Development of a variance-based deterministic algorithm for stochastic MST in distribution networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.329685Keywords:
spanning tree, stochastic graph, variance-based algorithm, deterministic transformation, uncertainty modeling, network optimizationAbstract
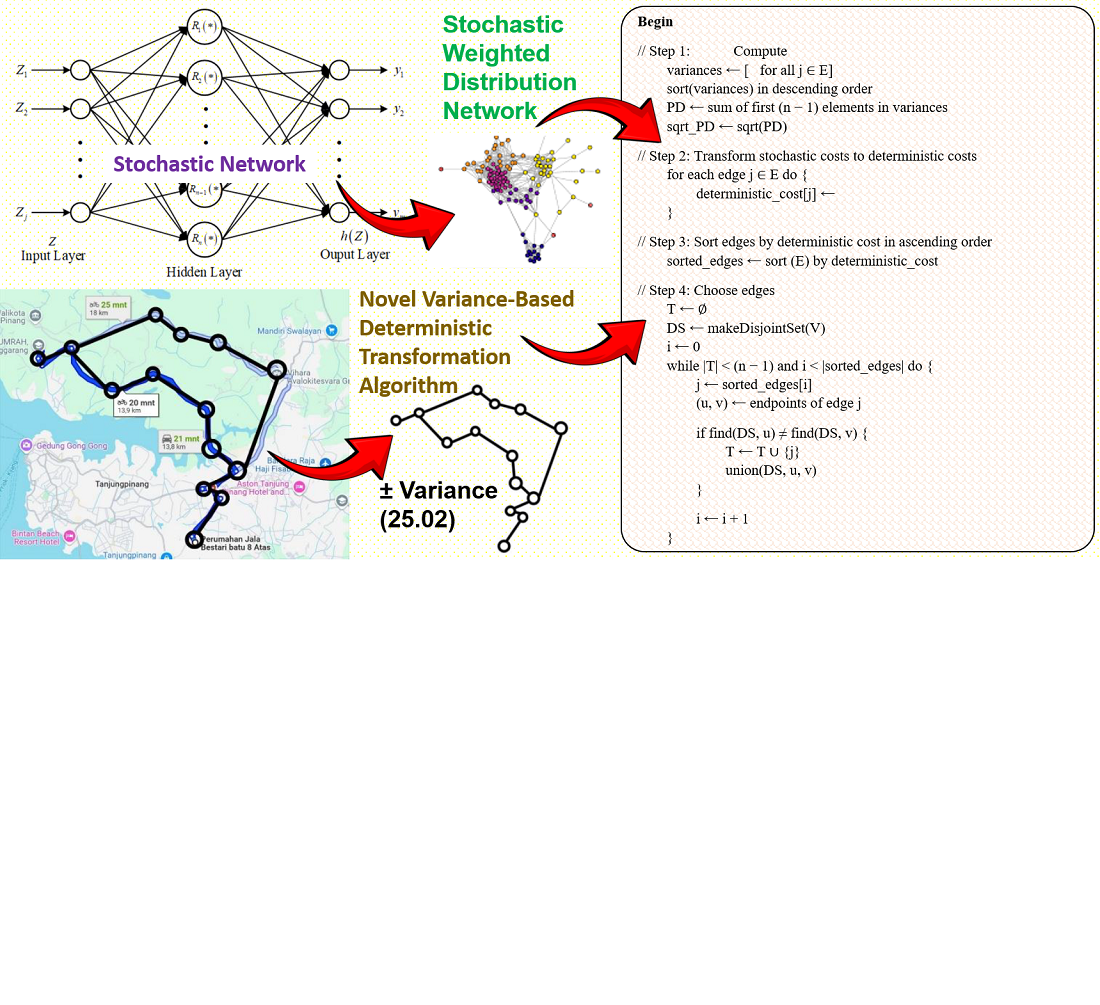
This study addresses constructing Minimum Spanning Trees (MST) in stochastic weighted distribution networks, where edge costs have inherent uncertainties with known means and variances. Traditional deterministic methods often fail, and existing stochastic approaches are frequently unstable or computationally complex under high uncertainty. A novel variance-based deterministic transformation algorithm is proposed. Its core feature is transforming stochastic edge costs into robust deterministic equivalents by computing an aggregate variance term from the largest (n – 1) edge variances, enabling MST construction via classical algorithms. This method fundamentally enhances stability and ensures feasibility, particularly in high-variance scenarios, improving upon traditional confidence interval-based techniques. The algorithm’s efficacy was rigorously validated. Its performance was compared against a probabilistic Qij-based method under moderate variance, demonstrating consistent and accurate MSTs. It was then applied to a complex 21-edge distribution network with high variance parameters. Results confirm the algorithm’s broad applicability, precision, and capability to construct reliable spanning trees under both moderate and substantial uncertainty. The algorithm demonstrates significant computational efficiency (O(r log r)), ensuring practicality and scalability across varying uncertainty levels. Unlike iterative or constraint-heavy models, this algorithm simplifies optimization while preserving uncertainty representation. This makes it well-suited for large-scale networks and real-world systems where cost variability is critical. Future research includes expanding this approach to multi-objective optimization or dynamic networks
References
- Luo, S., Yimamu, N., Li, Y., Wu, H., Irfan, M., Hao, Y. (2022). Digitalization and sustainable development: How could digital economy development improve green innovation in China? Business Strategy and the Environment, 32 (4), 1847–1871. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3223
- Feng, R., Qu, X. (2023). Innovation-Driven Industrial Agglomeration Impact on Green Economic Growth in the Yellow River Basin: An Empirical Analysis. Sustainability, 15 (17), 13264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713264
- Mor, S., Ravindra, K. (2023). Municipal solid waste landfills in lower- and middle-income countries: Environmental impacts, challenges and sustainable management practices. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 174, 510–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2023.04.014
- Sinha, S. K., Davis, C., Gardoni, P., Babbar-Sebens, M., Stuhr, M., Huston, D. et al. (2023). Water Sector Infrastructure Systems Resilience A Social-Ecological-Technical System-of-Systems and Whole-Life Approach. Cambridge Prisms: Water, 1–50. https://doi.org/10.1017/wat.2023.3
- Israilova, E., Voronina, A., Shatila, K. (2023). Impact of water scarcity on socio-economic development. E3S Web of Conferences, 458, 08027. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202345808027
- Koutsokosta, A., Katsavounis, S. (2024). Stochastic transitions of a mixed-integer linear programming model for the construction supply chain: chance-constrained programming and two-stage programming. Operational Research, 24 (3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-024-00856-3
- Talebi, A., Haeri Boroujeni, S. P., Razi, A. (2024). Integrating random regret minimization-based discrete choice models with mixed integer linear programming for revenue optimization. Iran Journal of Computer Science, 8 (1), 21–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42044-024-00193-w
- Heidari, A., Shishehlou, H., Darbandi, M., Navimipour, N. J., Yalcin, S. (2024). A reliable method for data aggregation on the industrial internet of things using a hybrid optimization algorithm and density correlation degree. Cluster Computing, 27 (6), 7521–7539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-024-04351-4
- Ishii, H., Shiode, S., Nishida, T., Namasuya, Y. (1981). Stochastic spanning tree problem. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 3 (4), 263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-218x(81)90004-4
- Akbari Torkestani, J., Meybodi, M. R. (2010). A learning automata-based heuristic algorithm for solving the minimum spanning tree problem in stochastic graphs. The Journal of Supercomputing, 59 (2), 1035–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-010-0484-1
- Zhao, L., Huang, Y., Dai, Q., Yang, L., Chen, F., Wang, L. et al. (2019). Multistage Active Distribution Network Planning With Restricted Operation Scenario Selection. IEEE Access, 7, 121067–121080. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2936936
- Xu, Y., Zhang, L. (2023). Target-based Distributionally Robust Minimum Spanning Tree Problem. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.10670
- Hoeksma, R., Speek, G., Uetz, M. (2024). Stochastic Minimum Spanning Trees with a Single Sample. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2409.16119
- Mathwieser, C., Çela, E. (2024). Special cases of the minimum spanning tree problem under explorable edge and vertex uncertainty. Networks, 83 (3), 587–604. https://doi.org/10.1002/net.22204
- Makowiec, L., Salvi, M., Sun, R. (2024). Random spanning trees in random environment. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2410.16830
- Adhikary, K., Pal, P., Poray, J. (2024). The minimum spanning tree problem on networks with neutrosophic numbers. Neutrosophic Sets and Systems, 63, 258–270. Available at: https://fs.unm.edu/NSS/SpanningTree16.pdf
- Hu, Z., Sun, W., Zhu, S. (2022). Chance constrained programs with Gaussian mixture models. IISE Transactions, 54 (12), 1117–1130. https://doi.org/10.1080/24725854.2021.2001608
- Chatterjee, S., Pandurangan, G., Pham, N. D. (2020). Distributed MST. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1145/3369740.3369778
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Anna Angela Sitinjak, Saib Suwilo, Mardiningsih Mardiningsih, Sutarman Sutarman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








