Improving the efficiency of structural and technological modernization of the grain processing industry
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.336963Keywords:
dynamics, grain processing industry, international trade, development prospects, consumption, export, efficiencyAbstract
This study's object is the activity of the grain processing industry, aimed at technological modernization.
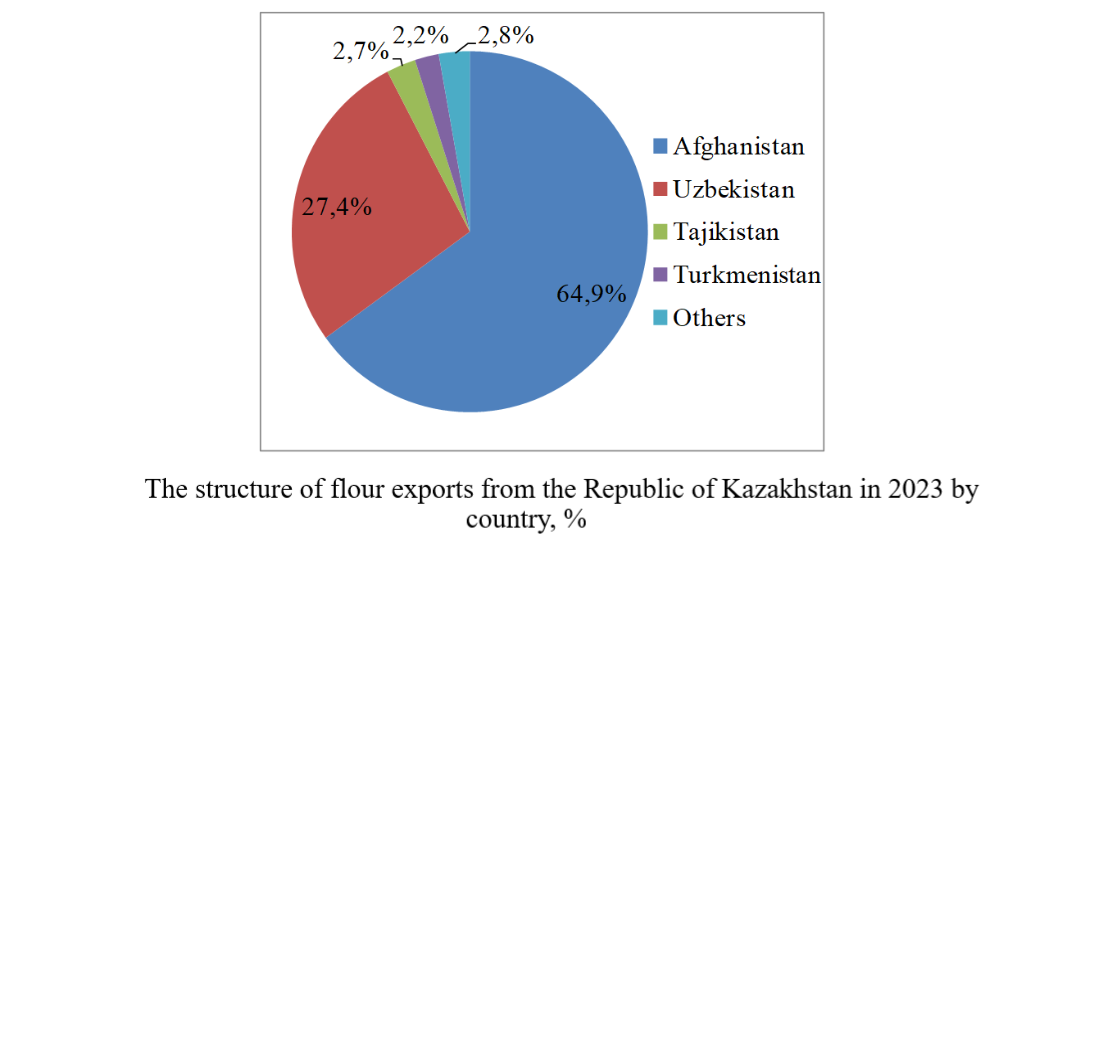
The study addresses issues related to the technological backwardness of production capacities. These include outdated equipment, unable to provide the required depth of grain processing and product quality. The limited domestic demand focused on the export of grain to the countries of Central Asia has been examined, which leads to underutilization of processing capacities under current conditions.
A potential modernization of the grain processing complex has been proposed, aimed at the development of deep grain processing and diversification of the product range:
– the global starch market is the largest of all grain processing products (3.8 times larger than the wheat gluten market and 20% larger than the flour market). The annual growth rate of the starch market is 5–6%;
– wheat gluten is a strategically important product of deep grain processing, combining high profitability, a wide range of applications, and export potential. It has high added value: the production of 1 ton of dry gluten requires the processing of approximately 3–4 tons of flour.
The practical significance of this study is the detailed analysis of the characteristics of exports oriented towards the markets of neighboring countries, the needs of these markets, as well as prospects for their development of products.
It has been shown that increasing the efficiency of the industry with an optimal level of utilization requires taking into account the prospects for the functioning of the domestic market and export deliveries until 2030
References
- Waza, S., Qadir, H. (2014). Agriculture and Economic Prosperity in India: A Developmental Perspective. Research Expo International Multidisciplinary Research Journal, 4 (1), 109–117. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350517453_Agriculture_and_Economic_Prosperity_in_India_A_Developmental_Perspective
- Cooper, R. N., Federico, G. (2006). Feeding the World: An Economic History of World Agriculture, 1800-2000. Foreign Affairs, 85 (3), 154. https://doi.org/10.2307/20031983
- Prokhorova, V., Budanov, M., Budanov, P., Zaitseva, A., Slastianykova, A. (2025). Devising a comprehensive methodology for estimating the economic efficiency of implementing an investment project for ensuring energy security of enterprises: organizational-economic aspect. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (13 (133)), 59–68. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.321965
- Beisekova, P., Ilyas, A., Kaliyeva, Y., Kirbetova, Z., Baimoldayeva, M. (2023). Development of a method for assessing the functioning of a grain product sub-complex using mathematical modeling. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (13 (122)), 92–101. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.276433
- Liu, X., Li, X. (2023). The Influence of Agricultural Production Mechanization on Grain Production Capacity and Efficiency. Processes, 11 (2), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020487
- Li, Y., You, X., Sun, X., Chen, J. (2024). Dynamic assessment and pathway optimization of agricultural modernization in China under the sustainability framework: An empirical study based on dynamic QCA analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 479, 144072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144072
- Rodríguez, A., van Grinsven, H. J. M., Einarsson, R., Beusen, A. H. W., Sanz-Cobena, A., Lassaletta, L. (2025). The NBCalCer model for calculating global benefits and costs of nitrogen fertilizer use for cereal cultivation: Model description, uncertainty analysis and validation. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 231, 110039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2025.110039
- Poutanen, K. S., Kårlund, A. O., Gómez-Gallego, C., Johansson, D. P., Scheers, N. M., Marklinder, I. M. et al. (2022). Grains – a major source of sustainable protein for health. Nutrition Reviews, 80 (6), 1648–1663. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuab084
- Neschadim, N., Popok, L., Gorpinchenko, K., Koval, A. (2020). Production Of Winter Crops’ Grain For Deep Processing Depending On Agrotechnologies. European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences, 132–138. https://doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2020.04.17
- Tanklevska, N., Petrenko, V., Karnaushenko, A., Melnykova, K. (2020). World corn market: analysis, trends and prospects of its deep processing. Agricultural and Resource Economics: International Scientific E-Journal, 6 (3), 96–111. https://doi.org/10.51599/are.2020.06.03.06
- Nocente, F., Gazza, L. (2025). Technological Development in Wholegrain Food Processing. Foods, 14 (12), 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122009
- Beisekova, P. D., Kaliyeva, E. V., Kirbetova, J. S., Bedelbekova, T. N. (2024). Perspective assessment of the export potential of the grain industry of Kazakhstan. Bulletin of “Turan” University, 4, 22–34. https://doi.org/10.46914/1562-2959-2024-1-4-22-34
- Suyunova, N., Yusuf, U., Toshtemirova, M., Maftuna, I. (2025). Research on food safety standards of Uzbekistan and international norms in the production, storage, and distribution of flour and flour products to the population. The American Journal of Applied Sciences, 7 (5), 31–36. https://doi.org/10.37547/tajas/volume07issue05-03
- Clapp, J., Ruder, S.-L. (2020). Precision Technologies for Agriculture: Digital Farming, Gene-Edited Crops, and the Politics of Sustainability. Global Environmental Politics, 20 (3), 49–69. https://doi.org/10.1162/glep_a_00566
- Bureau of National statistics of Agency for Strategic planning and reforms of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Available at: https://stat.gov.kz/en/
- Information-Analytical System. Bureau of National statistics of Agency for strategic planning and reforms of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Available at: https://taldau.stat.gov.kz/en/Search/SearchByKeyWord
- TradeMap. ITC. Available at: https://www.trademap.org
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Saule Momynkulova, Gulraikhan Aitkhojayeva, Saltanat Massakova, Bakyt Mutalipkyzy, Nazira Kaliyeva, Perizat Beisekova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








