Development an intelligent task scheduling method in heterogeneous distributed information systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.329263Keywords:
distributed computing systems, graph models, resource planning, intelligent management systemsAbstract
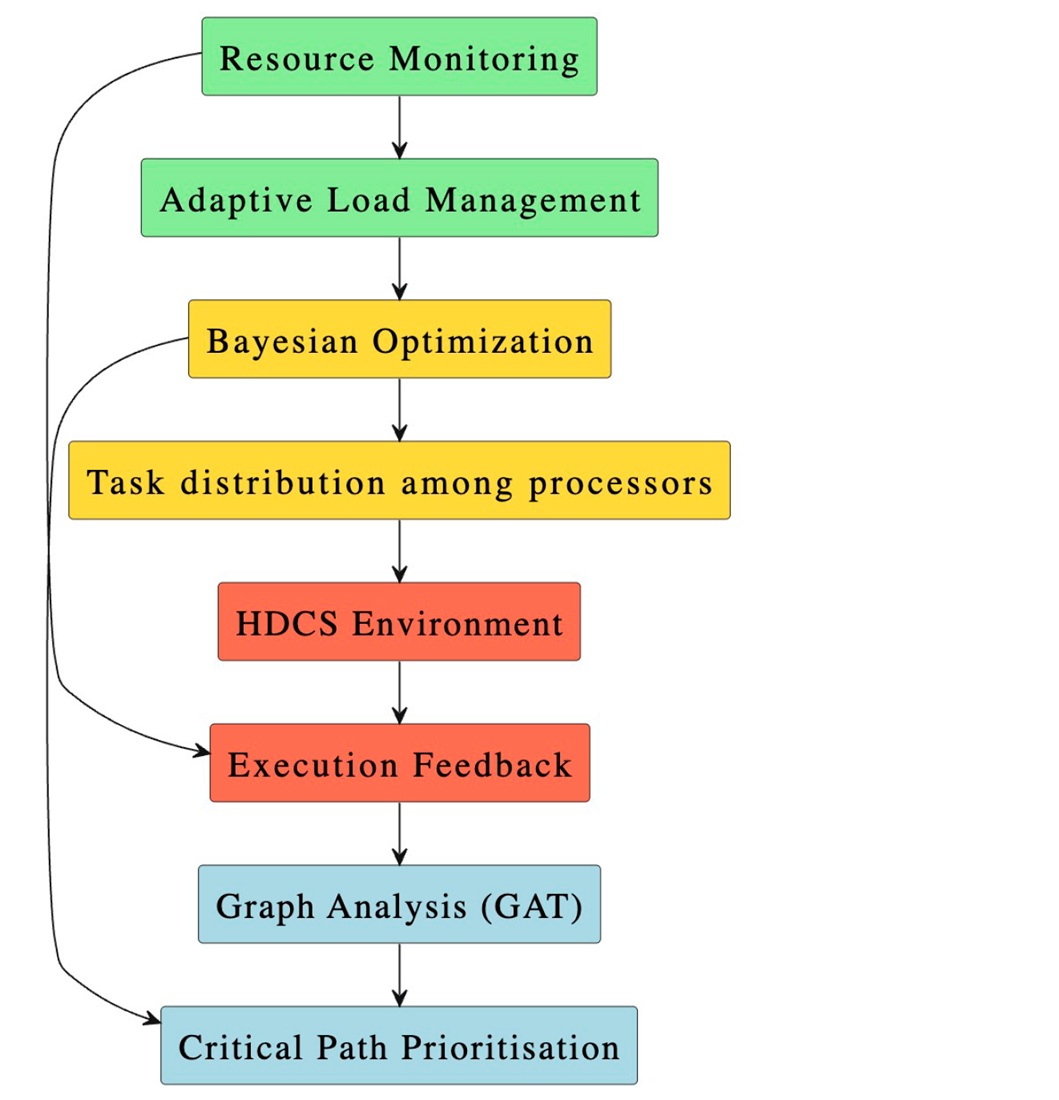
The object of this study is the task scheduling process in heterogeneous distributed information systems. The scientific task addressed relates to the low efficiency of resource management, especially under conditions of dynamic workload and significant uncertainty, which are typical for distributed information systems. An intelligent task scheduling method has been devised for heterogeneous distributed information systems, which effectively combines DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) and GERT (Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique) models with advanced artificial intelligence algorithms. The proposed method employs a Graph Attention Network (GAT) to account for probabilistic dependences between tasks and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) for dynamic control of task distribution within the system. Furthermore, a Bayesian method is used to optimize the assignment of tasks to computing nodes. The use of the proposed method reduced the average task execution time from 51.5 to 35.2 seconds, and the standard deviation of the load between nodes from 0.47 to 0.22.
These results are explained by the flexibility of the models to unforeseen changes and the ability to self-learn based on accumulated data. A feature of the method is the combination of classical graph models with probabilistic estimation and adaptive AI mechanisms, which made it possible not only to take into account the dynamics of the environment but also to ensure accurate response to changes in resource availability. By using GERT graphs, the algorithm forms alternative planning paths in case of failures or unforeseen delays, and machine learning components provide self-correction of decisions. The method is oriented towards application in cloud and IoT infrastructures, in which scalability, planning accuracy, and resilience to changes are critical
References
- Mikhav, V., Semenov, S., Meleshko, Y., Yakymenko, M., Shulika, Y. (2023). Constructing the mathematical model of a recommender system for decentralized peer-to-peer computer networks. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (9 (124)), 24–35. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286187
- Meleshko, Y., Raskin, L., Semenov, S., Sira, O. (2019). Methodology of probabilistic analysis of state dynamics of multidimensional semiMarkov dynamic systems. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (4 (102)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.184637
- Rama Krishna, M. S., Mangalampalli, S. (2023). A Systematic Review on Various Task Scheduling Algorithms in Cloud Computing. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Internet of Things, 10. https://doi.org/10.4108/eetiot.4548
- Sreenath, M., Vijaya, P. A. (2023). Comparative Study of Scheduling Algorithms for Multiprocessor Systems. 2023 International Conference on Intelligent and Innovative Technologies in Computing, Electrical and Electronics (IITCEE), 713–718. https://doi.org/10.1109/iitcee57236.2023.10091017
- Pachipala, Y., Sureddy, K. S., Kaitepalli, A. B. S. S., Pagadala, N., Nalabothu, S. S., Iniganti, M. (2024). Optimizing Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing: An Enhanced Shortest Job First Algorithm. Procedia Computer Science, 233, 604–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2024.03.250
- Semenov, S., Lymarenko, V., Yenhalychev, S., Gavrilenko, S. (2022). The Data Dissemination Planning Tasks Process Model Into Account the Entities Differentity. 2022 12th International Conference on Dependable Systems, Services and Technologies (DESSERT), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/dessert58054.2022.10018695
- Sinnen, O. (2006). Task Scheduling for Parallel Systems. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/0470121173
- Semenov, S., Mozhaiev, O., Kuchuk, N., Mozhaiev, M., Tiulieniev, S., Gnusov, Y. et al. (2022). Devising a procedure for defining the general criteria of abnormal behavior of a computer system based on the improved criterion of uniformity of input data samples. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (4 (120)), 40–49. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269128
- Semenov, S., Liqiang, Z., Weiling, C. (2020). Penetration Testing Process Mathematical Model. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Problems of Infocommunications. Science and Technology (PIC S&T), 142–146. https://doi.org/10.1109/picst51311.2020.9468039
- Jayswal, A. K., Lobiyal, D. K. (2022). A Comparative Study of Task Scheduling Metaheuristic Algorithms in Cloud Computing. 2022 12th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), 118–123. https://doi.org/10.1109/confluence52989.2022.9734189
- Pereira, I., Madureira, A., Costa e Silva, E., Abraham, A. (2021). A Hybrid Metaheuristics Parameter Tuning Approach for Scheduling through Racing and Case-Based Reasoning. Applied Sciences, 11 (8), 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083325
- Parizad, A., Hatziadoniu, C. (2022). Deep Learning Algorithms and Parallel Distributed Computing Techniques for High-Resolution Load Forecasting Applying Hyperparameter Optimization. IEEE Systems Journal, 16 (3), 3758–3769. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsyst.2021.3130080
- Savita, K., Gaurav, S., Bhawna, S. (2023). Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Load Prediction in Cloud Environment. International Journal of Performability Engineering, 19 (8), 507. https://doi.org/10.23940/ijpe.23.08.p3.507515
- Fang, Z., Ma, T., Huang, J., Niu, Z., Yang, F. (2025). Efficient Task Allocation in Multi-Agent Systems Using Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 15 (4), 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041905
- Liu, Z., Guo, M., Bao, W., Li, Z. (2024). Fast and Adaptive Multi-Agent Planning under Collaborative Temporal Logic Tasks via Poset Products. Research, 7. https://doi.org/10.34133/research.0337
- Kumar, H., Tyagi, I. (2020). Hybrid model for tasks scheduling in distributed real time system. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 12 (2), 2881–2903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02445-6
- Yanamandram Kuppuraju, S., Sankaran, P., Patil, S. (2025). Hybrid Task Scheduling Using Genetic Algorithms and Machine Learning for Improved Cloud Efficiency. International Journal For Multidisciplinary Research, 7 (2). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2025.v07i02.39380
- Torres-Toledano, J. G., Sucar, L. E. (1998). Bayesian Networks for Reliability Analysis of Complex Systems. Progress in Artificial Intelligence – IBERAMIA 98, 195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-49795-1_17
- Attar, S. F., Mohammadi, M., Pasandideh, S. H. R. (2025). A Bayesian network approach to production decisions by incorporating complex causal factors. Journal of Management Science and Engineering, 10 (2), 262–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmse.2025.03.002
- Huang, M.-C. (2024). A Sender-Initiated Fuzzy Logic Contrnol Method for Network Load Balancing. Journal of Computer and Communications, 12 (08), 110–122. https://doi.org/10.4236/jcc.2024.128007
- Semenov, S., Zhang, L., Cao, W., Bulba, S., Babenko, V., Davydov, V. (2021). Development of a fuzzy GERT-model for investigating common software vulnerabilities. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (114)), 6–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.243715
- Moskalenko, V., Kharchenko, V., Semenov, S. (2024). Model and Method for Providing Resilience to Resource-Constrained AI-System. Sensors, 24 (18), 5951. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185951
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Serhii Yenhalychev, Oleksii Leunenko, Viacheslav Davydov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








