Devising a method for forming a stable mobile cluster of the internet of things fog layer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322263Keywords:
Internet of Things, clustering, mobile device, stability, ultra-high density, cloud infrastructure, fog computingAbstract
The object of this study is the process of clustering the fog layer of the Internet of Things (IoT) with high and ultra-high density.
The task to increase the stability of mobile components in the fog layer has been solved by modifying the clustering method.
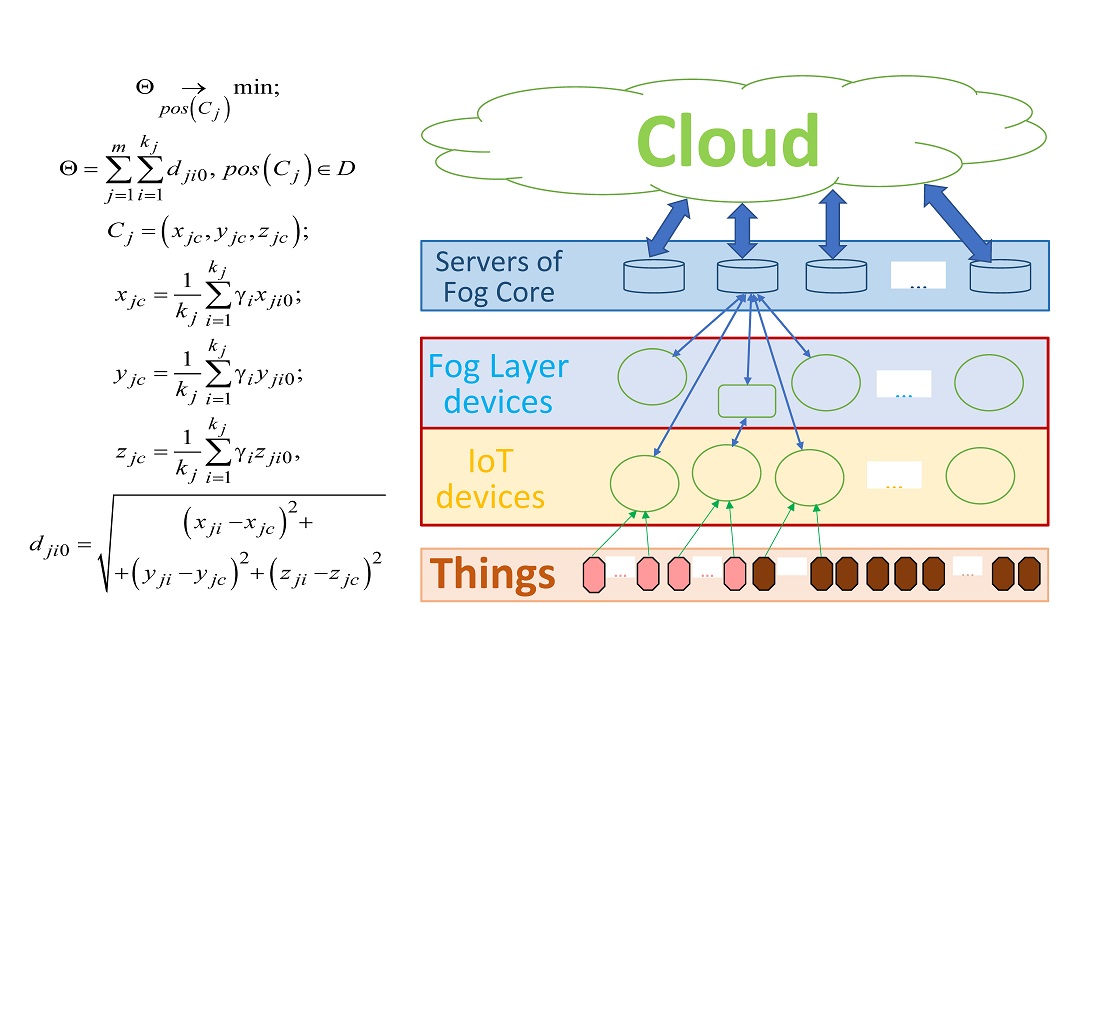
In the process of conducting research, an approach was devised to form the architecture of the mobile component in the fog layer of the IoT. The development took into account the decentralization of the fog layer and the specific features of mobile IoT devices. This has made it possible to propose a four-level architecture, which, unlike the standard one, contains separate mobile clusters at the lower level of fog devices.
A model of a mobile cluster of the fog layer has been proposed, which takes into account the randomness of the mobile IoT devices movement and is based on the Thomas point process. Unlike existing models, it takes into account both spatial and stability indicators of mobile cluster components. This model has made it possible to modify the standard FOREL clustering algorithm. The modification was carried out by introducing weight coefficients when finding the position of the center of the mobile cluster.
The proposed method increases the stability of a mobile cluster of the IoT fog layer with high and ultra-high density. Studies of the proposed method have shown that with an increase in the average relative deviation of IoT devices from the planned movement, the stability of the mobile cluster structure increases.
The research results can be explained by the approach of the center of the mobile cluster to its most unstable components. The proposed method could be used in the clustering of the IoT fog layer with mobile components. The method is effective when the average deviation of the movement of IoT mobile devices from the planned movement is no more than 20 % of the cluster radius
References
- Alsadie, D. (2024). Advancements in heuristic task scheduling for IoT applications in fog-cloud computing: challenges and prospects. PeerJ Computer Science, 10, e2128. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.2128
- Pardo, C., Wei, R., Ivens, B. S. (2022). Integrating the business networks and internet of things perspectives: A system of systems (SoS) approach for industrial markets. Industrial Marketing Management, 104, 258–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.04.012
- Mani Kiran, Ch. V. N. S., Jagadeesh Babu, B., Singh, M. K. (2022). Study of Different Types of Smart Sensors for IoT Application Sensors. Proceedings of Second International Conference in Mechanical and Energy Technology, 101–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-0108-9_11
- Fatlawi, A., Al-Dujaili, M. J. (2023). Integrating the internet of things (IoT) and cloud computing challenges and solutions: A review. 4th International Scientific Conference of Alkafeel University (ISCKU 2022), 2977, 020067. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0181842
- Hu, N. (2024). Internet of things edge data mining technology based on cloud computing model. International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control, 20 (6), 1749–1763. Available at: http://www.ijicic.org/ijicic-200611.pdf
- Hunko, M., Tkachov, V., Kovalenko, A., Kuchuk, H. (2023). Advantages of Fog Computing: A Comparative Analysis with Cloud Computing for Enhanced Edge Computing Capabilities. 2023 IEEE 4th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek). https://doi.org/10.1109/khpiweek61412.2023.10312948
- Kuchuk, H., Malokhvii, E. (2024). Integration Of Iot With Cloud, Fog, And Edge Computing: A Review. Advanced Information Systems, 8 (2), 65–78. https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2024.2.08
- Singh, C., Khilari, S., Taware, R. (2024). Active Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and IoT Communication Architecture for Mobile Devices and Sensor Nodes. Artificial Intelligence in Internet of Things (IoT): Key Digital Trends, 25–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-5786-2_3
- Kuchuk, N., Ruban, I., Zakovorotnyi, O., Kovalenko, A., Shyshatskyi, A., Sheviakov, I. (2023). Traffic Modeling for the Industrial Internet of NanoThings. 2023 IEEE 4th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/khpiweek61412.2023.10312856
- Sobchuk, V., Pykhnivskyi, R., Barabash, O., Korotin, S., Omarov, S. (2024). Sequential intrusion detection system for zero-trust cyber defense of iot/iiot networks. Advanced Information Systems, 8 (3), 92–99. https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2024.3.11
- Ding, H., Ding, X., Xia, F., Zhou, F. (2023). An Efficient Method for Implementing Applications of Smart Devices Based on Mobile Fog Processing in a Secure Environment. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 14 (10). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2023.0141011
- Qayyum, T., Trabelsi, Z., Waqar Malik, A., Hayawi, K. (2022). Mobility-aware hierarchical fog computing framework for Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Journal of Cloud Computing, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13677-022-00345-y
- Routray, K., Bera, P. (2024). Fog-Assisted Dynamic IoT Device Access Management Using Attribute-Based Encryption. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking, 346–352. https://doi.org/10.1145/3631461.3631466
- Saurabh, Dhanaraj, R. K. (2023). Enhance QoS with fog computing based on sigmoid NN clustering and entropy-based scheduling. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 83 (1), 305–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15685-3
- Kuchuk, H., Mozhaiev, O., Kuchuk, N., Tiulieniev, S., Mozhaiev, M., Gnusov, Y. et al. (2024). Devising a method for the virtual clustering of the Internet of Things edge environment. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (9 (127)), 60–71. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.298431
- Sharma, S., Saini, H. (2019). A novel four-tier architecture for delay aware scheduling and load balancing in fog environment. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 24, 100355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2019.100355
- Li, G., Liu, Y., Wu, J., Lin, D., Zhao, S. (2019). Methods of Resource Scheduling Based on Optimized Fuzzy Clustering in Fog Computing. Sensors, 19 (9), 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092122
- Jamil, B., Shojafar, M., Ahmed, I., Ullah, A., Munir, K., Ijaz, H. (2019). A job scheduling algorithm for delay and performance optimization in fog computing. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 32 (7). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5581
- Kuchuk, H., Kalinin, Y., Dotsenko, N., Chumachenko, I., Pakhomov, Y. (2024). Decomposition of integrated high-density IoT data flow. Advanced Information Systems, 8 (3), 77–84. https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2024.3.09
- Proietti Mattia, G., Beraldi, R. (2023). P2PFaaS: A framework for FaaS peer-to-peer scheduling and load balancing in Fog and Edge computing. SoftwareX, 21, 101290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2022.101290
- Lu, S., Wu, J., Wang, N., Duan, Y., Liu, H., Zhang, J., Fang, J. (2021). Resource provisioning in collaborative fog computing for multiple delay‐sensitive users. Software: Practice and Experience, 53 (2), 243–262. https://doi.org/10.1002/spe.3000
- Drabech, Z., Douimi, M., Zemmouri, E. (2024). A Markov random field model for change points detection. Journal of Computational Science, 83, 102429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2024.102429
- Zhu, Q., Hu, L., Wang, R. (2022). Image Clustering Algorithm Based on Predefined Evenly-Distributed Class Centroids and Composite Cosine Distance. Entropy, 24 (11), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24111533
- Laktionov, O., Yanko, A., Pedchenko, N. (2024). Identification of air targets using a hybrid clustering algorithm. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (4 (131)), 89–95. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.314289
- Mutambik, I. (2024). An Entropy-Based Clustering Algorithm for Real-Time High-Dimensional IoT Data Streams. Sensors, 24 (22), 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24227412
- Petrovska, I., Kuchuk, H., Kuchuk, N., Mozhaiev, O., Pochebut, M., Onishchenko, Y. (2023). Sequential Series-Based Prediction Model in Adaptive Cloud Resource Allocation for Data Processing and Security. 2023 13th International Conference on Dependable Systems, Services and Technologies (DESSERT), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/dessert61349.2023.10416496
- Filosi, M., Visintainer, R., Riccadonna, S., Jurman, G., Furlanello, C. (2014). Stability Indicators in Network Reconstruction. PLoS ONE, 9 (2), e89815. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089815
- Petrovska, I., Kuchuk, H., Mozhaiev, M. (2022). Features of the distribution of computing resources in cloud systems. 2022 IEEE 3rd KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/khpiweek57572.2022.9916459
- Kuchuk, N., Kashkevich, S., Radchenko, V., Andrusenko, Y., Kuchuk, H. (2024). Applying edge computing in the execution IoT operative transactions. Advanced Information Systems, 8 (4), 49–59. https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2024.4.07
- Thomas, P., Jose, D. V. (2023). Towards Computation Offloading Approaches in IoT-Fog-Cloud Environment: Survey on Concepts, Architectures, Tools and Methodologies. Third Congress on Intelligent Systems, 37–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9379-4_4
- Petrovska, I., Kuchuk, H. (2023). Adaptive resource allocation method for data processing and security in cloud environment. Advanced Information Systems, 7 (3), 67–73. https://doi.org/10.20998/2522-9052.2023.3.10
- Emami Khansari, M., Sharifian, S. (2024). A scalable modified deep reinforcement learning algorithm for serverless IoT microservice composition infrastructure in fog layer. Future Generation Computer Systems, 153, 206–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2023.11.022
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Heorhii Kuchuk, Oleksandr Mozhaiev, Serhii Tiulieniev, Mykhailo Mozhaiev, Nina Kuchuk, Liliia Tymoshchyk, Yurii Onishchenko, Volodymyr Tulupov, Tetiana Bykova, Viktoriia Roh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








