Development of barium hexaferrite core–shell composites as high-performance microwave absorption by optimizing hydrothermal synthesis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.291064Keywords:
barium hexaferrite, core-shell composite, hydrothermal, molybdenum disulfide, radar absorber material, reflection lossAbstract
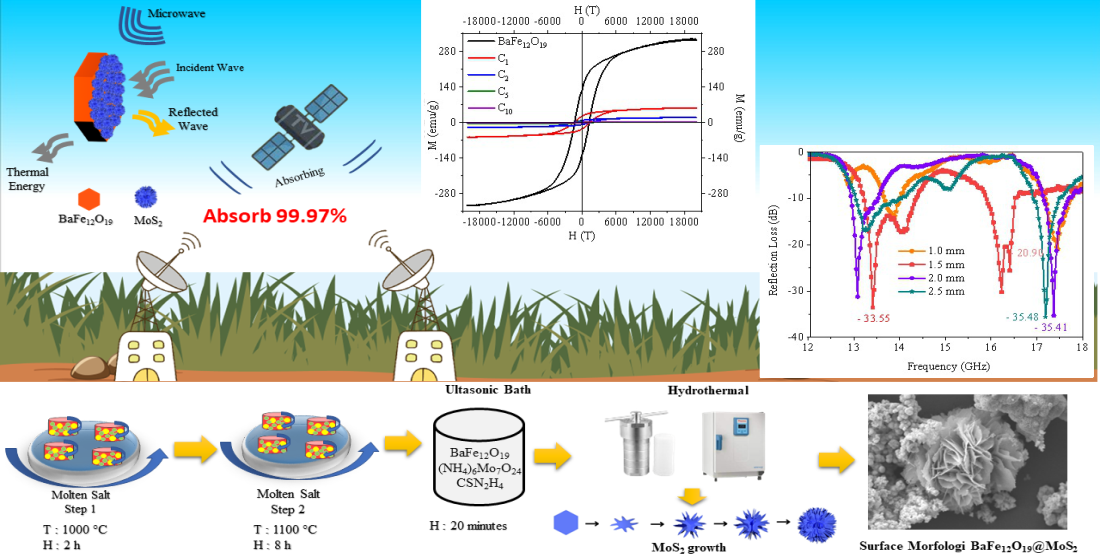
In conjunction with the enhancement of societal living standards and the rapid development of information technology, an extensive variety of high-capacity electronic devices are being introduced to the market. The heightened demands result in the generation of electromagnetic wave radiation, which poses a potential risk to human well-being. Barium hexaferrite (BHF) is one of the radar-absorbing materials (RAMs) that can absorb electromagnetic waves because it has a high anisotropic field. However, its drawbacks are narrow absorption and less stability. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), is the best candidate for the reinforcement of BHF. The study investigated the impact of increasing the thiourea, temperature, hydrothermal holding time, and sample thickness on reflection loss. This study used a two-step molten salt and hydrothermal synthesis to make a BaFe12O19@MoS2 core-cell composite. Two-step molten salt and hydrothermal synthesis methods created single-phase BaFe12O19@MoS2 core-cell composites that worked well. The results showed that adding MoS2 to BHF changed BHF's magnetic properties from hard to soft. Increasing the hydrothermal temperature up to 220 °C effectively reduced the reflection loss of BaFe12O19@MoS2. On a 2 mm thick sample containing 100 mmol thiourea, the study achieved an electromagnetic wave absorption of 99.97 % with a reflection loss of –35.41 dB (17.37 GHz). The results of this research can be applied to protect electronic devices vulnerable to signal interference from satellite radar systems at frequencies of 12–18 GHz
References
- Asghar, G., Asri, S., Khusro, S. N., Tariq, G. H., Awan, M. S., Irshad, M., Safeen, A. et al. (2020). Enhanced Magnetic Properties of Barium Hexaferrite. Journal of Electronic Materials, 49 (7), 4318–4323. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08125-7
- Hema, S., Sambhudevan, S. (2021). Ferrite-based polymer nanocomposites as shielding materials: a review. Chemical Papers, 75 (8), 3697–3710. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01664-1
- Nikmanesh, H., Hoghoghifard, S., Hadi-Sichani, B., Moradi, M. (2020). Erbium-chromium substituted strontium hexaferrite particles: Characterization of the physical and Ku-band microwave absorption properties. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 262, 114796. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114796
- Yustanti, E., Trenggono, A., Manaf, A. (2020). Physical and Microwave Absorption Characteristics of High Powered Ultrasonically Irradiated Crystalline BaFe9Mn1.5Ti1.5O19 Particles. International Journal of Technology, 11 (2), 310. doi: https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v11i2.2988
- Feng, G., Zhou, W., Deng, H., Chen, D., Qing, Y., Wang, C. et al. (2019). Co substituted BaFe12O19 ceramics with enhanced magnetic resonance behavior and microwave absorption properties in 2.6 – 18 GHz. Ceramics International, 45 (11), 13859–13864. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.083
- Yang, E., Qi, X., Xie, R., Bai, Z., Jiang, Y., Qin, S. et al. (2018). Core@shell@shell structured carbon-based magnetic ternary nanohybrids: Synthesis and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. Applied Surface Science, 441, 780–790. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.029
- Wang, M., Lin, Y., Yang, H., Qiu, Y., Wang, S. (2020). A novel plate-like BaFe12O19@MoS2 core-shell structure composite with excellent microwave absorbing properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 817, 153265. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153265
- Rianna, M., Sembiring, T., Situmorang, M., Kurniawan, C., Tetuko, A. P., Setiadi, E. A. et al. (2019). Effect of calcination temperature on Microstructures, magnetic properties, and microwave absorption on BaFe11.6Mg0.2Al0.2O19 synthesized from natural iron sand. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 13, 100393. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2019.100393
- Zhang, Y., Gao, S., Xing, H. (2019). Hierarchical core–shell Fe3O4@C@MoS2 composites synergistically enhance microwave absorption. Materials Letters, 246, 80–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.03.031
- Wang, P., Zhang, J., Wang, G., Duan, B., He, D., Wang, T., Li, F. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of MoS2/Fe@Fe3O4 nanocomposites exhibiting enhanced microwave absorption performance at normal and oblique incidences. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 35 (9), 1931–1939. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.05.021
- Zhang, D., Chai, J., Cheng, J., Jia, Y., Yang, X., Wang, H. et al. (2018). Highly efficient microwave absorption properties and broadened absorption bandwidth of MoS2-iron oxide hybrids and MoS2-based reduced graphene oxide hybrids with Hetero-structures. Applied Surface Science, 462, 872–882. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.152
- Almessiere, M. A., Slimani, Y., Korkmaz, A. D., Baykal, A., Güngüneş, H., Sözeri, H. et al. (2019). Impact of La3+ and Y3+ ion substitutions on structural, magnetic and microwave properties of Ni0.3Cu0.3Zn0.4Fe2O4 nanospinel ferrites synthesized via sonochemical route. RSC Advances, 9 (53), 30671–30684. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra06353f
- Huang, W., Tong, Z., Bi, Y., Ma, M., Liao, Z., Wu, G. et al. (2021). Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of coralloid core-shell structure NiS/Ni3S4@PPy@MoS2 nanowires. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 599, 262–270. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.107
- Yang, H., Zhang, X., Xiong, Z., Shen, Z., Liu, C., Xie, Y. (2021). Cu2O@nanoporous carbon composites derived from Cu-based MOFs with ultrabroad-bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorbing performance. Ceramics International, 47 (2), 2155–2164. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.053
- Dai, B., Ma, Y., Dong, F., Yu, J., Ma, M., Thabet, H. K. et al. (2022). Overview of MXene and conducting polymer matrix composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 5 (2), 704–754. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00510-6
- Karim Darboe, A., Qi, X., Gong, X., Peng, Q., Chen, Y., Xie, R. et al. (2022). Constructing MoSe2/MoS2 and MoS2/MoSe2 inner and outer-interchangeable flower-like heterojunctions: A combined strategy of interface polarization and morphology configuration to optimize microwave absorption performance. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 624, 204–218. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.05.078
- Chang, M., Jia, Z., Wu, G., Yin, P. (2023). Multiple dimension-component designed Co/Co9S8/Ti3C2Tx MXene composite for enhanced microwave absorption. Applied Physics Letters, 122 (13). doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0142497
- Hou, T., Wang, J., Zheng, T., Liu, Y., Wu, G., Yin, P. (2023). Anion Exchange of Metal Particles on Carbon‐Based Skeletons for Promoting Dielectric Equilibrium and High‐Efficiency Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Small, 19 (42). doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202303463
- Zheng, T., Zhang, Y., Jia, Z., Zhu, J., Wu, G., Yin, P. (2023). Customized dielectric-magnetic balance enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance in CuxS/CoFe2O4 composites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 457, 140876. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140876
- Wang, S., Gao, H., Sun, G., Zhang, J., Xia, Y., Xie, C. et al. (2020). M-type Barium Hexaferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by γ-Ray Irradiation Assisted Polyacrylamide Gel Method and Its Optical, Magnetic and Supercapacitive Performances. Journal of Cluster Science, 32 (3), 569–578. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01815-6
- Maswadeh, Y., Mahmood, S. H., Awadallah, A., Aloqaily, A. N. (2015). Synthesis and structural characterization of nonstoichiometric barium hexaferrite materials with Fe:Ba ratio of 11.5 – 16.16. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 92, 012019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/92/1/012019
- Quilty, C. D., Housel, L. M., Bock, D. C., Dunkin, M. R., Wang, L., Lutz, D. M. et al. (2019). Ex Situ and Operando XRD and XAS Analysis of MoS2: A Lithiation Study of Bulk and Nanosheet Materials. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2 (10), 7635–7646. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b01538
- Albiter, M. A., Huirache-Acuña, R., Paraguay-Delgado, F., Rico, J. L., Alonso-Nuñez, G. (2006). Synthesis of MoS2nanorods and their catalytic test in the HDS of dibenzothiophene. Nanotechnology, 17 (14), 3473–3481. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/14/020
- Sulaiman, N. I., Abu Bakar, M., Abu Bakar, N. H. H., Saito, N., Thai, V.-P. (2023). Modified sol–gel method for synthesis and structure characterisation of ternary and quaternary ferrite-based oxides for thermogravimetrically carbon dioxide adsorption. Chemical Papers, 77 (6), 3051–3074. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02687-6
- Hu, F., Nan, H., Wang, M., Lin, Y., Yang, H., Qiu, Y., Wen, B. (2021). Construction of core-shell BaFe12O19@MnO2 composite for effectively enhancing microwave absorption performance. Ceramics International, 47 (12), 16579–16587. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.229
- Lu, C.-H., Yeh, C.-H. (2000). Influence of hydrothermal conditions on the morphology and particle size of zinc oxide powder. Ceramics International, 26 (4), 351–357. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-8842(99)00063-2
- Goel, S., Garg, A., Gupta, R. K., Dubey, A., Prasad, N. E., Tyagi, S. (2020). Development of RGO/BaFe12O19-based composite medium for improved microwave absorption applications. Applied Physics A, 126 (6). doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03613-3
- Alshoaibi, A. (2023). Investigating the Supercapacitive Performance of Cobalt Sulfide Nanostructures Prepared Using a Hydrothermal Method. Materials, 16 (13). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134512
- Li, W., Shi, E., Fukuda, T. (2003). Particle size of powders under hydrothermal conditions. Crystal Research and Technology, 38 (10), 847–858. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200310103
- Zhai, Y., Zhu, D., Zhou, W., Min, D., Luo, F. (2018). Enhanced impedance matching and microwave absorption properties of the MAMs by using ball-milled flaky carbonyl iron-BaFe12O19 as compound absorbent. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 467, 82–88. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.07.031
- Ari Adi, W., Sarwanto, Y., Taryana, Y., Soegijono, B. (2018). Effects of the geometry factor on the reflection loss characteristics of the modified lanthanum manganite. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1091, 012028. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1091/1/012028
- Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Zhu, Q., Zheng, Y., Liotta, L. F., Wu, H. (2021). High-efficiency and wide-bandwidth microwave absorbers based on MoS2-coated carbon fiber. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 586, 457–468. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.109
- Sun, Y., Zhong, W., Wang, Y., Xu, X., Wang, T., Wu, L., Du, Y. (2017). MoS2-Based Mixed-Dimensional van der Waals Heterostructures: A New Platform for Excellent and Controllable Microwave-Absorption Performance. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (39), 34243–34255. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10114
- Hassan, A., Aslam, M. A., Bilal, M., Khan, M. S., ur Rehman, S., Ma, K. et al. (2021). Modulating dielectric loss of MoS2@Ti3C2Tx nanoarchitectures for electromagnetic wave absorption with radar cross section reduction performance verified through simulations. Ceramics International, 47 (14), 20706–20716. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.014
- Negi, P., Kumar, A. (2021). MoS2 nanoparticle/activated carbon composite as a dual-band material for absorbing microwaves. Nanoscale Advances, 3 (14), 4196–4206. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1na00292a
- Qu, B., Zhu, C., Li, C., Zhang, X., Chen, Y. (2016). Coupling Hollow Fe3O4–Fe Nanoparticles with Graphene Sheets for High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Material. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8 (6), 3730–3735. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b12789
- Lin, Y., Liu, X., Ye, T., Yang, H., Wang, F., Liu, C. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of graphene/0.8BaFe12O19/0.2Y3Fe5O12 nanocomposite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 683, 559–566. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.117
- Li, H., Zheng, L., Deng, D., Yi, X., Zhang, X., Luo, X. et al. (2021). Multiple natural resonances broaden microwave absorption bandwidth of substituted M-type hexaferrites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 862, 158638. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158638
- McComiskey, K. P. M., Tajber, L. (2018). Comparison of particle size methodology and assessment of nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) as a tool for live monitoring of crystallisation pathways. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 130, 314–326. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.07.012
- Jose, N., Deshmukh, G. P., Ravindra, M. R. (2019). Dynamic Light Scattering: Advantages and Applications. Acta Scientific Nutritional Health, 3 (3), 50–52. Available at: https://www.actascientific.com/ASNH/pdf/ASNH-03-0194.pdf
- Almessiere, M. A., Güner, S., Slimani, Y., Korkmaz, A. D., Baykal, A. (2022). Effect of Mo substitution on structure, morphology and magnetic features of Sr0.8Ni0.2Fe12−2xMoxO19 (x ≤ 0.35) hexaferrites. Chemical Papers, 77 (2), 947–956. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02527-z
- Yustanti, E., Noviyanto, A., Ikramullah, M., Marsillam, Y. A., Taryana, Y., Taufiq, A. (2023). High-performance microwave absorption by optimizing hydrothermal synthesis of BaFe12O19@MnO2 core–shell composites. RSC Advances, 13 (39), 27634–27647. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ra05114e
- Liu, D., Liu, H., Ning, S., Chu, Y. (2020). Chrysanthemum-like high-entropy diboride nanoflowers: A new class of high-entropy nanomaterials. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 9 (3), 339–348. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-020-0373-x
- Yin, P., Wu, G., Tang, Y., Liu, S., Zhang, Y., Bu, G. et al. (2022). Structure regulation in N-doping biconical carbon frame decorated with CoFe2O4 and (Fe,Ni) for broadband microwave absorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 446, 136975. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136975
- Khan, M. Z., Gul, I. H., Javaid, F., Ali, A., Hafeez, S., Baig, M. M. (2023). Synthesis and Characterization of Zr4+-Y3+ Substituted Ba-Sr Hexaferrite Nanoparticles for Microwave Absorption and Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Materials Research Bulletin, 168, 112468. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2023.112468
- Sparavigna, A. C. (2023). Iron Oxide Fe3O4 Nanoparticles with ICPs and Biochar to Improve Electromagnetic Shielding Performance. SSRN Electronic Journal. doi: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4331866
- Luo, Y., Yin, P., Wu, G., Zhang, L., Ma, G., Wang, J. et al. (2022). Porous carbon sphere decorated with Co/Ni nanoparticles for strong and broadband electromagnetic dissipation. Carbon, 197, 389–399. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.06.084
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Erlina Yustanti, Alfian Noviyanto, Annisa Nur Fauziah, Bachtiar Lubis, Adhitya Trenggono, Ahmad Taufiq

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








