Improvement of the delumping method in order to obtain detailed characteristics of the fluid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.310558Keywords:
delumping, lumping, pseudo-component, plus fraction, binary interaction parameters, K-value, equation of state, flash, compositional modeling, Kazakhstani oilAbstract
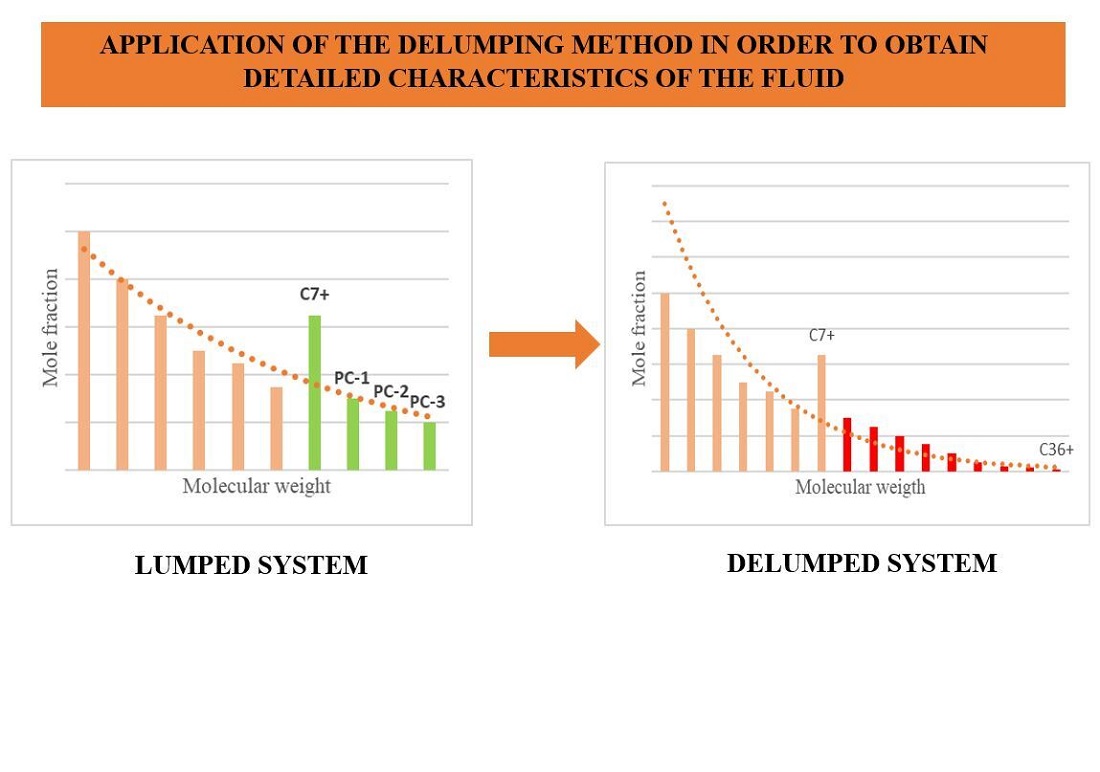
In compositional modeling, the phase characteristics and behavior of reservoir fluids are calculated using the equation of state. To simplify the calculations and speed them up, the components of the heptane plus fraction (C7+) are grouped into pseudo-components. However, after this procedure, the results of compositional modelling of the reservoir containing the pseudo-components need to be delumped so that they can be used in surface models. It follows from this that the problem lies in the fact that the grouped composition cannot be applied to the modeling of ground structures. The object of the study is Kazakhstani oil, on the example of which a detailed component composition was obtained by analytical delumping based on reduction parameters. In laboratory conditions, the component composition of oil, and other fluid properties were determined. The study presents the results that prove the importance of applying the delumping algorithm in the context of compositional modeling. The results obtained analytically correspond quite accurately to the numerical calculations of the PVTsim software and laboratory experiments. A comparison of existing methods showed a difference of 5 %, which suggests that delumping is an excellent method for describing and obtaining a detailed composition of the hydrocarbon mixture. In practice, the results of the detailed composition of hydrocarbons can be used for the design of refineries. Also, the findings from this research can enhance the planning and design of surface facilities, particularly when developed under reservoir conditions where the pressure exceeds the saturation pressure
References
- Yushchenko, T. S., Brusilovsky, A. I. (2022). A step-by-step approach to creating and tuning PVT-models of reservoir hydrocarbon systems based on the state equation. Georesursy, 24 (2), 164–181. https://doi.org/10.18599/grs.2022.3.14
- Leibovici, C. F., Barker, J. W., Waché, D. (2000). Method for Delumping the Results of Compositional Reservoir Simulation. SPE Journal, 5 (02), 227–235. https://doi.org/10.2118/64001-pa
- Assareh, M., Ghotbi, C., Pishvaie, M. R., Mittermeir, G. M. (2013). An analytical delumping methodology for PC-SAFT with application to reservoir fluids. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 339, 40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2012.11.025
- Whitson, C. H., Brulé, M. R. (2000). Phase Behavior. Society of Petroleum Engineers. https://doi.org/10.2118/9781555630874
- Barker, J. W., Leibovici, C. F. (1999). Delumping Compositional Reservoir Simulation Results: Theory and Applications. All Days. https://doi.org/10.2118/51896-ms
- Al-Meshari, A. A., McCain, W. D. (2005). New Strategic Method to Tune Equation-of-State for Compositional Simulation. All Days. https://doi.org/10.2118/106332-ms
- Al-Marhoun, M. (2023). Estimation of Missing Molecular Weight and Specific Gravity of Heptane Plus Fraction in PVT Laboratory Report. Middle East Oil, Gas and Geosciences Show. https://doi.org/10.2118/213430-ms
- Schlijper, A. G., Drohm, J. K. (1988). Inverse Lumping: Estimating Compositional Data From Lumped Information. SPE Reservoir Engineering, 3 (03), 1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.2118/14267-pa
- Leibovici, C., Stenby, E. H., Knudsen, K. (1996). A consistent procedure for pseudo-component delumping. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 117 (1-2), 225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3812(95)02957-5
- Nichita, D. V., Broseta, D., Leibovici, C. F. (2007). Reservoir fluid applications of a pseudo-component delumping new analytical procedure. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 59 (1-2), 59–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2007.03.003
- De Castro, D. T., Nichita, D. V., Broseta, D., Herriou, M., Barker, J. W. (2011). Improved Delumping of Compositional Simulation Results. Petroleum Science and Technology, 29 (1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916460903330098
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ayaulym Baibekova, Jamilyam Ismailova, Dinara Delikesheva, Aibek Abdukarimov, Aigerim Kaidar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








