (2016). Effect of low-pressure plasma on physico–chemical and functional properties of parboiled rice flour. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 69, 482–489. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.02.003
- Leethanapanich, K., Mauromoustakos, A., Wang, Y.-J. (2016). Impacts of parboiling conditions on quality characteristics of parboiled commingled rice. Journal of Cereal Science, 69, 283–289. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2016.04.003
- Patel, P., Thorat, S. S. (2019). Studies on chemical, textural and color characteristics of decorticated finger millet (Eleusine coracana) fortified sponge cake. The Pharma Innovation Journal, 8 (3), 64–67. Available at: https://www.thepharmajournal.com/archives/2019/vol8issue3/PartB/7-11-4-985.pdf
- Kumar, S. R., Sadiq, M. B., Anal, A. K. (2020). Comparative study of physicochemical and functional properties of pan and microwave cooked underutilized millets (proso and little). LWT, 128, 109465. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109465
- Singh, N., David, J., Thompkinson, D. K., Seelam, B. S., Rajput, H., Morya, S. (2018). Effect of roasting on functional and phytochemical constituents of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.). The Pharma Innovation Journal, 7 (4), 414–418. Available at: https://www.thepharmajournal.com/archives/2018/vol7issue4/PartG/7-3-90-468.pdf
- Yousaf, L., Hou, D., Liaqat, H., Shen, Q. (2021). Millet: A review of its nutritional and functional changes during processing. Food Research International, 142, 110197. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110197
- Tumwine, G., Atukwase, A., Tumuhimbise, G. A., Tucungwirwe, F., Linnemann, A. (2018). Production of nutrient‐enhanced millet‐based composite flour using skimmed milk powder and vegetables. Food Science & Nutrition, 7 (1), 22–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.777
- Ketnawa, S., Ogawa, Y. (2021). In vitro protein digestibility and biochemical characteristics of soaked, boiled and fermented soybeans. Scientific Reports, 11 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-93451-x
- Zhang, M., Liu, Y., Jin, M., Li, D., Wang, Z., Jiang, P., Zhou, D. (2023). The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestion and Absorption Properties of Protein in Sea Cucumber Body Wall. Foods, 12 (15), 2896. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152896
- Alimardanova, M., Tlevlessova, D., Bakiyeva, V., Akpanov, Z. (2021). Revealing the features of the formation of the properties of processed cheese with wild onions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (11 (112)), 73–81. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.239120
- Ghelich, R., Jahannama, M. R., Abdizadeh, H., Torknik, F. S., Vaezi, M. R. (2019). Central composite design (CCD)-Response surface methodology (RSM) of effective electrospinning parameters on PVP-B-Hf hybrid nanofibrous composites for synthesis of HfB2-based composite nanofibers. Composites Part B: Engineering, 166, 527–541. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.094
- Zhu, Y., Xie, F., Ren, J., Jiang, F., Zhao, N., Du, S. (2023). Structural analysis, nutritional evaluation, and flavor characterization of parched rice made from proso millet. Food Chemistry: X, 19, 100784. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100784
- Vashishth, R., Semwal, A. D., Murugan, M. P., Raj, T. G., Sharma, G. K. (2020). Engineering properties of horse gram (Macrotyloma uniflorum) varieties as a function of moisture content and structure of grain, Journal of Food Science and Technology, 57, 1477–1485. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04183-w
- Kesarwani, A., Sharma, M., Vaid, S. K., Chen, S. S. (2015). Impact of Production Practices on Organoleptic Intensity Scale of Different Rice Cultivars. Journal of Pharmacy and Nutrition Sciences, 5 (2), 114–120. doi: https://doi.org/10.6000/1927-5951.2015.05.02.3
- Okeyo, A. A., Luthra, K., Atungulu, G. G. (2023). Impact of degree of milling on cooking duration and textural attributes of long‐grain hybrid rice for instant rice processing. Cereal Chemistry, 100 (4), 830–840. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cche.10660
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Gaukhar Kuzembayeva, Kanash Kuzembayev, Dinara Tlevlessova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








