Query expansion based on context-dependent sentiment analysis in databases with domain-specific filtering
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322120Keywords:
query expansion, natural language processing (NLP), information retrieval (IR), semantic analysis, databaseAbstract
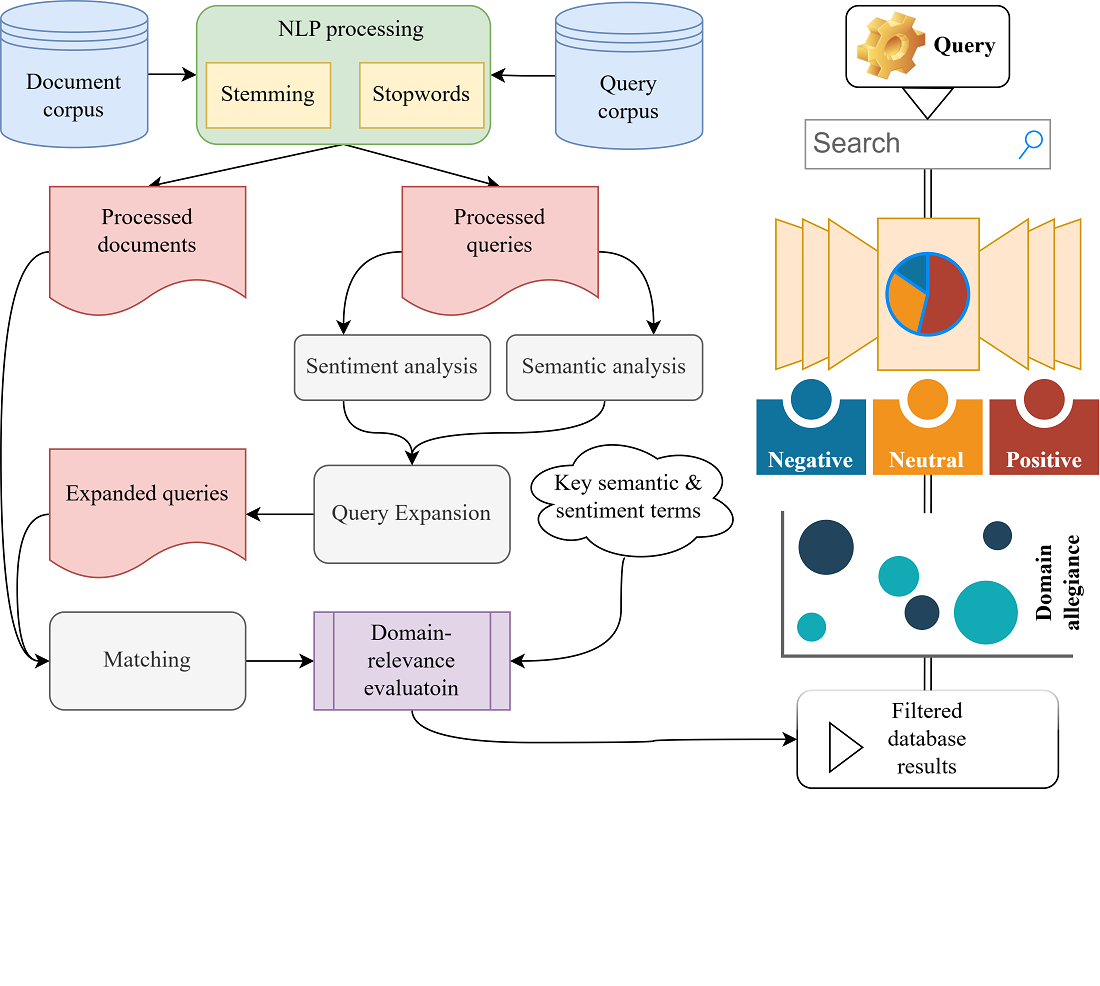
The object of this study is an improved query expansion method based on context-dependent text sentiment analysis in information retrieval systems for working with databases. Using natural language processing (NLP) methods, in particular contextual embeddings and transformer architectures, this paper focuses on adaptively determining user intent within the submitted query. The study involves analyzing and improving text processing mechanisms using subject-specific filtering to increase the accuracy and relevance of search results. The proposed method demonstrates an increase in the accuracy of context-sensitive models by 6 % compared to baseline approaches. The aggregate F1-measure indicator, which combines precision, completeness, and accuracy, reflects the relevance of the constructed models, showing an increase of 6–8 %. The difference between the least and most effective methods is 16 % in accuracy and 17 % in relevance. The proposed approach overcomes the limitations of static traditional synonym and statistical methods by dynamically interpreting the relationship between tone, context, and domain specificity of content. Improved semantic understanding allows for more accurate matching of extended queries with user goals. This method could be effectively applied in practice in settings where information retrieval systems operate within domain-specific databases. This applies to scenarios in which user queries contain complex, emotionally colored language constructs that require a deeper understanding of context and tone. However, its implementation requires training on high-quality domain-specific datasets with contextual labels that provide accurate adaptation
References
- Cai, F., de Rijke, M. (2016). A Survey of Query Auto Completion in Information Retrieval. Foundations and Trends® in Information Retrieval, 10 (4), 273–363. https://doi.org/10.1561/1500000055
- Sparck Jones, K. (1972). A statistical interpretation of term specificity and its application in retrieval. Journal of Documentation, 28 (1), 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb026526
- Manning, C. D., Raghavan, P., Schütze, H. (2008). Introduction to Information Retrieval. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511809071
- Hu, Z., Dychka, I., Potapova, K., Meliukh, V. (2024). Augmenting Sentiment Analysis Prediction in Binary Text Classification through Advanced Natural Language Processing Models and Classifiers. International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, 16 (2), 16–31. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijitcs.2024.02.02
- Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G. Dean, J. (2013). Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1301.3781
- Yuan, J., Zhao, Y., Qin, B. (2022). Learning to share by masking the non-shared for multi-domain sentiment classification. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 13 (9), 2711–2724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-022-01556-0
- Naseri, S., Dalton, J., Yates, A., Allan, J. (2022). CEQE to SQET: A study of contextualized embeddings for query expansion. Information Retrieval Journal, 25 (2), 184–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10791-022-09405-y
- Singh, J. (2017). Ranks Aggregation and Semantic Genetic Approach based Hybrid Model for Query Expansion. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 10 (1), 34. https://doi.org/10.2991/ijcis.2017.10.1.4
- Zheng, Z., Hui, K., He, B., Han, X., Sun, L., Yates, A. (2020). BERT-QE: Contextualized Query Expansion for Document Re-ranking. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2020. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.findings-emnlp.424
- Xu, B., Lin, H., Lin, Y., Yang, L., Xu, K. (2018). Improving Pseudo-Relevance Feedback With Neural Network-Based Word Representations. IEEE Access, 6, 62152–62165. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2876425
- Fang, F., Zhang, B.-W., Yin, X.-C. (2018). Semantic Sequential Query Expansion for Biomedical Article Search. IEEE Access, 6, 45448–45457. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2861869
- Wang, Y., Wang, N., Zhou, L. (2017). Keyword Query Expansion Paradigm Based on Recommendation and Interpretation in Relational Databases. Scientific Programming, 2017, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7613026
- Parlar, T., Özel, S. A., Song, F. (2018). QER: a new feature selection method for sentiment analysis. Human-Centric Computing and Information Sciences, 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13673-018-0135-8
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Vasyl Meliukh, Ekaterina Potapova, Mykola Nalyvaichuk, Andrii Dychka

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








