MLP-KAN: implementation of the Kolmogorov-Arnold layer in a multilayer perceptron
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.328928Keywords:
multilayer perceptron, neural network, Kolmogorov-Arnold network, weight coefficients, radial basis functionsAbstract
The object of this study is neural networks used for categorizing objects in images. The task addressed in the work is to identify options for building a multilayer perceptron architecture that apply the Kolmogorov-Arnold layer and are characterized by the best ratio of classification quality and computational effort.
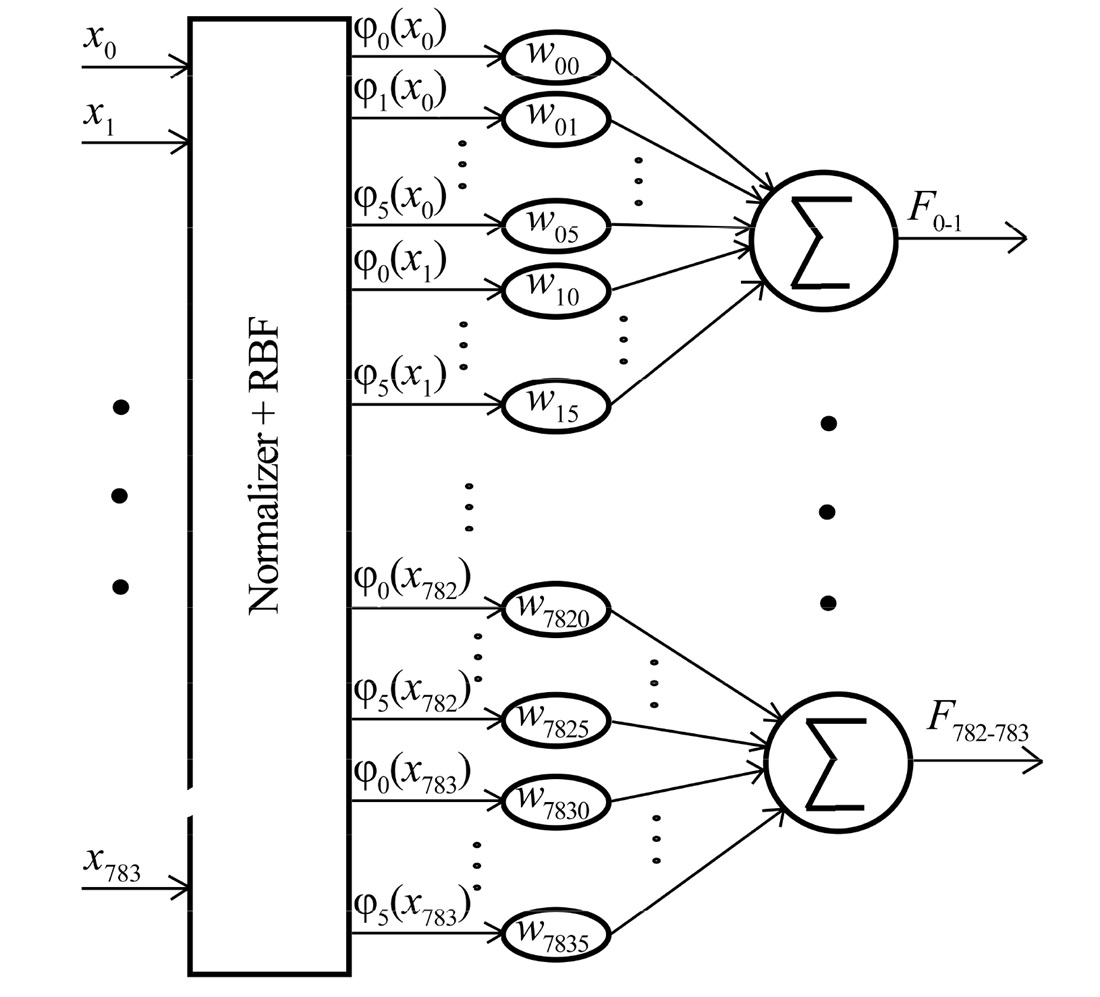
The paper proposes a modification to the multilayer perceptron (MLP) by replacing the first hidden layer with a Kolmogorov-Arnold layer. This allowed the use of the approximating properties of neurons and learning activation functions simultaneously. A feature of the designed MLP-KAN neural network, unlike the classical KAN network, is the use of only one activation function for each of the input elements. The training of activation functions is carried out on the basis of invariant radial basis functions, which are composed using learning weight coefficients. Such construction of the MLP-KAN neural network architecture allowed the use of typical libraries and optimizers for its training. In this case, unlike known analogs, there is no slowdown in the learning speed.
Experimental studies on the handwritten digit dataset (MNIST) have shown that MLP-KAN could provide higher classification quality with less computational effort. In particular, to obtain classification quality comparable to MLP, with the appropriate parameter setting, MLP-KAN requires 3.63 times less computational effort than MLP. This makes it possible to significantly improve the efficiency of image object classification devices built on microprocessors operating under an autonomous mode as part of robotic systems
References
- Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M., White, H. (1989). Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Networks, 2 (5), 359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8
- Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Vaidya, S., Ruehle, F., Halverson, J., Soljačić, M. et al. (2024). KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2404.19756
- Braun, J., Griebel, M. (2009). On a Constructive Proof of Kolmogorov’s Superposition Theorem. Constructive Approximation, 30 (3), 653–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00365-009-9054-2
- Guo, H., Li, F., Li, J., Liu, H. (2025). KAN v.s. MLP for Offline Reinforcement Learning. ICASSP 2025 - 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/icassp49660.2025.10888327
- Yu, R., Yu, W., Wang, X. (2024). KAN or MLP: A Fairer Comparison. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.16674
- He, Y., Xie, Y., Yuan, Z., Sun, L. (2024). MLP-KAN: Unifying Deep Representation and Function Learning. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2410.03027
- Xu, K., Chen, L., Wang, S. (2024). Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Time Series: Bridging Predictive Power and Interpretability. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.02496
- Gao, Y., Hu, Z., Chen, W.-A., Liu, M., Ruan, Y. (2025). A revolutionary neural network architecture with interpretability and flexibility based on Kolmogorov–Arnold for solar radiation and temperature forecasting. Applied Energy, 378, 124844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.124844
- Jamali, A., Roy, S. K., Hong, D., Lu, B., Ghamisi, P. (2024). How to Learn More? Exploring Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sensing, 16 (21), 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214015
- Roy, S. K., Krishna, G., Dubey, S. R., Chaudhuri, B. B. (2020). HybridSN: Exploring 3-D–2-D CNN Feature Hierarchy for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 17 (2), 277–281. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2019.2918719
- Li, W., Li, L., Peng, M., Tao, R. (2025). KANDiff: Kolmogorov-Arnold Network and Diffusion Model-Based Network for Hyperspectral and Multispectral Image Fusion. Remote Sensing, 17 (1), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010145
- Liu, X., Tang, Z., Wei, J. (2025). Multi-Layer Perceptron Model Integrating Multi-Head Attention and Gating Mechanism for Global Navigation Satellite System Positioning Error Estimation. Remote Sensing, 17 (2), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020301
- Guo, L., Wang, Y., Guo, M., Zhou, X. (2024). YOLO-IRS: Infrared Ship Detection Algorithm Based on Self-Attention Mechanism and KAN in Complex Marine Background. Remote Sensing, 17 (1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010020
- Abd Elaziz, M., Ahmed Fares, I., Aseeri, A. O. (2024). CKAN: Convolutional Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks Model for Intrusion Detection in IoT Environment. IEEE Access, 12, 134837–134851. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3462297
- Bodner, A. D., Tepsich, A. S., Spolski, J. N., Pourteau, S. (2024). Convolutional Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.13155
- Drokin, I. (2024). Kolmogorov-Arnold Convolutions: Design Principles and Empirical Studies. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2407.01092
- Cheon, M. (2024). Demonstrating the Efficacy of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks in Vision Tasks. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.14916
- Wang, C., Zhang, X., Liu, L. (2025). FloodKAN: Integrating Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Efficient Flood Extent Extraction. Remote Sensing, 17 (4), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040564
- Seydi, S. T. (2024). Exploring the Potential of Polynomial Basis Functions in Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks: A Comparative Study of Different Groups of Polynomials. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.02583
- Ismayilova, A., Ismayilov, M. (2023). On the universal approximation property of radial basis function neural networks. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, 92 (3), 691–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10472-023-09901-x
- He, Z.-R., Lin, Y.-T., Lee, S.-J., Wu, C.-H. (2018). A RBF Network Approach for Function Approximation. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), 105–109. https://doi.org/10.1109/icinfa.2018.8812435
- Panda, S., Panda, G. (2022). On the Development and Performance Evaluation of Improved Radial Basis Function Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 52 (6), 3873–3884. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2021.3076747
- Seghouane, A.-K., Shokouhi, N. (2021). Adaptive Learning for Robust Radial Basis Function Networks. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 51 (5), 2847–2856. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2019.2951811
- Wu, C., Kong, X., Yang, Z. (2018). An Online Self-Adaption Learning Algorithm for Hyper Basis Function Neural Network. 2018 2nd IEEE Advanced Information Management,Communicates,Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), 215–220. https://doi.org/10.1109/imcec.2018.8469684
- Galchonkov, O., Baranov, O., Antoshchuk, S., Maslov, O., Babych, M. (2024). Development of a neural network with a layer of trainable activation functions for the second stage of the ensemble classifier with stacking. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (9 (131)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.311778
- LeCun, Y., Cortes, C. and Burges, C. J. C. (1998). The MNIST Database of Handwritten Digits. New York.
- MLP-KAN. Available at: https://github.com/oleksii-m-baranov/MLP-KAN
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oleg Galchonkov, Oleksii Baranov, Oleh Maslov, Mykola Babych, Illia Baskov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








