Розробка інтелектуального методу планування задач у гетерогенних розподілених інформаційних системах
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.329263Ключові слова:
розподілені обчислювальні системи, графові моделі, ресурсне планування, інтелектуальні системи управлінняАнотація
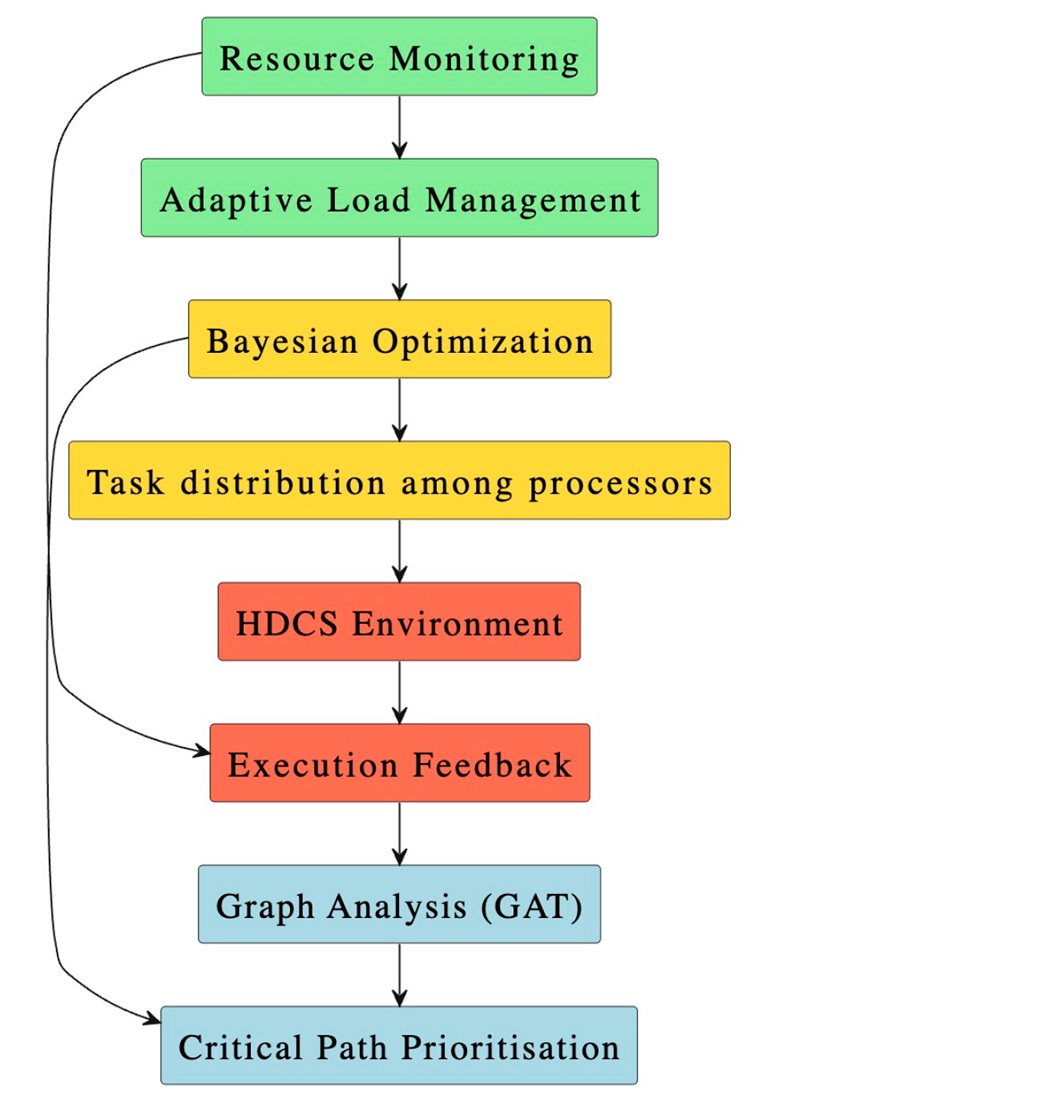
Об’єктом дослідження є процес планування задач у гетерогенних розподілених інформаційних системах. Розроблений метод використовує Graph Attention Network (GAT) для врахування ймовірнісні залежності між задачами та Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) для динамічного керування розподілом задач у системі. Наукова проблема полягає у низькій ефективності управління ресурсами, особливо в умовах динамічного навантаження та значної невизначеності, що характерно для розподілених інформаційних систем. Розроблено інтелектуальний метод планування задач у гетерогенних розподілених інформаційних системах, який ефективно поєднує графові моделі DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) і GERT (Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique) з передовими алгоритмами штучного інтелекту. Крім того, використовується метод Байєса для оптимізації призначення задач обчислювальним вузлам. Використання запропонованого методу дозволило зменшити середній час виконання задач з 51.5 до 35.2 секунди, а стандартне відхилення навантаження між вузлами – з 0.47 до 0.22. Такі результати пояснюються гнучкістю моделей до непередбачуваних змін і можливістю самонавчання на основі накопичених даних. Особливістю методу є поєднання класичних графових моделей із ймовірнісною оцінкою та адаптивними механізмами штучного інтелекту, що дозволило не лише врахувати динаміку середовища, а й забезпечити точне реагування на зміну доступності ресурсів. Завдяки використанню GERT-графів алгоритм формує альтернативні шляхи планування у випадку збоїв або непередбачених затримок, а компоненти машинного навчання забезпечують самокорекцію рішень. Метод орієнтований на застосування в хмарних та IoT-інфраструктурах, де критичними є масштабованість, точність планування та стійкість до змін
Посилання
- Mikhav, V., Semenov, S., Meleshko, Y., Yakymenko, M., Shulika, Y. (2023). Constructing the mathematical model of a recommender system for decentralized peer-to-peer computer networks. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (9 (124)), 24–35. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286187
- Meleshko, Y., Raskin, L., Semenov, S., Sira, O. (2019). Methodology of probabilistic analysis of state dynamics of multidimensional semiMarkov dynamic systems. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (4 (102)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.184637
- Rama Krishna, M. S., Mangalampalli, S. (2023). A Systematic Review on Various Task Scheduling Algorithms in Cloud Computing. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Internet of Things, 10. https://doi.org/10.4108/eetiot.4548
- Sreenath, M., Vijaya, P. A. (2023). Comparative Study of Scheduling Algorithms for Multiprocessor Systems. 2023 International Conference on Intelligent and Innovative Technologies in Computing, Electrical and Electronics (IITCEE), 713–718. https://doi.org/10.1109/iitcee57236.2023.10091017
- Pachipala, Y., Sureddy, K. S., Kaitepalli, A. B. S. S., Pagadala, N., Nalabothu, S. S., Iniganti, M. (2024). Optimizing Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing: An Enhanced Shortest Job First Algorithm. Procedia Computer Science, 233, 604–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2024.03.250
- Semenov, S., Lymarenko, V., Yenhalychev, S., Gavrilenko, S. (2022). The Data Dissemination Planning Tasks Process Model Into Account the Entities Differentity. 2022 12th International Conference on Dependable Systems, Services and Technologies (DESSERT), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/dessert58054.2022.10018695
- Sinnen, O. (2006). Task Scheduling for Parallel Systems. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/0470121173
- Semenov, S., Mozhaiev, O., Kuchuk, N., Mozhaiev, M., Tiulieniev, S., Gnusov, Y. et al. (2022). Devising a procedure for defining the general criteria of abnormal behavior of a computer system based on the improved criterion of uniformity of input data samples. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (4 (120)), 40–49. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.269128
- Semenov, S., Liqiang, Z., Weiling, C. (2020). Penetration Testing Process Mathematical Model. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Problems of Infocommunications. Science and Technology (PIC S&T), 142–146. https://doi.org/10.1109/picst51311.2020.9468039
- Jayswal, A. K., Lobiyal, D. K. (2022). A Comparative Study of Task Scheduling Metaheuristic Algorithms in Cloud Computing. 2022 12th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), 118–123. https://doi.org/10.1109/confluence52989.2022.9734189
- Pereira, I., Madureira, A., Costa e Silva, E., Abraham, A. (2021). A Hybrid Metaheuristics Parameter Tuning Approach for Scheduling through Racing and Case-Based Reasoning. Applied Sciences, 11 (8), 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083325
- Parizad, A., Hatziadoniu, C. (2022). Deep Learning Algorithms and Parallel Distributed Computing Techniques for High-Resolution Load Forecasting Applying Hyperparameter Optimization. IEEE Systems Journal, 16 (3), 3758–3769. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsyst.2021.3130080
- Savita, K., Gaurav, S., Bhawna, S. (2023). Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Load Prediction in Cloud Environment. International Journal of Performability Engineering, 19 (8), 507. https://doi.org/10.23940/ijpe.23.08.p3.507515
- Fang, Z., Ma, T., Huang, J., Niu, Z., Yang, F. (2025). Efficient Task Allocation in Multi-Agent Systems Using Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 15 (4), 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041905
- Liu, Z., Guo, M., Bao, W., Li, Z. (2024). Fast and Adaptive Multi-Agent Planning under Collaborative Temporal Logic Tasks via Poset Products. Research, 7. https://doi.org/10.34133/research.0337
- Kumar, H., Tyagi, I. (2020). Hybrid model for tasks scheduling in distributed real time system. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 12 (2), 2881–2903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02445-6
- Yanamandram Kuppuraju, S., Sankaran, P., Patil, S. (2025). Hybrid Task Scheduling Using Genetic Algorithms and Machine Learning for Improved Cloud Efficiency. International Journal For Multidisciplinary Research, 7 (2). https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2025.v07i02.39380
- Torres-Toledano, J. G., Sucar, L. E. (1998). Bayesian Networks for Reliability Analysis of Complex Systems. Progress in Artificial Intelligence – IBERAMIA 98, 195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-49795-1_17
- Attar, S. F., Mohammadi, M., Pasandideh, S. H. R. (2025). A Bayesian network approach to production decisions by incorporating complex causal factors. Journal of Management Science and Engineering, 10 (2), 262–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmse.2025.03.002
- Huang, M.-C. (2024). A Sender-Initiated Fuzzy Logic Contrnol Method for Network Load Balancing. Journal of Computer and Communications, 12 (08), 110–122. https://doi.org/10.4236/jcc.2024.128007
- Semenov, S., Zhang, L., Cao, W., Bulba, S., Babenko, V., Davydov, V. (2021). Development of a fuzzy GERT-model for investigating common software vulnerabilities. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (2 (114)), 6–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.243715
- Moskalenko, V., Kharchenko, V., Semenov, S. (2024). Model and Method for Providing Resilience to Resource-Constrained AI-System. Sensors, 24 (18), 5951. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24185951
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Serhii Yenhalychev, Oleksii Leunenko, Viacheslav Davydov

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









