Adaptation of Stadier's apparatus for electrophoresis of main milk proteins
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.296753Keywords:
apparatus for electrophoresis, casein fractions, milk whey proteins, electrophoretic systemsAbstract
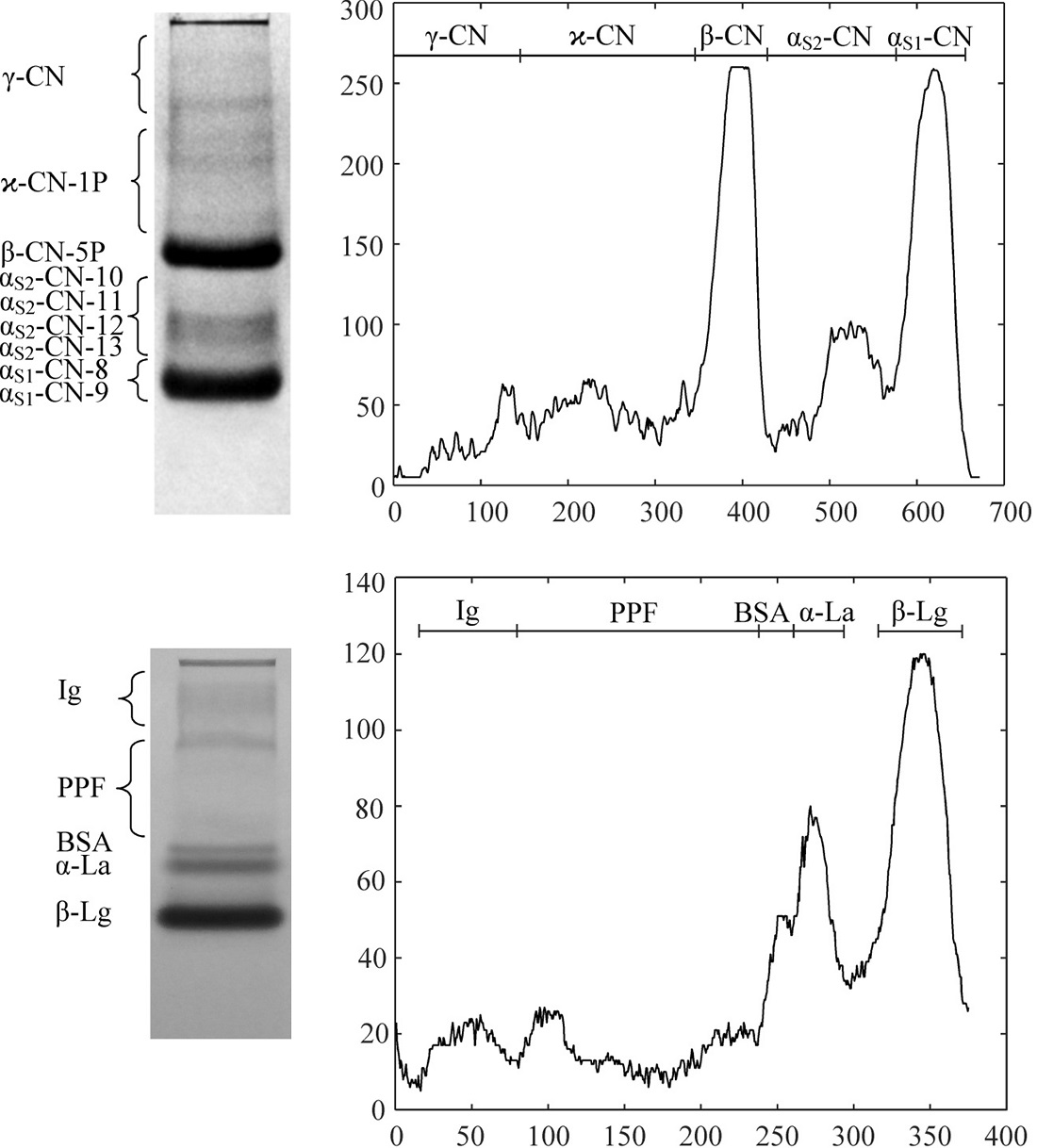
The object of research is a Stadier-type apparatus for analytical electrophoresis of proteins. In the milk proteins research, in addition, there is a need to carry out serial express analyzes of their various groups, as well as the isolation of individual homogeneous fractions. The dimensions of working chambers for analytical, express, and micro preparative electrophoresis of caseins and milk whey proteins were proposed to solve this task. For each type of electrophoresis, different chambers and formers are used without changing the design of the apparatus. The apparatus is suitable for electrophoretic systems used for the analysis of milk proteins. Analysis of casein in the anodic system of a homogeneous polyacrylamide gel in the presence of urea allows identification of the main fractions: αS1-CN-8P, αS1-CN-9P, αS2-CN-10P, αS2-CN-11P, αS2-CN-12P, αS2-CN-13P, β-CN-5P, ϰ-CN-1P and three β-casein fragments f(29-209), f(106-209) and f(108-209). Express electrophoresis in the presence of urea reveals four fractions of caseins: αS1-CN, αS2-CN, β-CN, and ϰ-CN. The analysis of whey proteins in the Davis native disc electrophoresis system allows identification of β-Lg A, β-Lg B, α-La, BSA fractions, and a group of immunoglobulin fractions. The express electrophoregram differs by a common band A and B variants of β-Lg. Due to an adequate selection of electrophoretic systems, it is possible to identify semi-quantitatively all the main fractions of milk proteins under analytical or express mode. The adapted apparatus also makes it possible to conduct micro preparative electrophoresis and obtain the main fractions of milk proteins. In this case, the yield of electrophoretically pure proteins is: β-CN-5P (23±5 %), β-Lg (A+B) (27±6 %), α-La (11±3 %), and purified groups of αS1-CN-8P+αS1-CN-9P (25±6 %), αS2-CN-(10-13P) (6±1.5 %) and ϰ-CN-1P (7±2 %). The apparatus could be used at enterprises producing dairy protein products
References
- Fox, P. F., Uniacke-Lowe, T., McSweeney, P. L. H., O’Mahony, J. A. (2015). Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry. Springer, 584. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14892-2
- Yukalo, V. H. (2021). Biolohichna aktyvnist proteiniv i peptydiv moloka. Ternopil: Vyd-vo TNTU imeni Ivana Puliuia, 372, 372. Available at: http://elartu.tntu.edu.ua/handle/lib/36801
- Kukhtyn, M., Vichko, O., Kravets, O., Karpyk, H., Shved, O., Novikov, V. (2019). Biochemical and microbiological changes during fermentation and storage of a fermented milk product prepared with Tibetan Kefir Starter. Archivos Latinoamericanos de Nutrición, 68 (4), 336–343. https://doi.org/10.37527/2018.68.4.007
- Kukhtyn, M., Salata, V., Horiuk, Y., Kovalenko, V., Ulko, L., Prosyanуi, S. et al. (2021). The influence of the denitrifying strain of Staphylococcus carnosus No. 5304 on the content of nitrates in the technology of yogurt production. Potravinarstvo Slovak Journal of Food Sciences, 15, 66–73. https://doi.org/10.5219/1492
- Minorova, A., Romanchuk, I., Verbytskyi, S., Danylenko, S., Krushelnytska, N., Potemska, O., Narizhnyi, S. (2022). Effect of protein and carbohydrate components upon quality parameters and viable probiotic bacteria content in milk mixtures during their drying and storage. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences, e3778. https://doi.org/10.55251/jmbfs.3778
- Slyvka, I., Tsisaryk, O., Musii, L., Kushnir, I., Koziorowski, M., Koziorowska, A. (2022). Identification and Investigation of properties of strains Enterococcus spp. Isolated from artisanal Carpathian cheese. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 39, 102259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102259
- Musiy, L., Tsisaryk, O., Slyvka, I., Mykhaylytska, O., Gutyj, B. (2017). Research into probiotic properties of cultured butter during storing. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (11 (87)), 31–36. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.103539
- Sharma, N., Sharma, R., Rajput, Y. S., Mann, B., Singh, R., Gandhi, K. (2021). Separation methods for milk proteins on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: Critical analysis and options for better resolution. International Dairy Journal, 114, 104920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2020.104920
- Duarte-Vázquez, M. A., García-Ugalde, C. R., Álvarez, B. E., Villegas, L. M., García-Almendárez, B. E. et al. (2018). Use of urea-polyacrylamide electrophoresis for discrimination of A1 and A2 beta casein variants in raw cow’s milk. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 55 (5), 1942–1947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3088-z
- Hinz, K., O’Connor, P. M., Huppertz, T., Ross, R. P., Kelly, A. L. (2012). Comparison of the principal proteins in bovine, caprine, buffalo, equine and camel milk. Journal of Dairy Research, 79 (2), 185–191. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022029912000015
- Yukalo, V., Datsyshyn, K., Storozh, L. (2019). Electrophoretic system for express analysis of whey protein fractions. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (11 (98)), 37–44. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.160186
- Nollet, L. M. L., Toldra, F. (Eds.) (2009). Handbook of Dairy Foods Analysis. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420046328
- Farrell, H. M., Jimenez-Flores, R., Bleck, G. T., Brown, E. M., Butler, J. E., Creamer, L. K. et al. (2004). Nomenclature of the Proteins of Cows’ Milk—Sixth Revision. Journal of Dairy Science, 87 (6), 1641–1674. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(04)73319-6
- Iukalo, А. V. (2015). Identification of protein fractions of milk cows casein complex. The Ukrainian Biochemical Journal, 87 (4), 87–91. https://doi.org/10.15407/ubj87.04.087
- Iukalo, A. V. (2014). New Approach for Isolation of Individual Caseins from Cow Milk by the Preparative Electrophoresis. Advances in Biological Chemistry, 04 (06), 382–387. https://doi.org/10.4236/abc.2014.46043
- Nurup, C. N., Czárán, T. L., Rattray, F. P. (2020). A chromatographic approach to understanding the plasmin-plasminogen system in acid whey. International Dairy Journal, 106, 104705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2020.104705
- Qian, F., Sun, J., Cao, D., Tuo, Y., Jiang, S., Mu, G. (2017). Experimental and Modelling Study of the Denaturation of Milk Protein by Heat Treatment. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 37 (1), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.5851/kosfa.2017.37.1.44
- Yukalo, A., Yukalo, V., Shynkaryk, M. (2009). Electrophoretic separation of the milk protein. Proceeding of the International Conference on Bio and Food Electrotechnologies, 227–231.
- Pesic, M., Barac, M., Vrvic, M., Ristic, N., Macej, O., Stanojevic, S. (2011). Qualitative and quantitative analysis of bovine milk adulteration in caprine and ovine milks using native-PAGE. Food Chemistry, 125 (4), 1443–1449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.10.045
- Yukalo, V., Datsyshyn, K., Krupa, O., Pavlistova, N. (2019). Obtaining of β-LG, α-LA and BSA protein fractions from milk whey. Ukrainian Food Journal, 8 (4), 788–798. https://doi.org/10.24263/2304-974x-2019-8-4-10
- Raak, N., Abbate, R., Lederer, A., Rohm, H., Jaros, D. (2018). Size Separation Techniques for the Characterisation of Cross-Linked Casein: A Review of Methods and Their Applications. Separations, 5 (1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations5010014
- Yukalo, V. G. (2005). Obtaining of casein protein complex fractions from cow milk. Nutracos, 5, 7–19.
- Studier, F. W. (1965). Sedimentation studies of the size and shape of DNA. Journal of Molecular Biology, 11 (2), 373–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x
- Choveaux, D., Krause, R. G. E., Goldring, J. P. D. (2012). Rapid Detection of Proteins in Polyacrylamide Electrophoresis Gels with Direct Red 81 and Amido Black. Protein Electrophoresis, 585–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-821-4_53
- Mao, X. Y., Tong, P. S., Gualco, S., Vink, S. (2012). Effect of NaCl addition during diafiltration on the solubility, hydrophobicity, and disulfide bonds of 80% milk protein concentrate powder. Journal of Dairy Science, 95 (7), 3481–3488. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2011-4691
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Volodymy Yukalo, Kateryna Datsyshyn, Olha Krupa, Liudmyla Storozh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








