Mathematical description of bending a surface of revolution into a helical conoid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.328825Keywords:
surface pitch, screw turn, truncated cone, approximate sweep, non-expandable surfaceAbstract
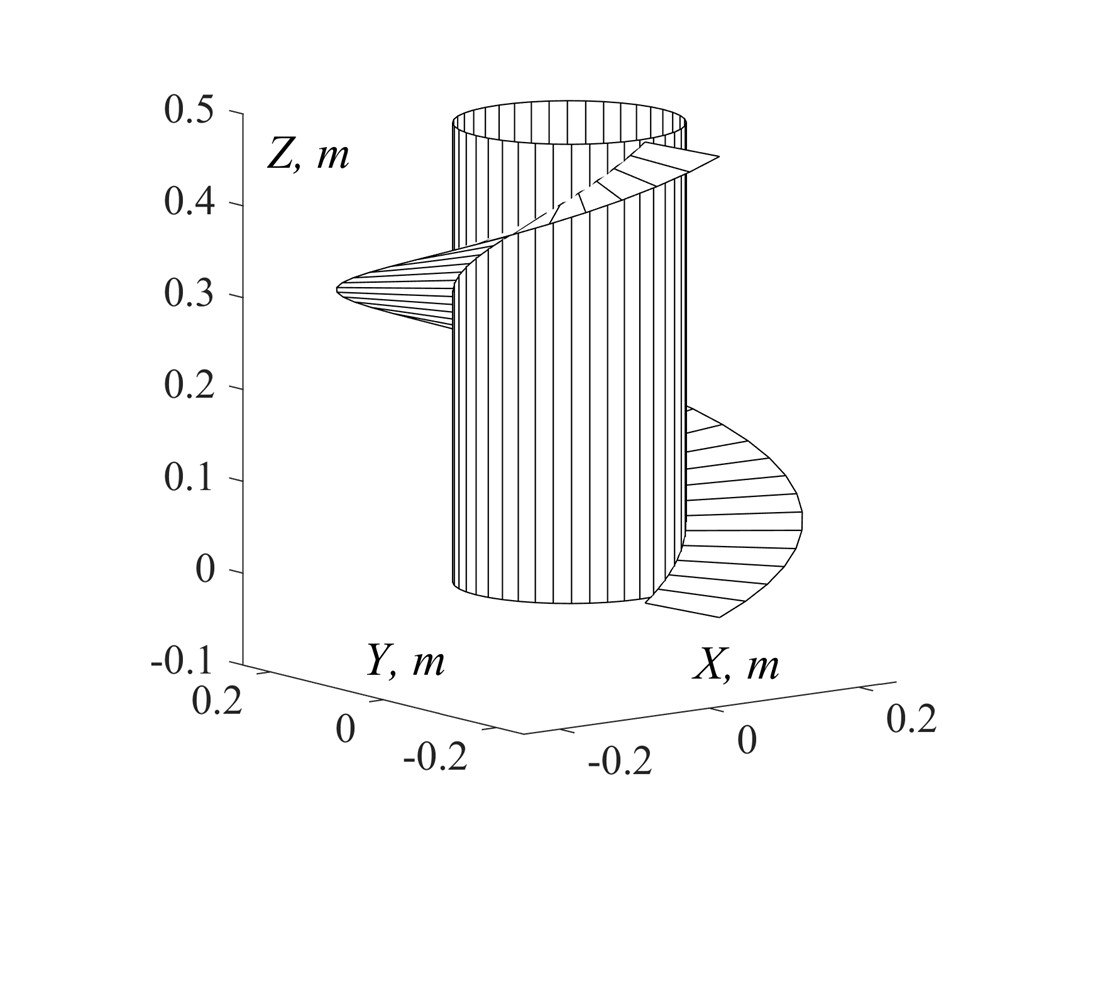
The object of this study is the process of theoretical gradual bending of a catenoid into a helical conoid coil. A helical conoid or a straight closed helicoid is formed by the helical motion of a segment around an axis, and this segment intersects the axis at a right angle during movement. It cannot be bent into a plane, but by gradually reducing the pitch it can be transformed into a known surface of revolution – a catenoid. With such deformation, the lengths of the lines and the area of the coil as a whole do not change, that is, the deformation occurs similarly to unfolded surfaces. Such deformation is based on the theory of bending surfaces of a separate section of differential geometry. According to it, any helical surface can be bent into a surface of revolution and vice versa. Bending the non-folded surface of a helical conoid into a catenoid is a classic example of differential geometry. This approach makes it possible to find an approximate flat workpiece for manufacturing a screw coil. This task is resolved by approximating the obtained catenoid by a truncated cone. The sweep of the truncated cone will be the approximate sweep of the screw turn. This is the peculiarity of finding the approximate sweep, which in engineering practice is calculated by other formulas. This is also the essence of the reported results.
In the work, parametric equations were derived that describe a one-parameter set of intermediate surfaces during bending of a screw conoid due to a gradual decrease in the surface pitch to zero. In the given example, one turn of the screw is considered, put on a shaft with a radius r = 0.125 m and limited by an external radius R = 0.25 m with a surface pitch H = 0.5 m. The dimensions of the truncated cone, which replaces the catenoid, are r = 0.148 m for the smaller base, R = 0.262 m for the larger base, and H = 0.05 m for the height of the cone. The specified dimensions of the cone are sufficient to find its exact sweep, which will be approximate for the turn of the screw conoid
References
- Tian, F., Xia, K., Wang, J., Song, Z., Yan, Y., Li, F., Wang, F. (2021). Design and experiment of self-propelled straw forage crop harvester. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 13 (7). https://doi.org/10.1177/16878140211024455
- Trokhaniak, O. (2022). Estimation of eddy currents and power losses in the rotor of a screw electrothermomechanical converter for additive manufacturing. Machinery & Energetics, 13 (3). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy.13(3).2022.92-98
- Kresan, Т., Ahmed, A. K., Pylypaka, S., Volina, T., Voloshko, T. (2024). Construction of the working surfaces of the tillage screw body from the compartments of the developable helicoid. Machinery & Energetics, 15 (3), 9–21. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/3.2024.09
- Klendii, M., Logusch, I., Dragan, A., Tsvartazkii, I., Grabar, A. (2022). Justification and calculation of design and strength parameters of screw loaders. Machinery & Energetics, 13 (4). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy.13(4).2022.48-59
- He, K., Li, G., Du, Y., Tang, Y. (2019). A digital method for calculation the forming cutter profile in machining helical surface. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 155, 370–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.03.018
- Rynkovskaya, M. (2018). Support Draft Calculation for a Ramp in the Form of Developable Helicoid. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 371, 012041. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/371/1/012041
- Lyashuk, O. L., Gypka, A. B., Pundys, Y. I., Gypka, V. V. (2019). Development of design and study of screw working surfaces of auger mechanisms of agricultural machines. Machinery & Energetics, 10 (4), 71–78. Available at: https://technicalscience.com.ua/en/journals/t-10-4-2019/rozrobka-konstruktsiyi-ta-doslidzhyennya-gvintovikh-robochikh-povyerkhon-shnyekovikh-myekhanizmiv-silskogospodarskikh-mashin
- Pylypaka, S., Hropost, V., Nesvidomin, V., Volina, T., Kalenyk, M., Volokha, M. et al. (2024). Designing a helical knife for a shredding drum using a sweep surface. Engineering Technological Systems, 4 (1 (130)), 37–44. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.308195
- Junge, S., Zablodskiy, M., Zaiets, N., Chuenko, R., Kovalchuk, S. (2023). The screw-type electrothermomechanical converter as a source of multiphysical influence on the technological environment. Machinery & Energetics, 14 (3), 34–46. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/3.2023.34
- Mushtruk, M., Gudzenko, M., Palamarchuk, I., Vasyliv, V., Slobodyanyuk, N., Kuts, A. et al. (2020). Mathematical modeling of the oil extrusion process with pre-grinding of raw materials in a twin-screw extruder. Potravinarstvo Slovak Journal of Food Sciences, 14, 937–944. https://doi.org/10.5219/1436
- Zablodskiy, M., Kovalchuk, S., Gritsyuk, V., Subramanian, P. (2023). Screw electromechanical hydrolyzer for processing poultry by-products. Machinery & Energetics, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2023.36
- Romasevych, Y., Loveikin, V., Malinevsky, O. (2022). The method of calculating the maximum torque when jamming the auger of the screw conveyor. Machinery & Energetics, 13 (2). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy.13(2).2022.83-90
- Trokhaniak, O. (2023). Determination of optimal parameters of hinged operating elements of screw conveyers. Machinery & Energetics, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2023.79
- Nieszporek, T., Gołębski, R., Boral, P. (2017). Shaping the Helical Surface by the Hobbing Method. Procedia Engineering, 177, 49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.02.181
- Tarelnyk, V. B., Gaponova, O. P., Konoplianchenko, Ye. V., Martsynkovskyy, V. S., Tarelnyk, N. V., Vasylenko, O. O. (2019). Improvement of Quality of the Surface Electroerosive Alloyed Layers by the Combined Coatings and the Surface Plastic Deformation. III. The Influence of the Main Technological Parameters on Microgeometry, Structure and Properties of Electrolytic Erosion Coatings. Metallofizika I Noveishie Tekhnologii, 41 (3), 313–335. https://doi.org/10.15407/mfint.41.03.0313
- Tarelnyk, V. B., Gaponova, O. P., Konoplianchenko, Ye. V., Martsynkovskyy, V. S., Tarelnyk, N. V., Vasylenko, O. O. (2019). Improvement of Quality of the Surface Electroerosive Alloyed Layers by the Combined Coatings and the Surface Plastic Deformation. II. The Analysis of a Stressedly-Deformed State of Surface Layer after a Surface Plastic Deformation of Electroerosive Coatings. Metallofizika I Noveishie Tekhnologii, 41 (2), 173–192. https://doi.org/10.15407/mfint.41.02.0173
- Chvartatskiy, I., Flonts, I., Grabar, A., Shatrov, R. (2021). Synthesis of energy-saving transport-technological systems with screw working bodies. Machinery & Energetics, 12 (4). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy2021.04.077
- Gritsyuk, V., Nevliudov, I., Zablodskiy, M., Subramanian, P. (2022). Estimation of eddy currents and power losses in the rotor of a screw electrothermomechanical converter for additive manufacturing. Machinery & Energetics, 13 (2). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy.13(2).2022.41-49
- Klendiy, M. B., Drahan, A. P. (2021). Substantiation of the design of the working body of the screw section of the combined tillage tool. Perspective technologies and devices, 18, 66–72. https://doi.org/10.36910/6775-2313-5352-2021-18-10
- Kresan, T. (2021). Movement of soil particles on surface of developable helicoid with horizontal axis of rotation with given angle of attack. Machinery & Energetics, 12 (2). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy2021.02.067
- Pylypaka, S., Kresan, Т., Hropost, V., Babka, V., Hryshchenko, I. (2022). Calculation of the bending parameters of a flat workpiece into a twist of a helicoid torso. Machinery & Energetics, 13 (4). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy.13(4).2022.81-88
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andrii Nesvidomin, Serhii Pylypaka, Tetiana Volina, Mykhailo Kalenyk, Svitlana Botvinovska, Iryna Hryshchenko, Dmytro Spirintsev, Vitalii Kolodnenko, Serhii Borodai, Irina Zakharova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








