Results of the analytical solution of the problem of radial vibrations of disks of variable thickness
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.300090Keywords:
disk of variable thickness, radial vibrations, natural frequencies, waveforms, stressesAbstract
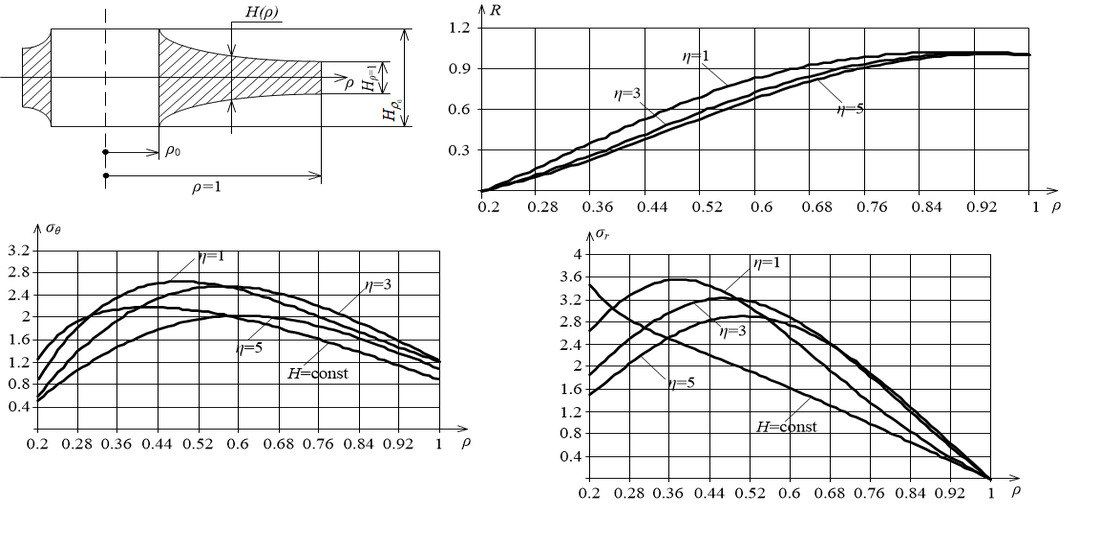
An analytical solution is obtained for the problem of radial vibrations of disks of variable thickness. A disk is considered that is rigidly fixed along the inner circular contour (ρ=0.2) and free on the outer contour (ρ=1). The thickness of the disk varies according to the law H=H0(ρν+μ+Cρν-μ)2, where H0,C,μ are arbitrary constants; ν is the Poisson's ratio. The exact solution of the problem is known only for H=const and H=1/ρ3. However, these solutions are not sufficient to study the vibrations of disks of other configurations. The proposed law of thickness variation H(ρ) allows us to obtain exact solutions to the problem at any value of the constant coefficients H0, C, μ, ν. By varying the values of these coefficients within a single given function, it is possible to set the disk profile of the desired appearance. The methods used to obtain these solutions are based on appropriate mathematical transformations of the original equation.
The problem of disk oscillations is solved for four variants of thickness change. The natural frequencies for the first three forms of vibration are calculated. Comparison of the natural frequencies found for the three cases of the disk profile gently sloping indicates an increase in their values with an increase in the bending of the disk thickness. Based on the obtained eigenfunctions, the stresses were calculated and the nature of their distribution along the radial coordinate of the disk was determined.
The strength of the disks under resonant radial vibrations was evaluated using a special criterion. It is found that the most limiting, i.e., destructive principal stress σ1=σr at the first (main) form of vibration should be chosen from the ratio σr≈0.79 [σ-1], where [σ-1] is the endurance limit of the disk material under uniform loading. The results obtained can be used to predict the stress-strain state of disks of variable profile under their radial vibrations
References
- Prabith, K., Krishna, I. R. P. (2020). The numerical modeling of rotor–stator rubbing in rotating machinery: a comprehensive review. Nonlinear Dynamics, 101 (2), 1317–1363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05832-y
- Doshi, S., Katoch, A., Suresh, A., Razak, F. A., Datta, S., Madhavan, S. et al. (2021). A Review on Vibrations in Various Turbomachines such as Fans, Compressors, Turbines and Pumps. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies, 9 (7), 1557–1575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-021-00313-x
- Salehian, M., Shahriari, B., Yousefi, M. (2018). Investigating the effect of angular acceleration of the rotating disk having variable thickness and density function on shear stress and tangential displacement. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 41 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1523-8
- Koul, A. K., Dainty, R. V. (2022). Fatigue Fracture of Aircraft Engine Compressor Disks. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 22 (5), 1995–2004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-022-01516-4
- Eldeeb, A. M., Shabana, Y. M., El-Sayed, T. A., Elsawaf, A. (2023). A nontraditional method for reducing thermoelastic stresses of variable thickness rotating discs. Scientific Reports, 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-39878-w
- Thakur, P., Kumar, N., Gupta, K. (2022). Thermal stress distribution in a hyperbolic disk made of rubber/brass material. Journal of Rubber Research, 25 (1), 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42464-022-00147-6
- Takkar, S., Gupta, K., Tiwari, V., Singh, S. P. (2019). Dynamics of Rotating Composite Disc. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies, 7 (6), 629–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-019-00155-8
- Koo, K.-N. (2006). Vibration analysis and critical speeds of polar orthotropic annular disks in rotation. Composite Structures, 76 (1-2), 67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2006.06.010
- Yıldırım, V. (2018). Numerical/analytical solutions to the elastic response of arbitrarily functionally graded polar orthotropic rotating discs. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 40 (6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1216-3
- Kutsal, S. M., Coşkun, S. B. (2023). Analytical approximations for elastic limit angular velocities of rotating annular disks with hyperbolic thickness. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 45 (6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-023-04132-x
- Shatalov, M. Y., Joubert, S. V., Peck, A. J. (2020). Axisymmetric and Non-Axisymmetric Vibration of Thin Growing Viscoelastic Disc. Mechanics of Solids, 55 (5), 741–759. https://doi.org/10.3103/s0025654420050179
- Wang, R., Wang, Q., Guan, X., Zhang, Y., Shao, W. (2021). Coupled free vibration analysis of functionally graded shaft-disk system by differential quadrature finite element method. The European Physical Journal Plus, 136 (2). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01131-6
- Wu, C., Su, Z., Wang, D., Jiang, H. (2023). Dynamic modeling method for active magnetic bearings-rotor system of steam turbines. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 37 (4), 1665–1673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-023-0308-x
- Biezeno, C. B., Grammel, R. (1939). Technische Dynamik. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-36257-0
- Collatz, L. (1963). Eigenwertaufgaben mit technischen anwendungen. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft. Leipzig, 500.
- Kamke, E. (1959). Differential gleichungen, Losungsmethoden und losungen. Leipzig, 244.
- Trapezon, A. G., Lyashenko, B. A. (2016). Fatigue of VT1-0 Titanium Alloy with Vacuum-Plasma Coating Under a Plane Stress State. Strength of Materials, 48 (2), 270–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-016-9762-3
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Kirill Trapezon, Alexandr Trapezon, Vitalii Kalinichenko, Vitaliy Didkovskii

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








