Implementation of blockchain technology in the system of accounting and analytical support for the public sector
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.290024Keywords:
accounting and analytical support, information technologies, blockchain, transactions, smart contracts, public sectorAbstract
The study addressed the problem of developing a mechanism for introducing blockchain technology into the system of accounting and analytical support for public sector entities.
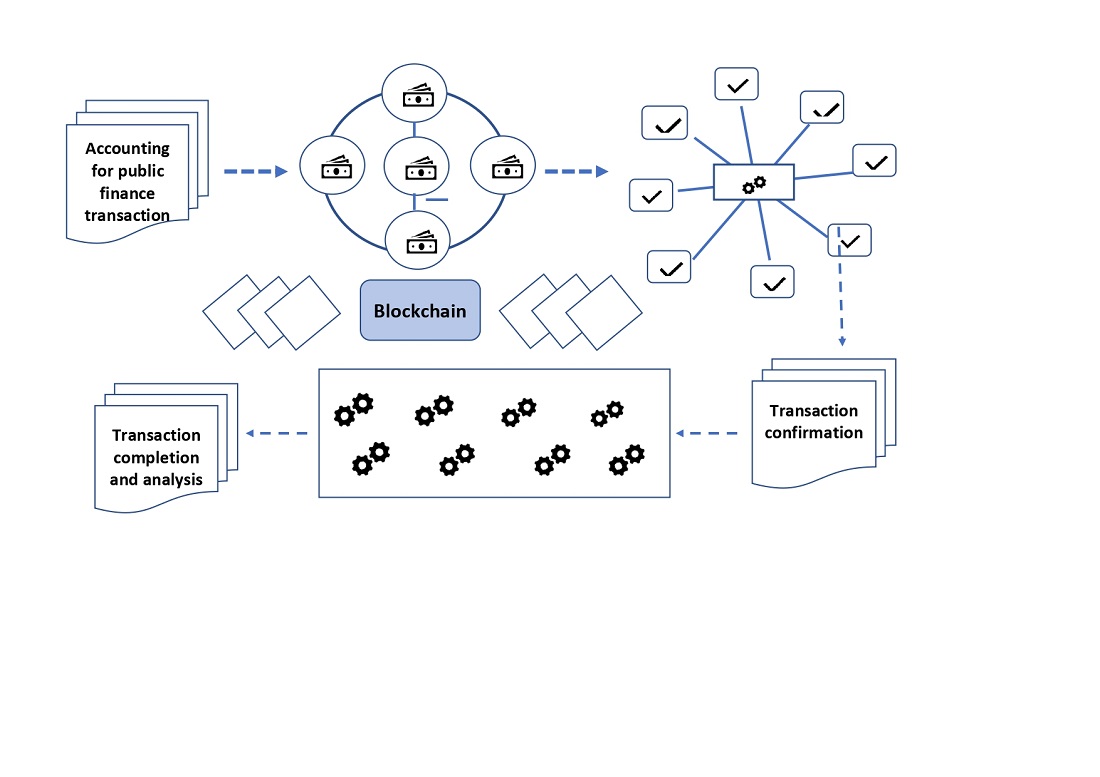
In the course of the research, the volumes and types of financial violations by public sector entities were analyzed. Identified violations were committed by public sector entities, and their significant share fell on the system of accounting and analytical support, in particular, financial reporting, budget execution. Legal restrictions on the introduction of blockchain technology for public sector entities were outlined. The absence of a number of acts in the field of digitization, protection of state secrets, cyber security, international standards, etc. in the legal field was established. The characteristics and mechanisms of blockchain technology were described, the types of blockchains based on permission models (open, closed) were defined. The technological characteristics of the use of blockchain platforms in the system of accounting and analytical support of public sector entities have been determined. The need to use blockchain applications such as smart contracts was indicated. It is noted that the use of smart contracts can be developed on blockchain platforms such as Ethereum, NXT, and Hyperledger; their key characteristics were described. A comparative description of transactions of state funds in the traditional accounting system and with the use of blockchain systems is given. The problem of the materiality of the transaction cost when transferring large volumes of data was outlined using the Ethereum platform as an example; its shortcomings were identified. The development of a mechanism for introducing blockchain technology into the system of accounting and analytical support using the Hyperledger platform, which has an open-source community focused on the development of a set of stable frameworks, tools, and libraries for deploying enterprise-level blockchains, was described. The advantages and disadvantages of introducing blockchain technology into the system of accounting and analytical support have been determined.
References
- Dutta, S. K. (2013). Statistical techniques for forensic accounting: understanding the theory and application of data analysis. New Jersey: FT Press, 400.
- Report to the Nations. Available at: https://www.acfe.com/fraud-resources/report-to-the-nations-archive
- Titarenko, K., Cherniavska, I. (2021). Nadmirna kryminalizatsiia ekonomichnoi diialnosti v Ukraini: yak tse vidbuvaietsia i shcho iz tsym robyty. Kyiv: Tsentr stratehichnykh rozrobok, 38.
- Tan, B. S., Low, K. Y. (2019). Blockchain as the Database Engine in the Accounting System. Australian Accounting Review, 29 (2), 312–318. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/auar.12278
- Maffei, M., Casciello, R., Meucci, F. (2021). Blockchain technology: uninvestigated issues emerging from an integrated view within accounting and auditing practices. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 34 (2), 462–476. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/jocm-09-2020-0264
- European Blockchain Observatory & Forum. Available at: https://www.eublockchainforum.eu/
- Janssen, M., Weerakkody, V., Ismagilova, E., Sivarajah, U., Irani, Z. (2020). A framework for analysing blockchain technology adoption: Integrating institutional, market and technical factors. International Journal of Information Management, 50, 302–309. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.08.012
- Dai, J., Vasarhelyi, M. A. (2017). Toward Blockchain-Based Accounting and Assurance. Journal of Information Systems, 31 (3), 5–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.2308/isys-51804
- Meijer, D., Ubacht, J. (2018). The governance of blockchain systems from an institutional perspective, a matter of trust or control? Proceedings of the 19th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research: Governance in the Data Age. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3209281.3209321
- Komitet z pytan biudzhetu rozghlianuv zvit Rakhunkovoi palaty za 2022 rik (2023). Available at: https://www.rada.gov.ua/news/news_kom/236692.html
- Informatsiia shchodo nadanykh orhanamy Derzhavnoi kaznacheiskoi sluzhby Ukrainy rozporiadnykam (oderzhuvacham) biudzhetnykh koshtiv poperedzhen pro nenalezhne vykonannia biudzhetnoho zakonodavstva (2023). Available at: https://www.treasury.gov.ua/news/informatsiia
- Blockchain Technology A game-changer in accounting? (2016). Deloitte. Available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/de/Documents/Innovation/
- Statystyka. Rakhunkova palata Ukrainy. Available at: http://rp.gov.ua/InformationRequest/StatisticsPI/?pid=139
- Pro derzhavnu taiemnytsiu (1994). Zakon Ukrainy No. 3855-XII. 21.01.1994. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/3855-12#Text
- Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Available at: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
- Brownworth, A. (2016). Blockchain 101: A Visual Demo. Boston: Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Available at: http://blockchain.mit.edu/how-blockchain-works
- Sybil Attacks Explained (2018). Binance Academy. Available at: https://academy.binance.com/en/articles/sybil-attacks-explained
- Hileman, G., Rauchs, M. (2017). Global Blockchain Benchmarking Study. Cambridge Center for Alternative Finance. Available at: https://j2-capital.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/GLOBAL-BLOCKCHAIN.pdf
- Wu, J., Tran, N. (2018). Application of Blockchain Technology in Sustainable Energy Systems: An Overview. Sustainability, 10 (9), 3067. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093067
- Ismail, L., Materwala, H. (2019). A review of blockchain architecture and consensus protocols: Use cases, challenges, and solutions. Symmetry, 11 (10), 1198. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11101198
- Khan, S. N., Loukil, F., Ghedira-Guegan, C., Benkhelifa, E., Bani-Hani, A. (2021). Blockchain smart contracts: Applications, challenges, and future trends. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 14 (5), 2901–2925. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-021-01127-0
- Liu, M., Wu, K., Xu, J. J. (2019). How Will Blockchain Technology Impact Auditing and Accounting: Permissionless versus Permissioned Blockchain. Current Issues in Auditing, 13 (2), A19–A29. doi: https://doi.org/10.2308/ciia-52540
- Odintcova, T. M., Rura, O. V. (2018). Transformatciia bukhgalterskogo ucheta v usloviiakh tcifrovoi ekonomiki i informatcionnogo obshchestva. Formirovanie tcifrovoi ekonomiki i promyshlennosti: novye vyzovy, 6, 41–61.
- Gas and Fees (2023).. Ethereum.org. Available at: https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/gas/
- Wood, G. (2023). Ethereum: a secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum project yellow paper. Available at: https://ethereum.github.io/yellowpaper/paper.pdf
- About Hyperledger. Available at: https://www.hyperledger.org/about
- Kupalova Г., Koreneva Н., Goncharenko Н. (2022). Theoretical and organizational aspects of blockchain technology application in entrepreneurship. Modeling the development of the economic systems, 2, 121–127. doi: https://doi.org/10.31891/mdes/2022-4-16
- Perboli, G., Musso, S., Rosano, M. (2018). Blockchain in Logistics and Supply Chain: A Lean Approach for Designing Real-World Use Cases. IEEE Access, 6, 62018–62028. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2875782
- Ahuja, M., Amir, G., Kunpeng, L. (2020). Blockchain and the supply chain. David Nazarian College of Business and Economics (CSUN). Available at: https://www.porttechnology.org/technical-papers/blockchain-and-the-supply-chain/
- Pedersen, A. B., Risius, M., Beck, R. (2019). A Ten-Step Decision Path to Determine When to Use Blockchain Technologies. MIS Quarterly Executive, 18 (2), 99–115. doi: https://doi.org/10.17705/2msqe.00010
- Fuller, S. H., Markelevich, A. (2019). Should accountants care about blockchain? Journal of Corporate Accounting & Finance, 31 (2), 34–46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcaf.22424
- Bonsón, E., Bednárová, M. (2019). Blockchain and its implications for accounting and auditing. Meditari Accountancy Research, 27 (5), 725–740. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/medar-11-2018-0406
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Tetiana Larikova, Volodymyr Ivankov, Liudmyla Novichenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








