Designing non-circular wheels using a fourth-degree polynomial
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.335176Keywords:
external rolling, center-to-center distance, arc length, axis of symmetry, radius vectorAbstract
This study’s object is the process of designing closed non-circular wheels with a given center-to-center distance with external rolling, provided that it occurs without mutual slip. Non-circular wheels serve as centroids in the design of cylindrical gear transmissions with a variable gear ratio. The gear ratio is characterized by the gear function. If the gear ratio is constant, then the centroids are circles. The gear ratio in this case is the ratio of the radii of these circles. Non-circular wheels can be designed according to a given gear function, which is determined by the kinematics of the mechanism’s links’ actuators. In this case, non-circular wheels can be non-closed.
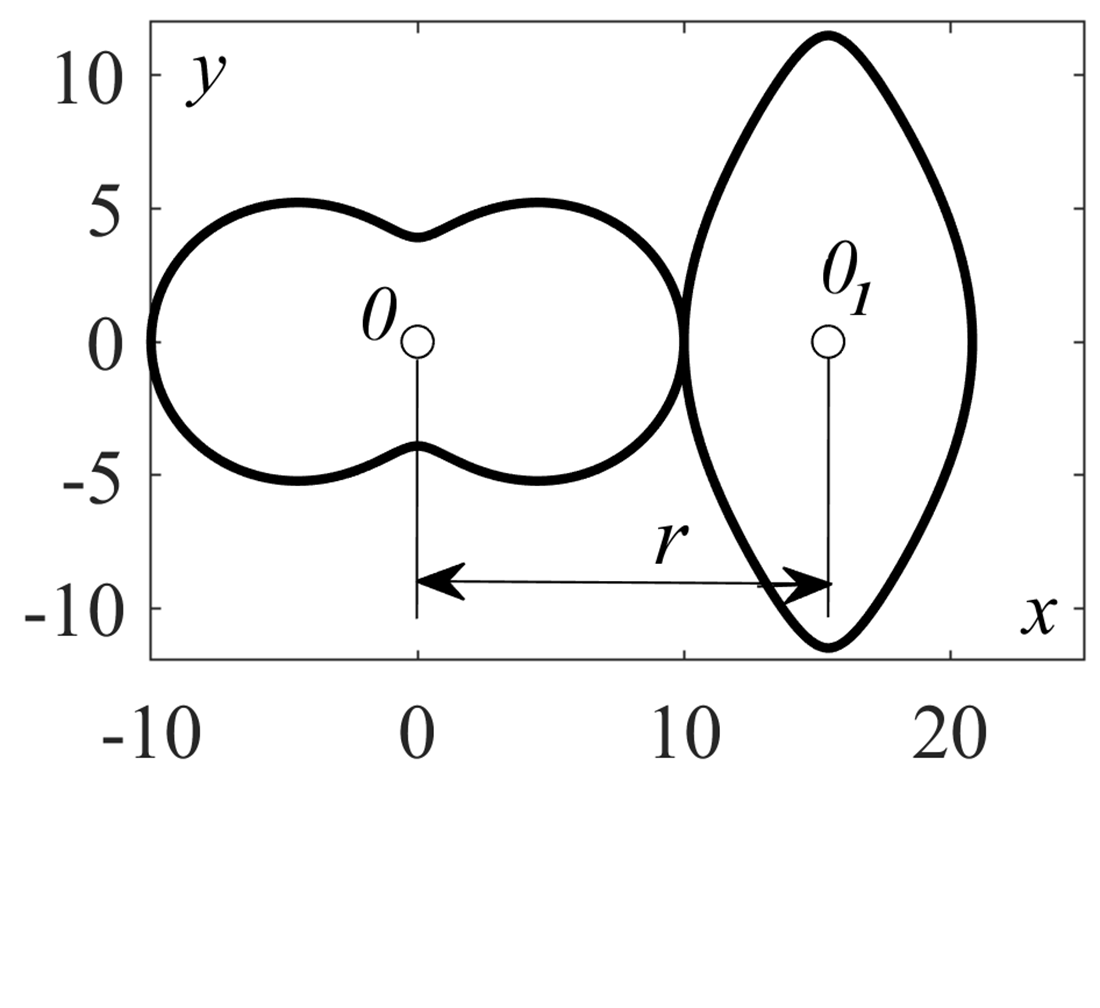
The study addresses another task related to designing non-circular wheels provided that they are closed. Various approaches can be used to this end. The current paper considers the use of a fourth-degree polynomial. In non-circular wheels, the radii, which are understood as the distances from the centers of rotation to the point of contact, are variable. The necessary conditions for constructing non-circular wheels are the constant value of the sum of these radii during the rotation of non-circular wheels, as well as the equality of the paths traveled, that is, the equality of the arcs that non-circular wheels pass during rotation. Pairs of wheels can have the same or different numbers of protrusions and depressions. This is explained by the use of a fourth-degree polynomial whose plot has an axis of symmetry. Accordingly, non-circular wheels or their protrusions also have an axis of symmetry.
As an example, the construction of a leading centroid with one protrusion and one depression is given, for which the maximum and minimum distances from the center are 10 and 6.1 linear units, respectively. For this centroid, a trailing centroid has been constructed, and the center-to-center distance has been found, which is 16.79 linear units
References
- Yu, Y., Liu, J., Ye, B., Yu, G., Jin, X., Sun, L., Tong, J. (2019). Design and Experimental Research on Seedling Pick-Up Mechanism of Planetary Gear Train with Combined Non-circular Gear Transmission. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 32 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-019-0357-3
- Wang, G., Zhou, M., Sun, H., Wei, Z., Dong, H., Xu, T., Yin, D. (2024). Mechanism Analysis and Optimization Design of Exoskeleton Robot with Non-Circular Gear–Pentabar Mechanism. Machines, 12 (5), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12050351
- Kresan, Т., Pylypaka, S., Babka, V., Kremets, Ya. S. (2019). Rolling of poligon on curvinal profile. Machinery & Energetics, 10 (2), 147–154. Available at: https://technicalscience.com.ua/en/journals/t-10-2-2019/kochyennya-bagatokutnika-po-krivoliniynomu-profilyu
- Jang, H.-S., Lee, C.-H., Park, G.-Y., Kim, C. (2021). Study on Design of Non-Circular Gears for Speed Control of the Squid Belly Opening and Gutting Machine (SBOGM). Applied Sciences, 11 (7), 3268. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073268
- Zhou, M., Yang, Y., Wei, M., Yin, D. (2020). Method for generating non-circular gear with addendum modification and its application in transplanting mechanism. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 13 (6), 68–75. https://doi.org/10.25165/j.ijabe.20201306.5659
- Nguyen, T. H. (2021). Shaping the tooth profile of elliptical gear with the involute ellipse curve. Science & Technology Development Journal - Engineering and Technology. https://doi.org/10.32508/stdjet.v4i3.820
- Xu, H., Fu, T., Song, P., Zhou, M., Fu, C., Mitra, N. J. (2020). Computational Design and Optimization of Non‐Circular Gears. Computer Graphics Forum, 39 (2), 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/cgf.13939
- Li, D., Wu, L. (2025). Research on load-bearing optimization of non-circular gear based on asymmetric pressure angles. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 17 (3). https://doi.org/10.1177/16878132251326414
- Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Dong, C. (2024). Research on pitch error measurement method of non-circular gear based on digital twin. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 239 (7), 2262–2274. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062241303384
- Liu, Y., Wang, J., Dong, C., Guo, J. (2025). An Analytical Calculation of Time-Varying Mesh Stiffness of Non-circular Planetary Gear System with Crack. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, 49 (3), 1569–1584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-024-00830-6
- Zhao, H., Chen, J., Xu, G. (2024). Design methodology and characteristics analysis of high-order multi-segment deformed eccentric non-circular gear. Facta Universitatis, Series: Mechanical Engineering, 217. https://doi.org/10.22190/fume2302270018z
- Kresan, T., Pylypaka, S., Ruzhylo, Z., Rogovskii, I., Trokhaniak, O. (2020). External rolling of a polygon on closed curvilinear profile. Acta Polytechnica, 60 (4), 313–317. https://doi.org/10.14311/ap.2020.60.0313
- Kresan, T. A., Pylypaka, S. F., Grischenko, I. Yu., Kremets, Ya. S. (2020). Simulation of centroids of non-circular wheels with internal and external rolling from arcs of symmetrical curves. Machinery & Energetics, 11 (4), 23–32. https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy2020.04.023
- Kresan, T., Pylypaka, S. (2021). Internal rolling of non-circular centroids formed from the arcs of logarithmic spiral. Machinery & Energetics, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.31548/machenergy2021.01.109
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Tetiana Kresan, Serhii Pylypaka, Tetiana Volina, Vitaliy Babka, Svitlana Botvinovska, Alexander Sarzhanov, Taras Pylypaka, Artem Borodai, Dmytro Borodai, Yulia Sirenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








