Розробка композитів ядро–оболонка гексаферриту барію в якості високоефективного поглинання мікрохвиль шляхом оптимізації гідротермального синтезу
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.291064Ключові слова:
гексаферрит барію, композит ядро-оболонка, гідротермальний, дисульфід молібдену, матеріал радіопоглинача, втрати на відбиттяАнотація
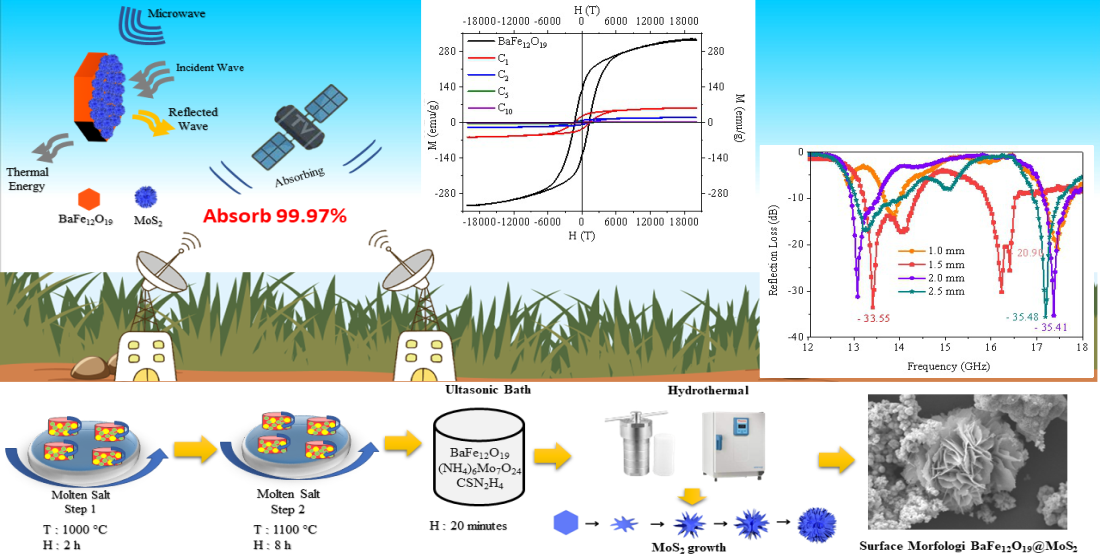
У поєднанні з підвищенням рівня життя в суспільстві та швидким розвитком інформаційних технологій на ринок з’являється велика різноманітність електронних пристроїв великої ємності. Підвищені вимоги призводять до генерації випромінювання електромагнітних хвиль, що становить потенційну небезпеку для здоров’я людини. Гексаферрит барію (ГФБ) є одним із радіопоглинаючих матеріалів (РАМ), які можуть поглинати електромагнітні хвилі, оскільки він має високе анізотропне поле. Однак його недоліками є вузьке поглинання і менша стабільність. Дисульфід молібдену (MoS2) є найкращим кандидатом для зміцнення ГФБ. Дослідження вивчало вплив збільшення тіосечовини, температури, часу гідротермічної витримки та товщини зразка на втрати відбиття. У цьому дослідженні використовувався двостадійний розплав солі та гідротермальний синтез для виготовлення композиту ядро-комірка BaFe12O19@MoS2. Методи двостадійного розплавленої солі та гідротермального синтезу створили однофазні композити BaFe12O19@MoS2 ядро-комірка, які добре працювали. Результати показали, що додавання MoS2 до ГФБ змінило магнітні властивості ГФБ з твердих на м’які. Підвищення гідротермальної температури до 220 °C ефективно зменшило втрати BaFe12O19@MoS2 на відображення. На зразку товщиною 2 мм, що містить 100 ммоль тіосечовини, дослідження досягло поглинання електромагнітних хвиль 99,97 % із втратою відбиття –35,41 дБ (17,37 ГГц). Результати цього дослідження можуть бути застосовані для захисту електронних пристроїв, вразливих до перешкод сигналу від супутникових радіолокаційних систем на частотах 12–18 ГГц
Посилання
- Asghar, G., Asri, S., Khusro, S. N., Tariq, G. H., Awan, M. S., Irshad, M., Safeen, A. et al. (2020). Enhanced Magnetic Properties of Barium Hexaferrite. Journal of Electronic Materials, 49 (7), 4318–4323. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08125-7
- Hema, S., Sambhudevan, S. (2021). Ferrite-based polymer nanocomposites as shielding materials: a review. Chemical Papers, 75 (8), 3697–3710. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01664-1
- Nikmanesh, H., Hoghoghifard, S., Hadi-Sichani, B., Moradi, M. (2020). Erbium-chromium substituted strontium hexaferrite particles: Characterization of the physical and Ku-band microwave absorption properties. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 262, 114796. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114796
- Yustanti, E., Trenggono, A., Manaf, A. (2020). Physical and Microwave Absorption Characteristics of High Powered Ultrasonically Irradiated Crystalline BaFe9Mn1.5Ti1.5O19 Particles. International Journal of Technology, 11 (2), 310. doi: https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v11i2.2988
- Feng, G., Zhou, W., Deng, H., Chen, D., Qing, Y., Wang, C. et al. (2019). Co substituted BaFe12O19 ceramics with enhanced magnetic resonance behavior and microwave absorption properties in 2.6 – 18 GHz. Ceramics International, 45 (11), 13859–13864. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.083
- Yang, E., Qi, X., Xie, R., Bai, Z., Jiang, Y., Qin, S. et al. (2018). Core@shell@shell structured carbon-based magnetic ternary nanohybrids: Synthesis and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. Applied Surface Science, 441, 780–790. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.029
- Wang, M., Lin, Y., Yang, H., Qiu, Y., Wang, S. (2020). A novel plate-like BaFe12O19@MoS2 core-shell structure composite with excellent microwave absorbing properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 817, 153265. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153265
- Rianna, M., Sembiring, T., Situmorang, M., Kurniawan, C., Tetuko, A. P., Setiadi, E. A. et al. (2019). Effect of calcination temperature on Microstructures, magnetic properties, and microwave absorption on BaFe11.6Mg0.2Al0.2O19 synthesized from natural iron sand. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 13, 100393. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2019.100393
- Zhang, Y., Gao, S., Xing, H. (2019). Hierarchical core–shell Fe3O4@C@MoS2 composites synergistically enhance microwave absorption. Materials Letters, 246, 80–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.03.031
- Wang, P., Zhang, J., Wang, G., Duan, B., He, D., Wang, T., Li, F. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of MoS2/Fe@Fe3O4 nanocomposites exhibiting enhanced microwave absorption performance at normal and oblique incidences. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 35 (9), 1931–1939. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.05.021
- Zhang, D., Chai, J., Cheng, J., Jia, Y., Yang, X., Wang, H. et al. (2018). Highly efficient microwave absorption properties and broadened absorption bandwidth of MoS2-iron oxide hybrids and MoS2-based reduced graphene oxide hybrids with Hetero-structures. Applied Surface Science, 462, 872–882. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.152
- Almessiere, M. A., Slimani, Y., Korkmaz, A. D., Baykal, A., Güngüneş, H., Sözeri, H. et al. (2019). Impact of La3+ and Y3+ ion substitutions on structural, magnetic and microwave properties of Ni0.3Cu0.3Zn0.4Fe2O4 nanospinel ferrites synthesized via sonochemical route. RSC Advances, 9 (53), 30671–30684. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra06353f
- Huang, W., Tong, Z., Bi, Y., Ma, M., Liao, Z., Wu, G. et al. (2021). Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of coralloid core-shell structure NiS/Ni3S4@PPy@MoS2 nanowires. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 599, 262–270. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.107
- Yang, H., Zhang, X., Xiong, Z., Shen, Z., Liu, C., Xie, Y. (2021). Cu2O@nanoporous carbon composites derived from Cu-based MOFs with ultrabroad-bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorbing performance. Ceramics International, 47 (2), 2155–2164. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.053
- Dai, B., Ma, Y., Dong, F., Yu, J., Ma, M., Thabet, H. K. et al. (2022). Overview of MXene and conducting polymer matrix composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 5 (2), 704–754. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00510-6
- Karim Darboe, A., Qi, X., Gong, X., Peng, Q., Chen, Y., Xie, R. et al. (2022). Constructing MoSe2/MoS2 and MoS2/MoSe2 inner and outer-interchangeable flower-like heterojunctions: A combined strategy of interface polarization and morphology configuration to optimize microwave absorption performance. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 624, 204–218. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.05.078
- Chang, M., Jia, Z., Wu, G., Yin, P. (2023). Multiple dimension-component designed Co/Co9S8/Ti3C2Tx MXene composite for enhanced microwave absorption. Applied Physics Letters, 122 (13). doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0142497
- Hou, T., Wang, J., Zheng, T., Liu, Y., Wu, G., Yin, P. (2023). Anion Exchange of Metal Particles on Carbon‐Based Skeletons for Promoting Dielectric Equilibrium and High‐Efficiency Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Small, 19 (42). doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202303463
- Zheng, T., Zhang, Y., Jia, Z., Zhu, J., Wu, G., Yin, P. (2023). Customized dielectric-magnetic balance enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance in CuxS/CoFe2O4 composites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 457, 140876. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140876
- Wang, S., Gao, H., Sun, G., Zhang, J., Xia, Y., Xie, C. et al. (2020). M-type Barium Hexaferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by γ-Ray Irradiation Assisted Polyacrylamide Gel Method and Its Optical, Magnetic and Supercapacitive Performances. Journal of Cluster Science, 32 (3), 569–578. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01815-6
- Maswadeh, Y., Mahmood, S. H., Awadallah, A., Aloqaily, A. N. (2015). Synthesis and structural characterization of nonstoichiometric barium hexaferrite materials with Fe:Ba ratio of 11.5 – 16.16. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 92, 012019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/92/1/012019
- Quilty, C. D., Housel, L. M., Bock, D. C., Dunkin, M. R., Wang, L., Lutz, D. M. et al. (2019). Ex Situ and Operando XRD and XAS Analysis of MoS2: A Lithiation Study of Bulk and Nanosheet Materials. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2 (10), 7635–7646. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b01538
- Albiter, M. A., Huirache-Acuña, R., Paraguay-Delgado, F., Rico, J. L., Alonso-Nuñez, G. (2006). Synthesis of MoS2nanorods and their catalytic test in the HDS of dibenzothiophene. Nanotechnology, 17 (14), 3473–3481. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/14/020
- Sulaiman, N. I., Abu Bakar, M., Abu Bakar, N. H. H., Saito, N., Thai, V.-P. (2023). Modified sol–gel method for synthesis and structure characterisation of ternary and quaternary ferrite-based oxides for thermogravimetrically carbon dioxide adsorption. Chemical Papers, 77 (6), 3051–3074. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02687-6
- Hu, F., Nan, H., Wang, M., Lin, Y., Yang, H., Qiu, Y., Wen, B. (2021). Construction of core-shell BaFe12O19@MnO2 composite for effectively enhancing microwave absorption performance. Ceramics International, 47 (12), 16579–16587. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.229
- Lu, C.-H., Yeh, C.-H. (2000). Influence of hydrothermal conditions on the morphology and particle size of zinc oxide powder. Ceramics International, 26 (4), 351–357. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-8842(99)00063-2
- Goel, S., Garg, A., Gupta, R. K., Dubey, A., Prasad, N. E., Tyagi, S. (2020). Development of RGO/BaFe12O19-based composite medium for improved microwave absorption applications. Applied Physics A, 126 (6). doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03613-3
- Alshoaibi, A. (2023). Investigating the Supercapacitive Performance of Cobalt Sulfide Nanostructures Prepared Using a Hydrothermal Method. Materials, 16 (13). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134512
- Li, W., Shi, E., Fukuda, T. (2003). Particle size of powders under hydrothermal conditions. Crystal Research and Technology, 38 (10), 847–858. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200310103
- Zhai, Y., Zhu, D., Zhou, W., Min, D., Luo, F. (2018). Enhanced impedance matching and microwave absorption properties of the MAMs by using ball-milled flaky carbonyl iron-BaFe12O19 as compound absorbent. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 467, 82–88. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.07.031
- Ari Adi, W., Sarwanto, Y., Taryana, Y., Soegijono, B. (2018). Effects of the geometry factor on the reflection loss characteristics of the modified lanthanum manganite. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1091, 012028. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1091/1/012028
- Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Zhu, Q., Zheng, Y., Liotta, L. F., Wu, H. (2021). High-efficiency and wide-bandwidth microwave absorbers based on MoS2-coated carbon fiber. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 586, 457–468. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.109
- Sun, Y., Zhong, W., Wang, Y., Xu, X., Wang, T., Wu, L., Du, Y. (2017). MoS2-Based Mixed-Dimensional van der Waals Heterostructures: A New Platform for Excellent and Controllable Microwave-Absorption Performance. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (39), 34243–34255. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10114
- Hassan, A., Aslam, M. A., Bilal, M., Khan, M. S., ur Rehman, S., Ma, K. et al. (2021). Modulating dielectric loss of MoS2@Ti3C2Tx nanoarchitectures for electromagnetic wave absorption with radar cross section reduction performance verified through simulations. Ceramics International, 47 (14), 20706–20716. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.014
- Negi, P., Kumar, A. (2021). MoS2 nanoparticle/activated carbon composite as a dual-band material for absorbing microwaves. Nanoscale Advances, 3 (14), 4196–4206. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1na00292a
- Qu, B., Zhu, C., Li, C., Zhang, X., Chen, Y. (2016). Coupling Hollow Fe3O4–Fe Nanoparticles with Graphene Sheets for High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Material. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8 (6), 3730–3735. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b12789
- Lin, Y., Liu, X., Ye, T., Yang, H., Wang, F., Liu, C. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of graphene/0.8BaFe12O19/0.2Y3Fe5O12 nanocomposite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 683, 559–566. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.117
- Li, H., Zheng, L., Deng, D., Yi, X., Zhang, X., Luo, X. et al. (2021). Multiple natural resonances broaden microwave absorption bandwidth of substituted M-type hexaferrites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 862, 158638. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158638
- McComiskey, K. P. M., Tajber, L. (2018). Comparison of particle size methodology and assessment of nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) as a tool for live monitoring of crystallisation pathways. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 130, 314–326. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.07.012
- Jose, N., Deshmukh, G. P., Ravindra, M. R. (2019). Dynamic Light Scattering: Advantages and Applications. Acta Scientific Nutritional Health, 3 (3), 50–52. Available at: https://www.actascientific.com/ASNH/pdf/ASNH-03-0194.pdf
- Almessiere, M. A., Güner, S., Slimani, Y., Korkmaz, A. D., Baykal, A. (2022). Effect of Mo substitution on structure, morphology and magnetic features of Sr0.8Ni0.2Fe12−2xMoxO19 (x ≤ 0.35) hexaferrites. Chemical Papers, 77 (2), 947–956. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02527-z
- Yustanti, E., Noviyanto, A., Ikramullah, M., Marsillam, Y. A., Taryana, Y., Taufiq, A. (2023). High-performance microwave absorption by optimizing hydrothermal synthesis of BaFe12O19@MnO2 core–shell composites. RSC Advances, 13 (39), 27634–27647. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ra05114e
- Liu, D., Liu, H., Ning, S., Chu, Y. (2020). Chrysanthemum-like high-entropy diboride nanoflowers: A new class of high-entropy nanomaterials. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 9 (3), 339–348. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-020-0373-x
- Yin, P., Wu, G., Tang, Y., Liu, S., Zhang, Y., Bu, G. et al. (2022). Structure regulation in N-doping biconical carbon frame decorated with CoFe2O4 and (Fe,Ni) for broadband microwave absorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 446, 136975. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136975
- Khan, M. Z., Gul, I. H., Javaid, F., Ali, A., Hafeez, S., Baig, M. M. (2023). Synthesis and Characterization of Zr4+-Y3+ Substituted Ba-Sr Hexaferrite Nanoparticles for Microwave Absorption and Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Materials Research Bulletin, 168, 112468. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2023.112468
- Sparavigna, A. C. (2023). Iron Oxide Fe3O4 Nanoparticles with ICPs and Biochar to Improve Electromagnetic Shielding Performance. SSRN Electronic Journal. doi: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4331866
- Luo, Y., Yin, P., Wu, G., Zhang, L., Ma, G., Wang, J. et al. (2022). Porous carbon sphere decorated with Co/Ni nanoparticles for strong and broadband electromagnetic dissipation. Carbon, 197, 389–399. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.06.084
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2023 Erlina Yustanti, Alfian Noviyanto, Annisa Nur Fauziah, Bachtiar Lubis, Adhitya Trenggono, Ahmad Taufiq

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









