Substantiating the reliability conditions for the production process at metallurgical enterprises through the fault-tolerant functioning of the system «extraction of raw materials – technological railroad routes – metallurgical production»
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.310679Keywords:
insurance stock, dispatch route, discrete-event principle, population of agents, level of fault toleranceAbstract
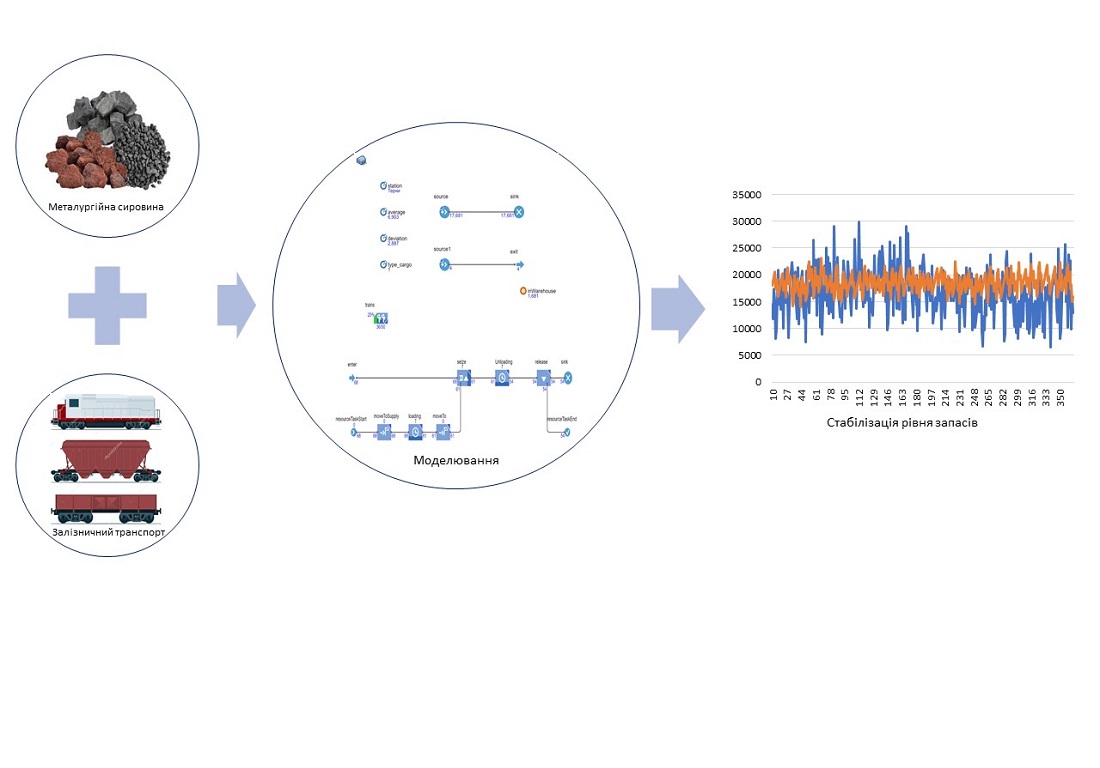
The object of this study is the process of formation of insurance reserves at enterprises in the metallurgical industry. Under conditions of uneven supply of raw materials to metallurgical enterprises due to disruption of the transportation process or other reasons, there is a need to create insurance stocks in order to ensure the continuity of production. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account existing restrictions, such as the limited capacity of railroad sections and the impossibility of organizing parallel movement of trains, etc. The presence of these limitations makes it impossible to use classical methods for solving similar problems, such as linear programming. Therefore, to resolve the task, a simulation model was built, based on the discrete-event principle in the AnyLogic University Researcher environment using Oracle libraries and the Java SE compiler. With the help of the model, the process of rotation of dispatch routes at the railroad yard with multiple suppliers and one consignee was formalized. The optimization criterion was chosen to be the minimum deviations of fluctuations in reserves of iron ore concentrate and coke. Analysis of the simulation results revealed that the optimal size of the fleet of railroad routes on the selected rotation polygon is 30 units; at the same time, their utilization rate will be 65 %. It was also established that fluctuations in raw material stocks have a «natural character», which is confirmed by the normal distribution of the density of stock volumes. Under these conditions, the value of fluctuations in the volumes of the main raw materials will be ±13115 t/day for iron ore concentrate, and ±5298 t/day for coke. Reducing the range of fluctuation of raw materials volumes could make it possible to optimize the costs of creating stocks and streamline the transport work of the enterprise for providing raw materials
References
- Matsiuk, V. (2017). A study of the technological reliability of railway stations by an example of transit trains processing. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (3 (85)), 18–24. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.91074
- Parida, P. (2014). Unlocking Mineral Resource Potential in Southern African Countries: Is Rail Infrastructure up to the Challenge? Transportation Research Procedia, 1 (1), 206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2014.07.021
- Vaezi, A., Verma, M. (2017). An analytics approach to dis-aggregate national freight data to estimate hazmat traffic on rail-links and at rail-yards in Canada. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 7 (4), 291–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrtpm.2017.12.001
- Grushevska, K., Notteboom, T., Shkliar, A. (2016). Institutional rail reform: The case of Ukrainian Railways. Transport Policy, 46, 7–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2015.11.001
- Gupta, D., Dhar, S. (2022). Exploring the freight transportation transitions for mitigation and development pathways of India. Transport Policy, 129, 156–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2022.10.013
- Guglielminetti, P., Piccioni, C., Fusco, G., Licciardello, R., Musso, A. (2017). Rail Freight Network in Europe: Opportunities Provided by Re-launching the Single Wagonload System. Transportation Research Procedia, 25, 5185–5204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2018.02.047
- Crozet, Y. (2017). Rail freight development in Europe: how to deal with a doubly-imperfect competition? Transportation Research Procedia, 25, 425–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2017.05.420
- Bouraima, M. B., Qiu, Y., Yusupov, B., Ndjegwes, C. M. (2020). A study on the development strategy of the railway transportation system in the West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU) based on the SWOT/AHP technique. Scientific African, 8, e00388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00388
- Skoczylas, A., Stefaniak, P., Gryncewicz, W., Rot, A. (2023). The Concept of an Intelligent Decision Support System for Ore Transportation in Underground Mine. Procedia Computer Science, 225, 922–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2023.10.079
- Katsman, M. D., Matsiuk, V. I., Myronenko, V. K. (2023). Modeling the reliability of transport under extreme conditions of operation as a queuing system with priorities. Reliability: Theory & Applications, 2 (73), 167–179. https://doi.org/10.24412/1932-2321-2023-273-167-179
- Matsiuk, V., Opalko, V., Savchenko, L., Zagurskiy, O., Matsiuk, N. (2023). Optimisation of transport and technological system parameters of an agricultural enterprise in conditions of partial uncertainty. Naukovij Žurnal «Tehnìka Ta Energetika», 14 (3), 61–71. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/3.2023.61
- Anufriyeva, T., Matsiuk, V., Shramenko, N., Ilchenko, N., Pryimuk, O., Lebid, V. (2023). Construction of a simulation model for the transportation of perishable goods along variable routes. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (4 (122)), 42–51. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.277948
- Karmanesh, Y., Bagheri, M., Mohammad Hasany, R., Saman Pishvaee, M. (2024). Two-stage stochastic programming approach for fleet sizing and allocating rail wagon under uncertain demand. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 188, 109878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2023.109878
- Michal, G., Huynh, N., Shukla, N., Munoz, A., Barthelemy, J. (2017). RailNet: A simulation model for operational planning of rail freight. Transportation Research Procedia, 25, 461–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2017.05.426
- Prokhorchenko, А., Parkhomenko, L., Kyman, A., Matsiuk, V., Stepanova, J. (2019). Improvement of the technology of accelerated passage of low-capacity car traffic on the basis of scheduling of grouped trains of operational purpose. Procedia Computer Science, 149, 86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.01.111
- Tang, X., Jin, J. G., Shi, X. (2022). Stockyard storage space allocation in large iron ore terminals. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 164, 107911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107911
- Song, L., Yu, L., Li, S. (2023). Route optimization of hazardous freight transportation in a rail-truck transportation network considering road traffic restriction. Journal of Cleaner Production, 423, 138640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138640
- Okorokov, A. (2015). Development of techniques to optimize the technical parameters of transport cargo complexes. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (3 (74)), 9–14. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2015.39792
- Ren, Q., Xu, M. (2024). Injury severity analysis of highway-rail grade crossing crashes in non-divided two-way traffic scenarios: A random parameters logit model. Multimodal Transportation, 3 (1), 100109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.multra.2023.100109
- Schöbel, A., Aksentijevic, J., Stefan, M., Blieberger, J. (2017). Optimization of rail traffic flow using Kronecker algebra during maintenance on infrastructure. Transportation Research Procedia, 27, 545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2017.12.040
- Matsiuk, V., Galan, O., Prokhorchenko, A., Tverdomed, V. (2021). An Agent-Based Simulation for Optimizing the Parameters of a Railway Transport System. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on ICT in Education, Research and Industrial Applications. Integration, Harmonization and Knowledge Transfer. Volume I: Main Conference. https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3013/20210121.pdf
- Kozachenko, D., Vernigora, R., Balanov, V., Berezovy, N., Yelnikova, L., Germanyuk, Y. (2016). Evaluation of the Transition to the Organization of Freight Trains Traffic By the Schedule. Transport Problems, 11 (1), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.20858/tp.2016.11.1.4
- Namazov, M., Matsiuk, V., Bulgakova, I., Nikolaienko, I., Vernyhora, R. (2023). Agent-based simulation model of multimodal iron ore concentrate transportation. Naukovij Žurnal «Tehnìka Ta Energetika», 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2023.46
- Bulakh, M., Okorokov, A., Baranovskyi, D. (2021). Risk System and Railway Safety. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 666 (4), 042074. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/666/4/042074
- Panchenko, S., Prokhorchenko, A., Dekarchuk, O., Gurin, D., Mkrtychian, D., Matsiuk, V. (2020). Development of a method for studying the impact of the time reserve value on the reliability of the train schedule based on the epidemiological SIR model. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 1002 (1), 012016. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1002/1/012016
- D’Ariano, A., Meng, L., Centulio, G., Corman, F. (2019). Integrated stochastic optimization approaches for tactical scheduling of trains and railway infrastructure maintenance. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 127, 1315–1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.12.010
- Pashchenko, F. F., Kuznetsov, N. A., Ryabykh, N. G., Minashina, I. K., Zakharova, E. M., Tsvetkova, O. A. (2015). Implementation of Train Scheduling System in Rail Transport using Assignment Problem Solution. Procedia Computer Science, 63, 154–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.08.326
- Yi, X., Marlière, G., Pellegrini, P., Rodriguez, J., Pesenti, R. (2023). Coordinated train rerouting and rescheduling in large infrastructures. Transportation Research Procedia, 72, 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2023.11.410
- Samà, M., Meloni, C., D’Ariano, A., Corman, F. (2015). A multi-criteria decision support methodology for real-time train scheduling. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 5 (3), 146–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrtpm.2015.08.001
- Gupta, P., Bazargan, M., McGrath, R. N. (2003). Simulation model for aircraft line maintenance planning. Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium. https://doi.org/10.1109/rams.2003.1182020
- Secchi, D., Grimm, V., Herath, D. B., Homberg, F. (2024). Modeling and theorizing with agent-based sustainable development. Environmental Modelling & Software, 171, 105891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105891
- Hoffmann, T., Ye, M., Zino, L., Cao, M., Rauws, W., Bolderdijk, J. W. (2024). Overcoming inaction: An agent-based modelling study of social interventions that promote systematic pro-environmental change. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 94, 102221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2023.102221
- Achter, S., Borit, M., Cottineau, C., Meyer, M., Polhill, J. G., Radchuk, V. (2024). How to conduct more systematic reviews of agent-based models and foster theory development - Taking stock and looking ahead. Environmental Modelling & Software, 173, 105867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105867
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oleksandr Zaruba, Andrii Okorokov, Roman Vernyhora, Iryna Zhuravel, Nataliia Barkalova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








