Estimation of software structures dimension influence on data processing time increasing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322989Keywords:
program performance, computer memory (RAM), operation time, linear regression, differential analysisAbstract
The object of the study is the phenomenon of an extreme increase in the time of program code execution at certain sizes of data processed by it. The problem to be solved was to verify the general nature of the phenomenon for different equipment.
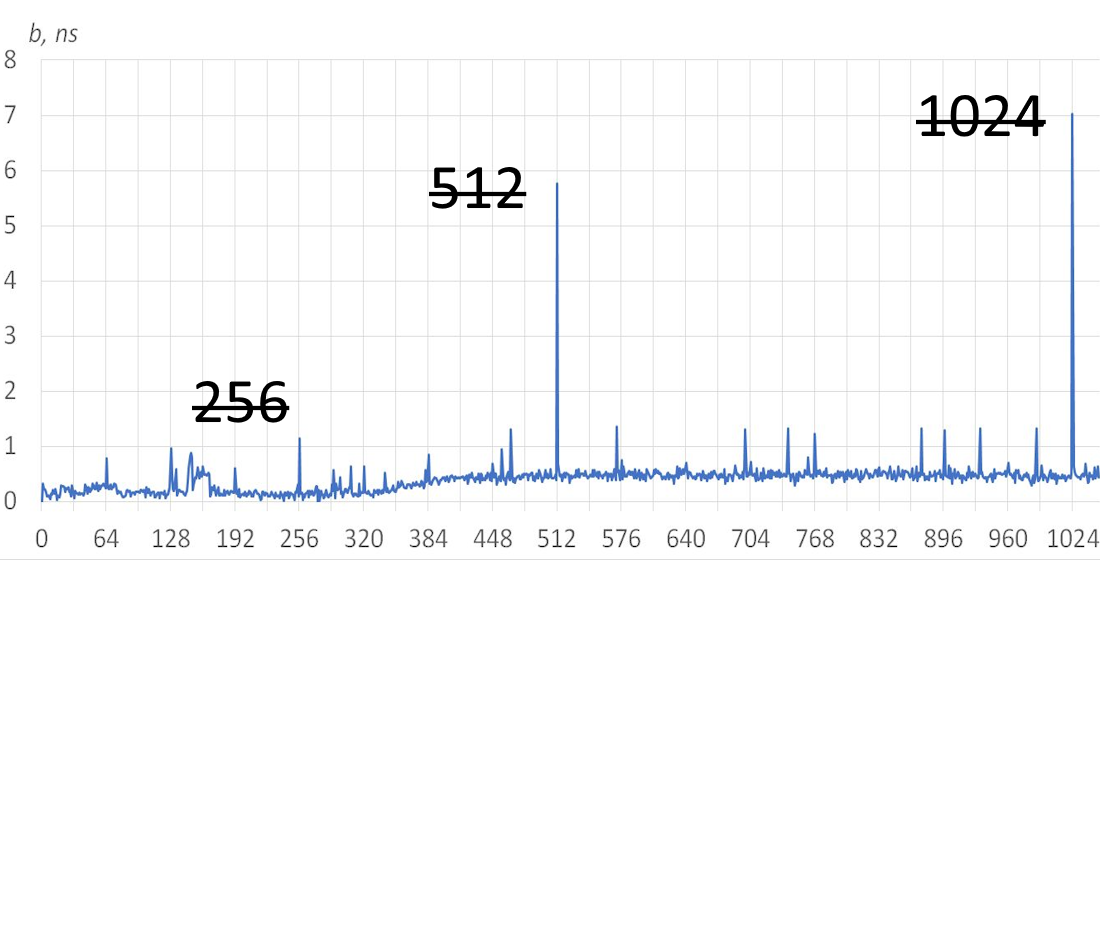
The evolution of modern computing technology, its RAM often takes place in an extensive way – by increasing the number of structural elements. Problems can manifest themselves in the fact that periodic processes in the code begin to exhibit a resonance effect, which leads to different indicators of data processing time, the sizes of which are multiples and non-multiples of the block structures. The work is studied the influence of the dimensionality of data blocks on the speed of execution of the cycle that iterates them. The tools of differential regression analysis are used. Experiments were carried out on equipment with different architecture, type and amount of RAM, running different operating systems. In all of them resonant effects were revealed. It led to differences in the average code execution time by 1.6–3.6 times, and the time of memory access operations increased up to 136 times. Special attention was drawn to the fact that the increase in operating time was found for structures whose size is a power of two multiple (2N), specifically for the values 512 and 1024. These dimensions are present in many types of tasks, in particular, cryptographic purposes or stream-based data processing. Following the recommendations given in the paper can help identify time delays in applications, and improve the performance of applications by eliminating them
References
- Cheng, G., Wan, Z., Ding, W., Sun, R. (2023). Memory Allocation Strategy in Edge Programmable Logic Controllers Based on Dynamic Programming and Fixed-Size Allocation. Applied Sciences, 13 (18), 10297. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810297
- de Lecea, A. F., Hassan, M., Mezzetti, E., Abella, J., Cazorla, F. J. (2023). Improving Timing-Related Guarantees for Main Memory in Multicore Critical Embedded Systems. 2023 IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS), 265–278. https://doi.org/10.1109/rtss59052.2023.00031
- Over, A., Strazdins, P., Clarke, B. (2005). Cycle Accurate Memory Modelling: A Case-Study in Validation. 13th IEEE International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems, 85–96. https://doi.org/10.1109/mascots.2005.22
- Fletchery, C. W., Ren, L., Yu, X., Van Dijk, M., Khan, O., Devadas, S. (2014). Suppressing the Oblivious RAM timing channel while making information leakage and program efficiency trade-offs. 2014 IEEE 20th International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), 213–224. https://doi.org/10.1109/hpca.2014.6835932
- Samoilenko, D. (2011). Memory tracing influence on algorithm complexity. Electrotechnic and computer systems, 4 (80), 209–212. Available at: https://eltecs.op.edu.ua/index.php/journal/article/view/907
- Asifuzzaman, K., Verdejo, R. S., Radojković, P. (2022). Performance and Power Estimation of STT-MRAM Main Memory with Reliable System-level Simulation. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 21 (1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1145/3476838
- Worlanyo Gbedawo, V., Agyeman Owusu, G., Komla Ankah, C., Ibrahim Daabo, M. (2023). An Overview of Computer Memory Systems and Emerging Trends. American Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 7 (2), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajece.20230702.11
- Simple Linear Regression. Available at: https://www.ncl.ac.uk/webtemplate/ask-assets/external/maths-resources/statistics/regression-and-correlation/simple-linear-regression.html
- Mukundan, J., Hunter, H., Kim, K., Stuecheli, J., Martínez, J. F. (2013). Understanding and mitigating refresh overheads in high-density DDR4 DRAM systems. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 41 (3), 48–59. https://doi.org/10.1145/2508148.2485927
- Sousi, A.-L., Yehya, D., Joudi, M. (2020). AES Encryption: Study & Evaluation. Rafik Hariri University. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346446212_AES_Encryption_Study_Evaluation
- Laghari, A. A., Shahid, S., Yadav, R., Karim, S., Khan, A., Li, H., Shoulin, Y. (2023). The state of art and review on video streaming. Journal of High Speed Networks, 29 (3), 211–236. https://doi.org/10.3233/jhs-222087
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yevhen Danylets, Dmytro Korchevskyi, Serhii Novak, Denys Samoilenko, Mykola Sulima

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








