Method for solving distributional problems of mathematical programming under conditions of fuzzy initial data
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.310569Keywords:
distribution problem of mathematical programming, fuzzy initial data, method for solving the problemAbstract
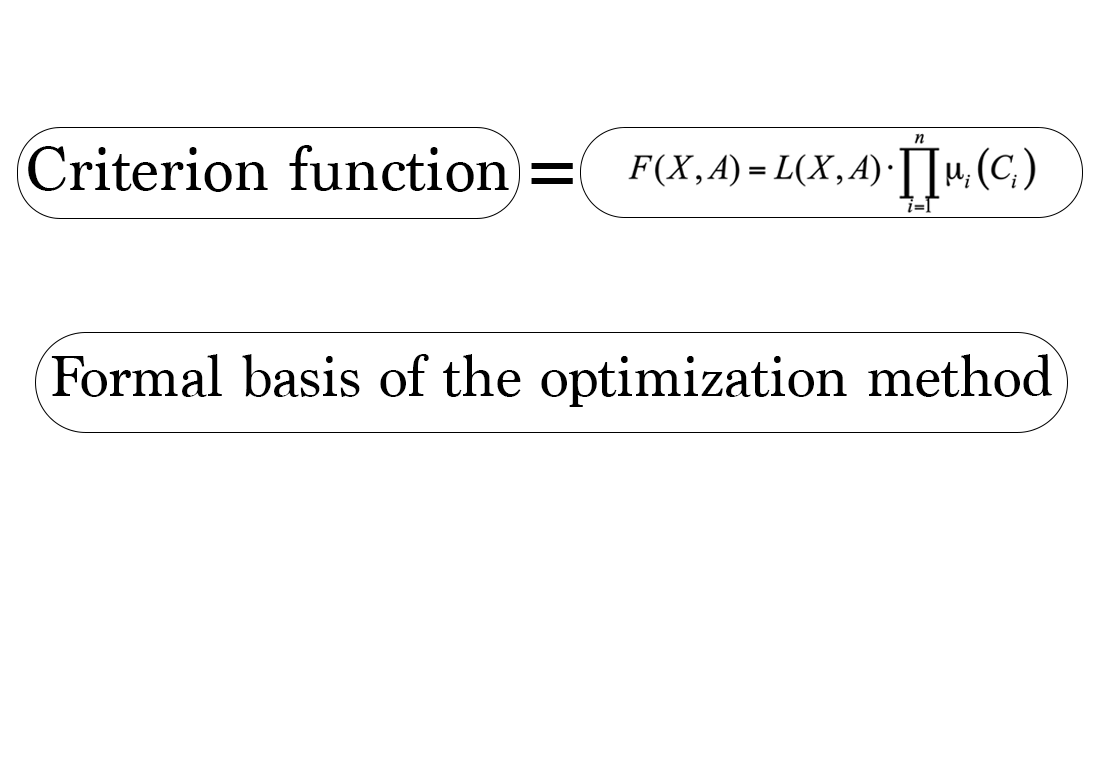
The object of this study is a large class of mathematical programming problems under conditions of uncertainty of initial data. The formulated object generates a subclass of problems of rational distribution of a limited resource under conditions of initial data described in terms of fuzzy mathematics. The conventional, standardly used method for solving such problems is based on optimization on average. To obtain such a solution, it is sufficient to replace all fuzzy initial data with their modal values in the analytical description of the mathematical model of the corresponding problem. To solve the resulting deterministic problem, one can use known methods of mathematical programming. However, the results of such a solution can be used in practice if the carriers of fuzzy parameters are specified compactly, that is, the intervals of possible values of fuzzy parameters of the problem are small. Otherwise, the implementation of this solution may lead to unpredictably large losses. Other alternative approaches are based on the use of insufficiently informative estimates of the best or worst possible values of fuzzy parameters of the problem. These circumstances make the statement of the problem and the objective of the study relevant: devising a method for solving the problem of rational distribution of a limited resource under conditions of fuzzy initial data. To solve the stated problem of rational distribution of a limited resource, a productive idea of constructing the proposed general optimization method under conditions of uncertainty of the initial data has been constructively implemented. In this case, the initial problem is reduced to a clear problem of optimizing a complex criterion constructed on the basis of the objective function of the initial problem and a set of membership functions of its fuzzy parameters. An example of solving the problem has been considered, leading to a solution that is better than that obtained on the basis of the modal values of the fuzzy parameters of the problem
References
- Gill, P. E., Murray, W., Wright, M. H. (1981). Practical optimization. Academic Press Inc.
- Taha, H. A. (2007). Operations Research: An Introduction. Pearson. Available at: https://dl.icdst.org/pdfs/files3/7e932ab65f9aa3de7122b4cea3587377.pdf
- Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8 (3), 338–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0019-9958(65)90241-x
- Liao, T. W., Egbelu, P. J., Sarker, B. R., Leu, S. S. (2011). Metaheuristics for project and construction management – A state-of-the-art review. Automation in Construction, 20 (5), 491–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2010.12.006
- Mandi, J., Demirovi, E., Stuckey, P. J., Guns, T. (2020). Smart Predict-and-Optimize for Hard Combinatorial Optimization Problems. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 34 (02), 1603–1610. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i02.5521
- İnce, N. (2021). Generalized Fuzzy Entropy Optimization Methods for Fuzzy Data Analysis. Intelligent and Fuzzy Techniques for Emerging Conditions and Digital Transformation, 453–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85626-7_53
- Li, F.-C., Jin, C.-X. (2008). Study on fuzzy optimization methods based on principal operation and inequity degree. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 56 (6), 1545–1555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2008.02.042
- Mai, D. S., Dang, T. H., Ngo, L. T. (2020). Optimization of interval type-2 fuzzy system using the PSO technique for predictive problems. Journal of Information and Telecommunication, 5 (2), 197–213. https://doi.org/10.1080/24751839.2020.1833141
- Ekel, P. Ya. (1999). Approach to decision making in fuzzy environment. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 37 (4-5), 59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0898-1221(99)00059-0
- Liu, G., Yu, J. (2007). Gray correlation analysis and prediction models of living refuse generation in Shanghai city. Waste Management, 27 (3), 345–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.03.010
- Halilović, D., Gligorić, M., Gligorić, Z., Pamučar, D. (2023). An Underground Mine Ore Pass System Optimization via Fuzzy 0–1 Linear Programming with Novel Torricelli–Simpson Ranking Function. Mathematics, 11 (13), 2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132914
- Kicsiny, R., Hufnagel, L., Varga, Z. (2022). Allocation of limited resources under quadratic constraints. Annals of Operations Research, 322 (2), 793–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-05114-3
- Bertalanfi, L. fon. (1973). Istoriya i status obschey teorii sistem. V kn.: Sistemnye issledovaniya. Metodologicheskie problemy. Ezhegodnik. Moscow: «Nauka», 20–37.
- Raskin, L., Sira, O. (2016). Method of solving fuzzy problems of mathematical programming. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (4 (83)), 23–28. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2016.81292
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Lev Raskin, Oksana Sira, Artur Hatunov, Roman Riabokon, Rodyslav Sinitsyn

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








