Development of transformation of lecturer performance through Pro Growth Constructive Interaction with a multidimensional approach and machine learning based mathematical models
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322723Keywords:
lecturer performance optimization, mathematical model, deep neural network, accuracy, educationAbstract
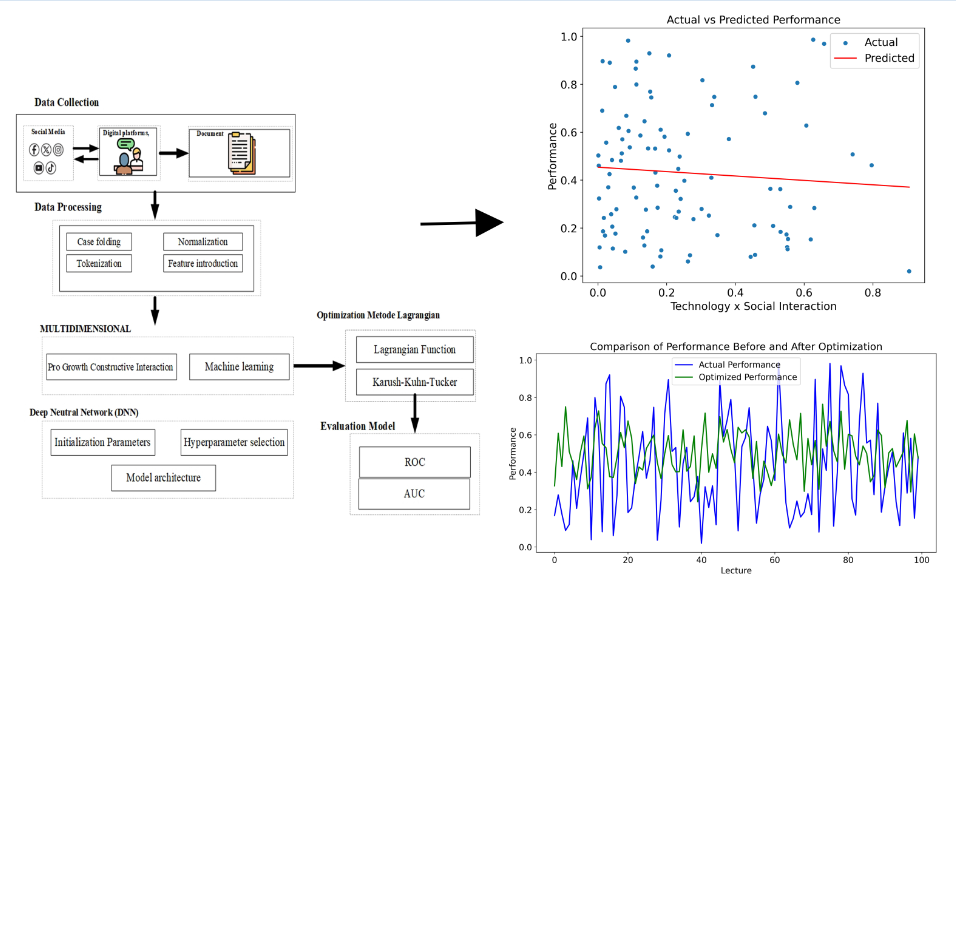
The object of this research is to focus on the Pro Growth Constructive Interaction (PGCI) approach as a strategy to improve lecturer performance. PGCI integrates multidimensional interactions involving academic, social, technological, individual, external and temporal dimensions to achieve optimal productivity and efficiency. In this research, there is a main problem to be addressed, namely identifying and optimizing the factors that influence lecturer performance by developing a comprehensive model that is able to predict and improve performance through multidimensional interactions. The research results obtained were the dimension contribution showing the highest contribution to lecturer performance (0.177062), followed by the technological (0.174122), social (0.167044), external (0.165670), and individual (0.163610) dimensions). In the results of the mathematical model with the Lagrangian method optimized with a machine learning algorithm distributing weights with a focus on external dimensions (0.2650) and technology (0.2179), resulting in a performance increase of 7.35 %. This model is able to achieve an accuracy of 92.4 % in predicting lecturer performance using a deep neural network algorithm. In this research, there is a brief interpretation of the research findings showing that the temporal and technological dimensions have an important role in determining lecturer performance. By prioritizing these two dimensions, the optimized model yields significant improvements. Characteristics obtained from research, multidimensional analysis covering various aspects of performance and high accuracy and measurable performance improvements prove the reliability of the model. The results of this research have significant practical applications in higher education institutions
References
- Weng, A. K.-W., Chang, H.-Y., Lai, K.-K., Lin, Y.-B. (2024). Topic Modeling on Peer Interaction in Online and Mobile Learning of Higher Education: 1993–2022. Education Sciences, 14 (8), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080867
- Chu, W., Liu, H., Fang, F. (2021). A Tale of Three Excellent Chinese EFL Teachers: Unpacking Teacher Professional Qualities for Their Sustainable Career Trajectories from an Ecological Perspective. Sustainability, 13 (12), 6721. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126721
- Nam, P. S., Tuong, H. A., Weinhandl, R., Lavicza, Z. (2022). Mathematics Teachers’ Professional Competence Component Model and Practices in Teaching the Linear Functional Concept – An Experimental Study. Mathematics, 10 (21), 4007. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10214007
- Suh, J., Matson, K., Seshaiyer, P., Jamieson, S., Tate, H. (2021). Mathematical Modeling as a Catalyst for Equitable Mathematics Instruction: Preparing Teachers and Young Learners with 21st Century Skills. Mathematics, 9 (2), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9020162
- Ponce-Jara, M. A., Ruiz, E., Gil, R., Sancristóbal, E., Pérez-Molina, C., Castro, M. (2017). Smart Grid: Assessment of the past and present in developed and developing countries. Energy Strategy Reviews, 18, 38–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2017.09.011
- Manzhos, S., Ihara, M. (2022). Advanced Machine Learning Methods for Learning from Sparse Data in High-Dimensional Spaces: A Perspective on Uses in the Upstream of Development of Novel Energy Technologies. Physchem, 2 (2), 72–95. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202203.0007.v1
- Mystakidis, S., Berki, E., Valtanen, J.-P. (2021). Deep and Meaningful E-Learning with Social Virtual Reality Environments in Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences, 11 (5), 2412. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052412
- Tang, J., Zhou, X., Wan, X., Daley, M., Bai, Z. (2022). ML4STEM Professional Development Program: Enriching K-12 STEM Teaching with Machine Learning. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 33 (1), 185–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-022-00292-4
- Kyriakides, L., Creemers, B. P. M., Antoniou, P. (2009). Teacher behaviour and student outcomes: Suggestions for research on teacher training and professional development. Teaching and Teacher Education, 25 (1), 12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2008.06.001
- Antoni, A., Arfah, M., Fachrizal, F., Nugroho, O. (2024). Developing a model of association rules with machine learning in determining user habits on social media. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (2 (129)), 55–61. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.305116
- Rahmatika, A., Al-khowarizmi, A., Akrim, A., Nugroho, O., Anu, T. A. (2024). Using relational learning in exploring the effectiveness of using hashtags in future topics and user relations in X. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (2 (129)), 62–68. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.306726
- Liu, H., Ding, J., Yang, L. T., Guo, Y., Wang, X., Deng, A. (2020). Multi-Dimensional Correlative Recommendation and Adaptive Clustering via Incremental Tensor Decomposition for Sustainable Smart Education. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Computing, 5 (3), 389–402. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsusc.2019.2954456
- Yanes, N., Mostafa, A. M., Ezz, M., Almuayqil, S. N. (2020). A Machine Learning-Based Recommender System for Improving Students Learning Experiences. IEEE Access, 8, 201218–201235. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3036336
- Mahmud, M., Kaiser, M. S., Hussain, A., Vassanelli, S. (2018). Applications of Deep Learning and Reinforcement Learning to Biological Data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29 (6), 2063–2079. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2018.2790388
- Jdid, B., Hassan, K., Dayoub, I., Lim, W. H., Mokayef, M. (2021). Machine Learning Based Automatic Modulation Recognition for Wireless Communications: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access, 9, 57851–57873. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3071801
- Kim, J. (2023). Leading teachers’ perspective on teacher-AI collaboration in education. Education and Information Technologies, 29 (7), 8693–8724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12109-5
- Wang, Z. A. (2024). Physical Education Teaching Quality Assessment Model Based on Gaussian Process Machine Learning Algorithm. International Journal of Maritime Engineering, 1 (1). https://doi.org/10.5750/ijme.v1i1.1399
- Phillips, P. A., Wright, C. (2009). E-business’s impact on organizational flexibility. Journal of Business Research, 62 (11), 1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2008.09.014
- Arnold, V., Benford, T., Canada, J., Sutton, S. G. (2011). The role of strategic enterprise risk management and organizational flexibility in easing new regulatory compliance. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 12 (3), 171–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accinf.2011.02.002
- Okorie, O., Subramoniam, R., Charnley, F., Patsavellas, J., Widdifield, D., Salonitis, K. (2020). Manufacturing in the Time of COVID-19: An Assessment of Barriers and Enablers. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 48 (3), 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1109/emr.2020.3012112
- Shukla, S. K., Sushil, Sharma, M. K. (2019). Managerial Paradox Toward Flexibility: Emergent Views Using Thematic Analysis of Literature. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 20 (4), 349–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-019-00220-x
- Leelaluk, S., Minematsu, T., Taniguchi, Y., Okubo, F., Shimada, A. (2022). Predicting student performance based on Lecture Materials data using Neural Network Models. Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Predicting Performance Based on the Analysis of Reading Behavior - DC in LAK22 co-located with 12th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference (LAK22), 11–20. Available at: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3120/paper2.pdf
- Kang, W. (2021). Explaining Effects of Transformational Leadership on Teachers’ Cooperative Professional Development through Structural Equation Model and Phantom Model Approach. Sustainability, 13 (19), 10888. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910888
- Goga, M., Kuyoro, S., Goga, N. (2015). A Recommender for Improving the Student Academic Performance. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 180, 1481–1488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.02.296
- Suyatmo, S., Ekohariadi, E., Wardhono, A. (2024). Identify Factors That Influence Hard Skill Competency and Soft Skill Competency Through the Quality of Teaching in Aviation Vocational Education. IJORER : International Journal of Recent Educational Research, 5 (3), 599–611. https://doi.org/10.46245/ijorer.v5i3.584
- Cao, B., Hassan, N. C., Omar, M. K. (2024). The Impact of Social Support on Burnout among Lecturers: A Systematic Literature Review. Behavioral Sciences, 14 (8), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080727
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Julfansyah Margolang, Yeni Absah, Sirojuzilam Hasyim, Parapat Gultom

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








