Design and evaluation of an intelligent waste monitoring system based on RGIS integration for smart cities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.337033Keywords:
monitoring system, waste management, geographic information system, routing, container, detectionAbstract
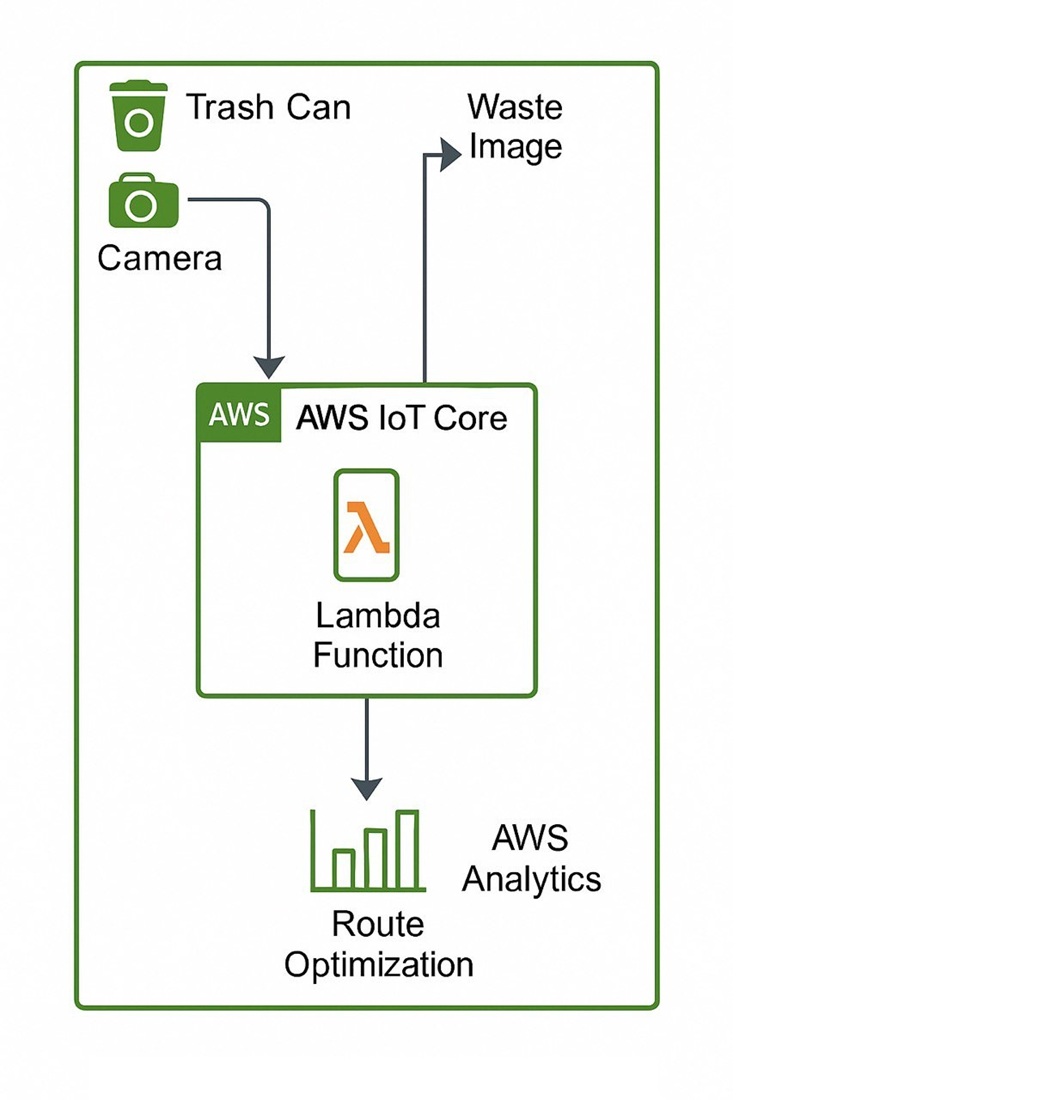
The object of this study is the municipal solid waste management system within a modern urban environment, where rapid urbanization and population growth pose significant challenges to ecological sustainability. The key problem addressed is the inefficiency of waste collection due to overflowing containers, poor route planning, and suboptimal resource allocation. To tackle these issues, an intelligent waste monitoring system has been developed that integrates Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, computer vision, data analytics, and a Regional Geographic Information System (RGIS). The system includes a computer vision model that analyzes images of waste containers to determine their fill level. Fine-tuning the model on locally collected image data, reflecting regional characteristics such as lighting, container types, and weather conditions, significantly improved detection accuracy and adaptability. Route optimization for waste collection is implemented using a mathematical formulation of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), solved via Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP), which helped reduce fuel consumption, travel time, and staff workload. Integration with RGIS and GPS enables dynamic routing and real-time geospatial visualization of operational data. The proposed system forms a closed-loop control cycle that links automated detection, spatial analysis, and decision-making. Experimental results demonstrate high efficiency, adaptability to regional conditions, and scalability, confirming the system’s practical applicability to other urban areas. In the future, the system may be expanded to include environmental monitoring modules such as air quality, noise, and soil conditions and predictive modeling of waste generation, thereby supporting the sustainable development of smart city infrastructure
References
- Kaza, S., Yao, L. C., Bhada-Tata, P., Van Woerden, F. (2018). What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050. Washington, DC: World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1329-0
- Thousands of tons of waste removed in Astana: How offenders are tracked (2025). Available at: https://tengrinews.kz/kazakhstan_news/astane-vyivozyat-tyisyachi-tonn-musora-lovyat-teh-ego-567746/
- Soni, G., Kandasamy, S. (2017). Smart Garbage Bin Systems – A Comprehensive Survey. Smart Secure Systems – IoT and Analytics Perspective, 194–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7635-0_15
- Skol'ko v Kazakhstane potratili na sbor i pererabotku musora [How much was spent on waste collection and recycling in Kazakhstan] (2018). LSM.kz. Available at: https://lsm.kz/skol-ko-v-kazahstane-potratili-na-sbor-i-pererabotku-musora
- Aatamila, M., Verkasalo, P. K., Korhonen, M. J., Viluksela, M. K., Pasanen, K., Tiittanen, P., Nevalainen, A. (2010). Odor Annoyance near Waste Treatment Centers: A Population-Based Study in Finland. Journal of the Air &; Waste Management Association, 60 (4), 412–418. https://doi.org/10.3155/1047-3289.60.4.412
- Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Abdykadyrov, A., Kabdoldina, A. et al. (2024). Usprawnienie cyfrowego korelacyjno-interferometrycznego ustalania kierunku za pomocą przestrzennego sygnału analitycznego. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (3), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6177
- Agnew, C., Mewada, D., Grua, E. M., Eising, C., Denny, P., Heffernan, M. et al. (2023). Detecting the overfilled status of domestic and commercial bins using computer vision. Intelligent Systems with Applications, 18, 200229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswa.2023.200229
- Department of Digital Technologies of Aktobe. Regional Geoinformation System of Aktobe. Available at: https://eaqtobe.kz/#/
- Roboflow. Garbage and trashes model (v4). Roboflow Universe. Available at: https://universe.roboflow.com/trash-and-garbage/garbage-and-trashes/model/4
- Ren, Y., Li, Y., Gao, X. (2024). An MRS-YOLO Model for High-Precision Waste Detection and Classification. Sensors, 24 (13), 4339. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134339
- Lun, Z., Pan, Y., Wang, S., Abbas, Z., Islam, M. S., Yin, S. (2023). Skip-YOLO: Domestic Garbage Detection Using Deep Learning Method in Complex Multi-scenes. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 16 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44196-023-00314-6
- Serik, M., Nurgaliyeva, S. (2024). Enhancing competence in mobile robot development: Integrating robotic technologies for future computer science teachers. Global Journal of Engineering Education, 26 (3), 205–211. Available at: https://www.wiete.com.au/journals/GJEE/Publish/vol26no3/11-Nurgaliyeva-S.pdf
- Smailov, N., Batyrgaliyev, A., Akhmediyarova, A., Seilova, N., Koshkinbayeva, M., Baigulbayeva, M. et al. (2020). Approaches to Evaluating the Quality of Masking Noise Interference. International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications, 67 (1), 59–64. https://doi.org/10.24425/ijet.2021.135944
- Khan, S., Ali, B., Alharbi, A. A. K., Alotaibi, S., Alkhathami, M. (2024). Efficient IoT-Assisted Waste Collection for Urban Smart Cities. Sensors, 24 (10), 3167. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103167
- Smailov, N., Zhadiger, T., Tashtay, Y., Abdykadyrov, A., Amir, A. (2024). Fiber laser-based two-wavelength sensors for detecting temperature and strain on concrete structures. International Journal of Innovative Research and Scientific Studies, 7 (4), 1693–1710. https://doi.org/10.53894/ijirss.v7i4.3481
- Momynkulov, Z., Dosbayev, Z., Suliman, A., Abduraimova, B., Smailov, N., Zhekambayeva, M., Zhamangarin, D. (2023). Fast Detection and Classification of Dangerous Urban Sounds Using Deep Learning. Computers, Materials & Continua, 75 (1), 2191–2208. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2023.036205
- Kisała, P., Wójcik, W., Smailov, N., Kalizhanova, A., Harasim, D. (2015). Elongation determination using finite element and boundary element method. International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications, 61 (4), 389–394. https://doi.org/10.2478/eletel-2015-0051
- Gupta, S. K., & Bhatia, R. K. (2017). Route Optimization of Municipal Solid Waste Collection in Jabalpur City using ARC GIS. International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development, 2 (1), 457–464. https://doi.org/10.31142/ijtsrd7000
- Smailov, N., Orynbet, M., Nazarova, A., Torekhan, Z., Koshkinbayev, S., Yssyraiyl, K. et al. (2025). Optymalizacja pracy światłowodowych czujników w warunkach kosmicznych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (2), 130–134. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.7200
- Kengesbayeva, S., Smailov, N., Tashtay, Y., Kiesewetter, D., Malyugin, V., Amir, A. (2024). Research of Deformation of Concrete Structures Using Fiber Optic Sensors and Bragg Gratings. 2024 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Photonics (EExPolytech), 15–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/eexpolytech62224.2024.10755828
- Sekenov, B., Smailov, N., Tashtay, Y., Amir, A., Kuttybayeva, A., Tolemanova, A. (2024). Fiber-Optic Temperature Sensors for Monitoring the Influence of the Space Environment on Nanosatellites: A Review. Advances in Asian Mechanism and Machine Science, 371–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67569-0_42
- Smailov, N., Akmardin, S., Ayapbergenova, A., Ayapbergenova, G., Kadyrova, R., Sabibolda, A. (2025). Analiza wydajności VLC w optycznych systemach komunikacji bezprzewodowej do zastosowań wewnętrznych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (2), 135–138. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6971
- Wójcik, W., Kalizhanova, A., Kulyk, Y., Knysh, B., Kvyetnyy, R., Kulyk, A. et al. (2022). The Method of Time Distribution for Environment Monitoring Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles According to an Inverse Priority. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 23 (11), 179–187. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/153458
- Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Tsyporenko, V., Smailov, N., Zhunussov, K., Abdykadyrov, A. et al. (2022). Improving the accuracy and performance speed of the digital spectral-correlation method for measuring delay in radio signals and direction finding. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (9 (115)), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.252561
- Mikhailov, P., Ualiyev, Z., Kabdoldina, A., Smailov, N., Khikmetov, A., Malikova, F. (2021). Multifunctional fiber-optic sensors for space infrastructure. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (5 (113)), 80–89. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.242995
- Smailov, N., Uralova, F., Kadyrova, R., Magazov, R., Sabibolda, A. (2025). Optymalizacja metod uczenia maszynowego do deanonimizacji w sieciach społecznościowych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (1), 101–104. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.7098
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Symbat Nurgaliyeva, Muratali Amangali, Zhuldyz Basheyeva, Nurzhamal Kashkimbayeva, Daniyar Amantayev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








